HP 2100 ER User Manual
Page 62
A-4
Appendix A
Fibre Channel Overview
Defining Fibre Channel
A fully implemented Fabric system supports over 16 million device
addresses, allowing a user to send data from each device at 100 MB per
second. Using fiber optic cable, Fibre Channel devices can be spaced at
maximum intervals of 10 km, supporting distributed hosts in a campus
environment, with centralized storage systems. Fibre Channel uses
three connection topologies, illustrated in the following table:
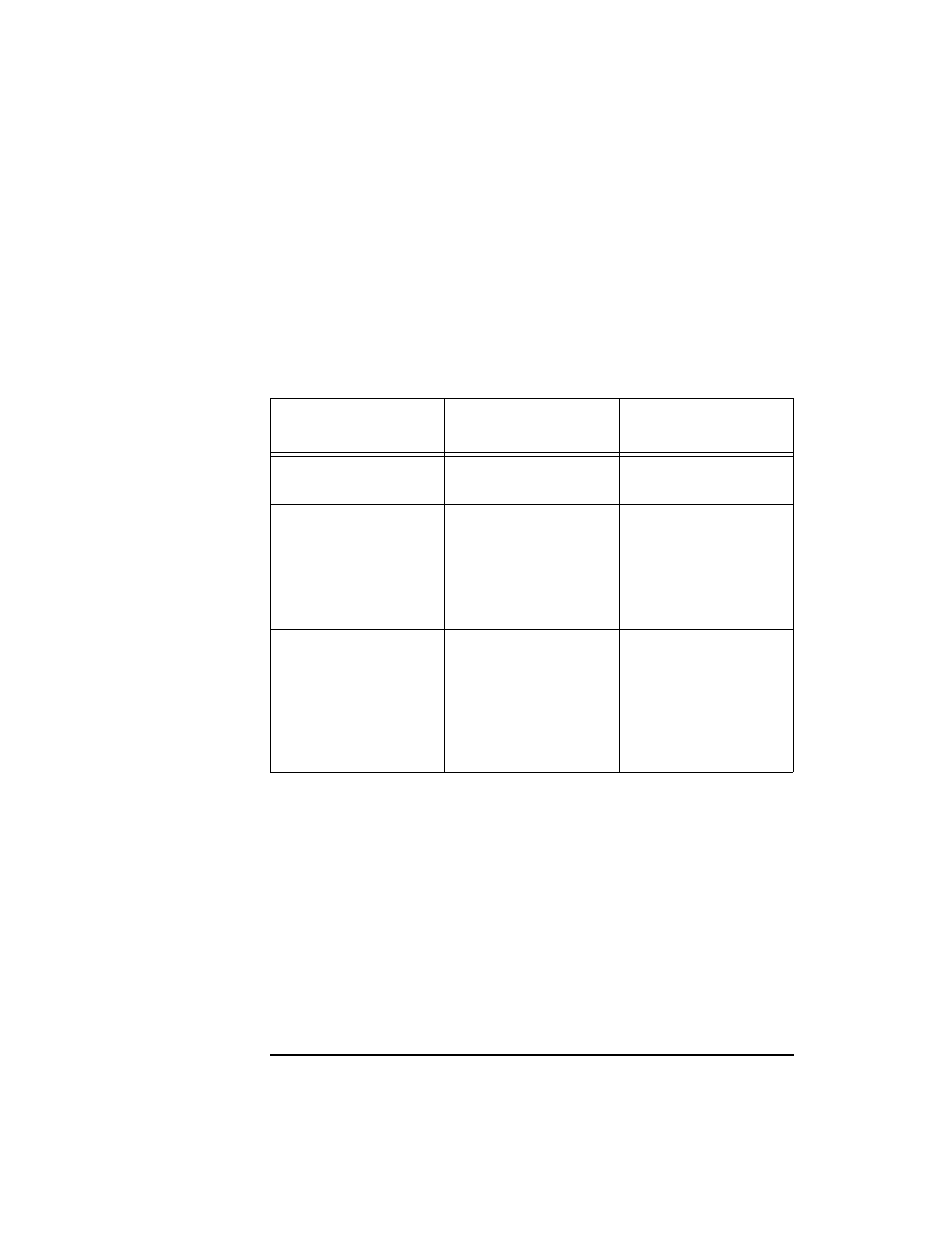
Table A-1
Fibre Channel Supported Fabric Topologies
Topology
Description
Advantages/
Disadvantages
Point to point
Dedicated connection
between two devices.
Low cost, high
performance.
Fibre Channel
Arbitrated Loop
(FC-AL)
Supports up to 126
devices, distributing
the 100 MBps data
bandwidth among all
devices on the loop.
Supports more
devices.
Increasing the
number of devices
reduces performance.
Fabric
A switching concept,
similar to a telephone
system, providing
simultaneous
data-transmission
among multiple
devices at 100 MBps.
Supports multiple
devices without
performance
reduction.
Higher cost.
- Surestore 2.20 Tape Library Surestore DLT 4000 15 Tape Library Surestore 1.8 Tape Library Surestore DLT 718 Tape Autoloader Surestore DLT 818 Tape Autoloader Surestore DLT 7000 28.48 Tape Library Surestore 2.28 Tape Library Surestore E 4.40 Tape Library Surestore E 6.60 Tape Library Surestore DLT 418 Tape Autoloader Surestore DLT 7000 15 Tape Library Surestore E 2.20 Tape Library Surestore 4.40 Tape Library Surestore 6.60 Tape Library Surestore 10.588 Tape Library Surestore 2.15 Tape Library Surestore 3.30 Tape Library Surestore 6.100 Tape Library Surestore SCSI-FC Bridges Surestore DLT 4000 28.48 Tape Library
