7 mvr configuration – PLANET SGSW-24040 User Manual
Page 176
User’s Manual of SGSW-24040 / 24240 Series
176
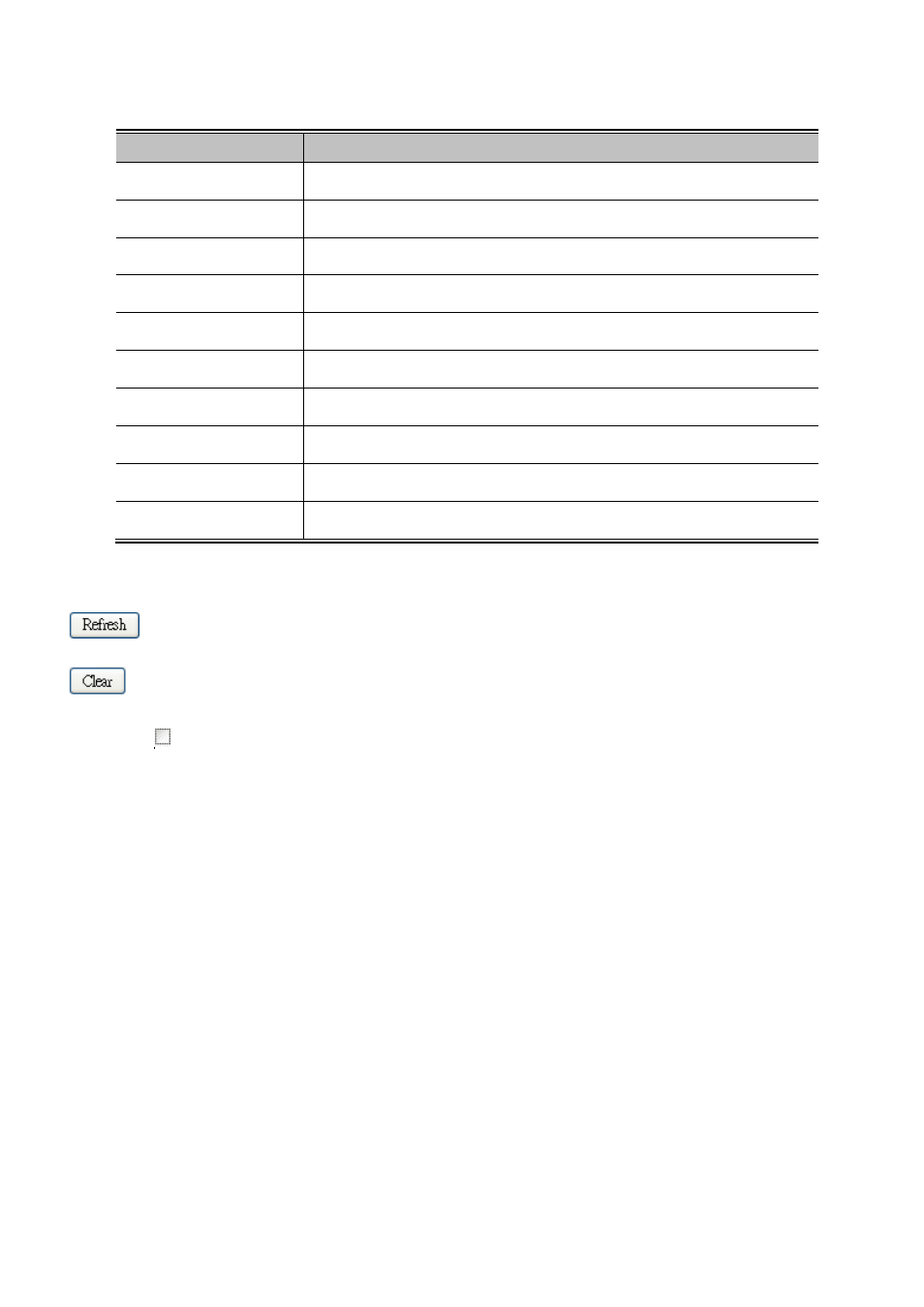
The page includes the following fields:
Object
Description
•
VLAN ID
The VLAN ID of the entry.
•
Groups
The present IGMP groups. Max. are 128 groups for each VLAN.
•
Port Members
The ports that are members of the entry.
•
Querier Status
Show the Querier status is "ACTIVE" or "IDLE".
•
Querier Transmit
The number of Transmitted Querier.
• Querier Receive
The number of Received Querier.
• V1 Reports Receive
The number of Received V1 Reports.
• V2 Reports Receive
The number of Received V2 Reports.
• V3 Reports Receive
The number of Received V3 Reports.
• V2 Leave Receive
The number of Received V2 Leave.
Buttons
: Click to refresh the page immediately.
: Clears all Statistics counters.
Auto-refresh
: Check this box to enable an automatic refresh of the page at regular intervals.
4.8.7 MVR Configuration
In multicast VLAN networks, subscribers to a multicast group can exist in more than one VLAN. If the VLAN boundary
restrictions in a network consist of Layer 2 switches
Multicast VLAN Registration (MVR) is a protocol fornetworks that enablestraffic from a source VLAN
to be shared with subscriber-VLANs. The alternative would be to usor a similar protocol to route the traffic through a
network, it might be necessary to replicate the multicast stream to the same group in different subnets, even if they are
on the same physical network. Multicast VLAN Registration (MVR) routes packets received in a multicast source VLAN to one or
more receive VLANs. Clients are in the receive VLANs and the multicast server is in the source VLAN. Multicast routing has to
be disabled when MVR is enabled. Refer to the configuration guide atfor more
information on MVR. MVR is typically used for IPTV-like services and is therefore usually only available on enterprise-level
switches. Many manufacturers provide support for MVR on their high-end switches.
The main reason for using MVR is to save bandwidth by preventing duplicate multicast streams being sent in the core network,
instead the stream(s) are received on the MVR-VLAN and forwarded to the VLANs where hosts have requested it/them.
