1 fundamentals, Position encoders and reference marks, Reference system – HEIDENHAIN TNC 620 (81760x-02) ISO programming User Manual
Page 92: Fundamentals
Programming: Fundamentals, file management
3.1
Fundamentals
3
92
TNC 620 | User's ManualDIN/ISO Programming | 2/2015
3.1
Fundamentals
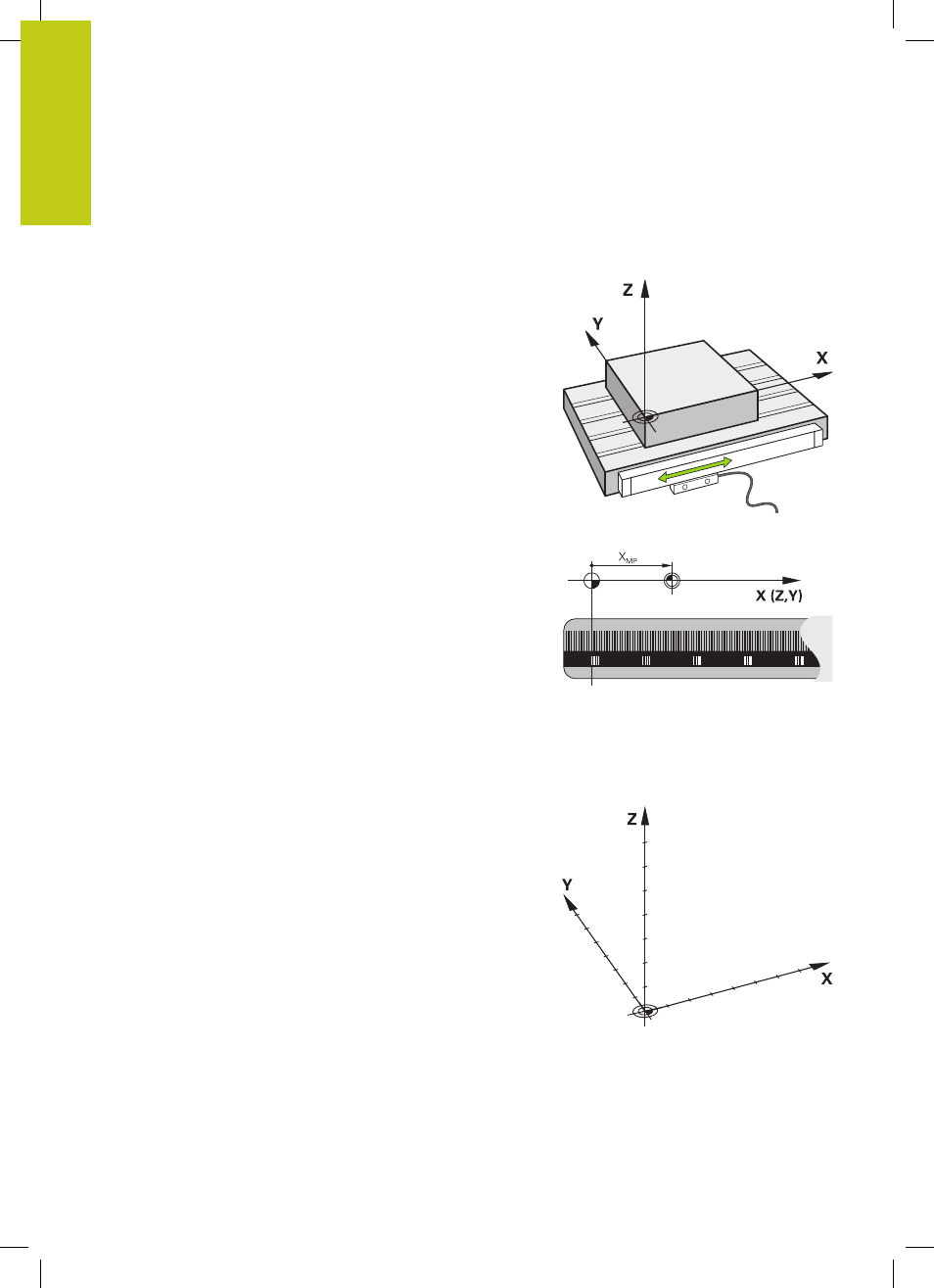
Position encoders and reference marks
The machine axes are equipped with position encoders that
register the positions of the machine table or tool. Linear axes are
usually equipped with linear encoders, rotary tables and tilting axes
with angle encoders.
When a machine axis moves, the corresponding position encoder
generates an electrical signal. The TNC evaluates this signal and
calculates the precise actual position of the machine axis.
If there is a power interruption, the calculated position will no
longer correspond to the actual position of the machine slide.
To recover this association, incremental position encoders are
provided with reference marks. The scales of the position encoders
contain one or more reference marks that transmit a signal to the
TNC when they are crossed over. From that signal the TNC can
re-establish the assignment of displayed positions to machine
positions. For linear encoders with distance-coded reference
marks, the machine axes need to move by no more than 20 mm,
for angle encoders by no more than 20°.
With absolute encoders, an absolute position value is transmitted
to the control immediately upon switch-on. In this way the
assignment of the actual position to the machine slide position is
re-established directly after switch-on.
Reference system
A reference system is required to define positions in a plane or in
space. The position data are always referenced to a predetermined
point and are described through coordinates.
The Cartesian coordinate system (a rectangular coordinate system)
is based on the three coordinate axes X, Y and Z. The axes are
mutually perpendicular and intersect at one point called the datum.
A coordinate identifies the distance from the datum in one of these
directions. A position in a plane is thus described through two
coordinates, and a position in space through three coordinates.
Coordinates that are referenced to the datum are referred to
as absolute coordinates. Relative coordinates are referenced to
any other known position (reference point) you define within the
coordinate system. Relative coordinate values are also referred to
as incremental coordinate values.
