Dnp slave driver data flow, 4 dnp slave driver data flow – ProSoft Technology 5201-DFNT-DNPS User Manual
Page 53
Reference ProLinx
DNPS
♦ ProLinx Gateway
User Manual
DNP 3.0 Slave
ProSoft Technology, Inc.
Page 53 of 86
December 1, 2009
The float and double point numbers are offset based on the analog count number
since the float and double point are in fact analog variations. The following table
shows how the points are generated based on an example configuration.
Data Area
Point Count Configuration Value First Point Number
Analog Inputs
5
0
Float Inputs
15
5
Double Inputs
10
20
Analog Outputs
25
0
Float Outputs
7
25
Double Outputs
10
32
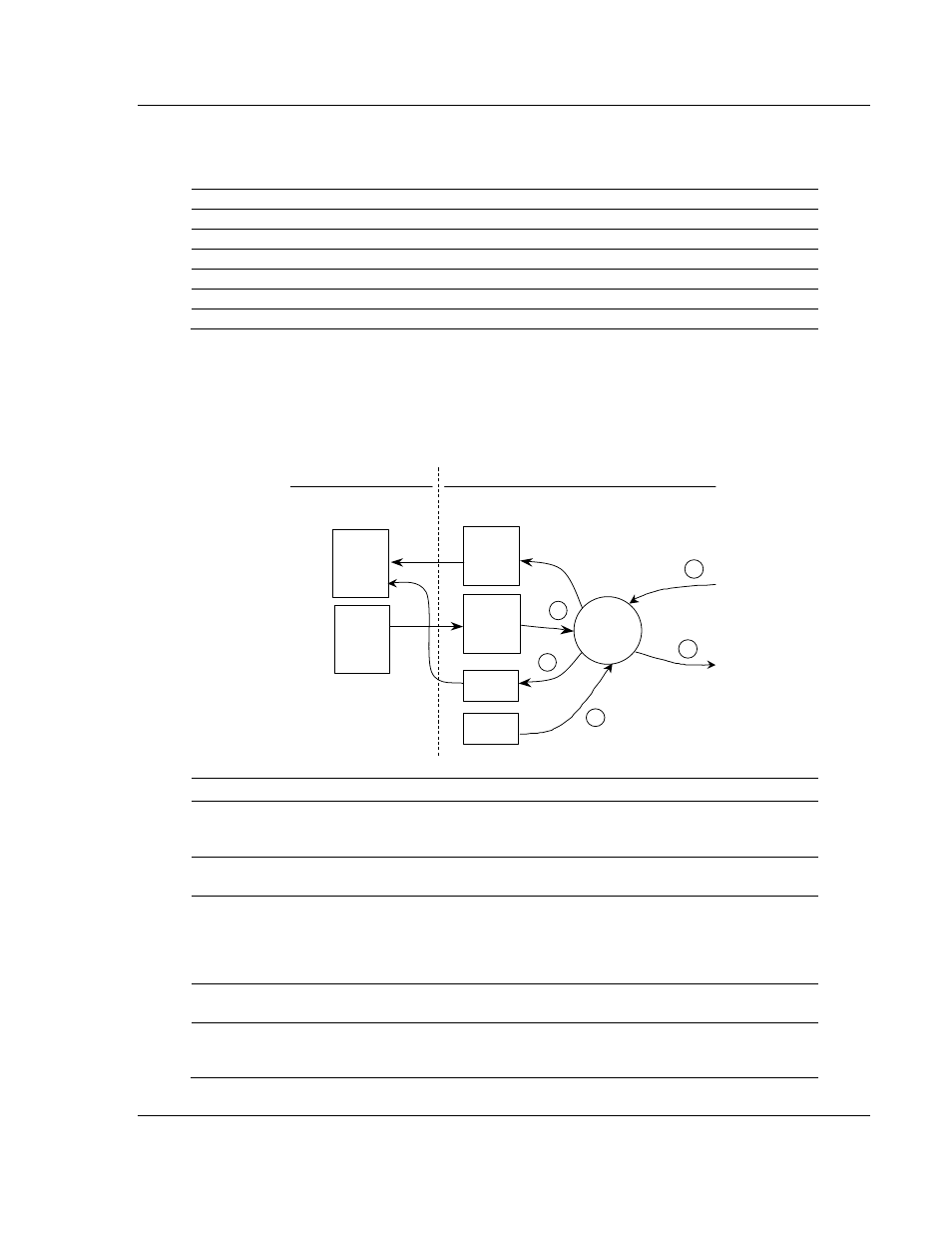
3.3.4 DNP Slave Driver Data Flow
The DNP Slave Driver allows the module to respond to data read and write
commands issued by a master on the DNP network. The following flow chart and
associated table describe the flow of data into and out of the module.
Input
Im age
Module’s
Database
Slave
Mode
Driver
DNP Module
Configuration
Status
4
2
3
5
1
Output
Data
Output
Im age
Input
Data
Other Protocol
Step Description
1
The DNP slave driver receives the configuration information from the Flash Disk in the
module. This information configures the serial port and defines the slave node
characteristics.
2
A Host device issues read or write commands to the module’s node address. The port
driver qualifies the message before accepting it into the module.
3
After the module accepts the command, the data is immediately transferred to or from
the internal database in the module. If the command is a read command (binary input,
analog input, counter, event, and so on), the data is read out of the database and a
response message is built. If the command is a write command (binary output or analog
output), the data is written directly into the database and a response message is built.
4
After the data processing has been completed in Step 3, the response is issued to the
originating master node.
5
Error/Status data are available in a Status Block that can be placed anywhere in the
module’s database. This area can be accessed by the other protocol on the module
using the correct database offset.
