How msdp works, Msdp peers – H3C Technologies H3C SecPath F1000-E User Manual
Page 63
2
How MSDP Works
MSDP peers
With one or more pairs of MSDP peers configured in the network, an MSDP interconnection map is
formed, where the RPs of different PIM-SM domains are interconnected in series. Relayed by these MSDP
peers, an SA message sent by an RP can be delivered to all other RPs.
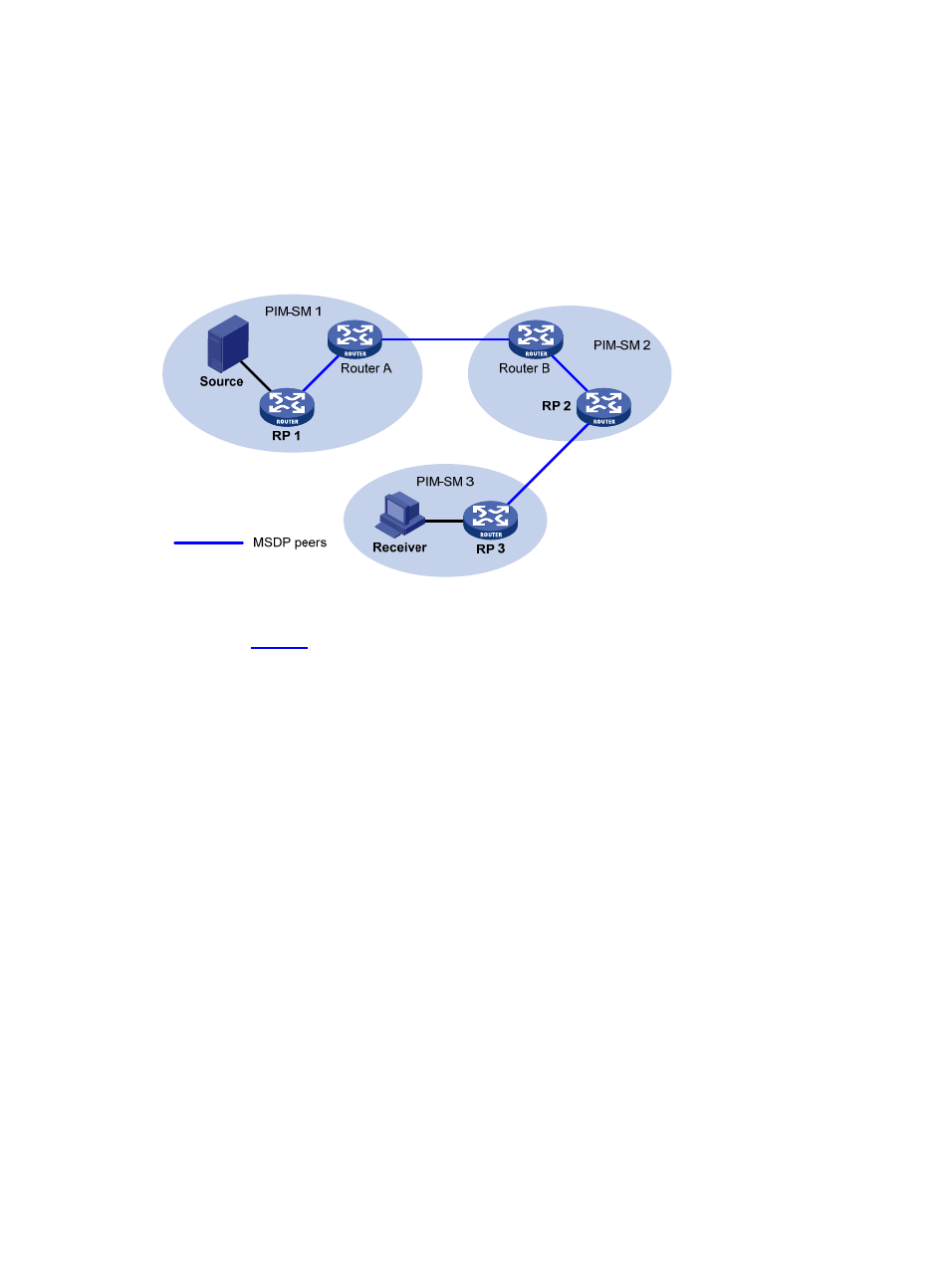
Figure 1 Where MSDP peers are in the network
As shown in
, an MSDP peer can be created on any PIM-SM router. MSDP peers created on
PIM-SM routers that assume different roles function differently.
1.
MSDP peers on RPs
•
Source-side MSDP peer: the MSDP peer nearest to the multicast source (Source), typically the
source-side RP, like RP 1. The source-side RP creates SA messages and sends the messages to its
remote MSDP peer to notify the MSDP peer of the locally registered multicast source information. A
source-side MSDP peer must be created on the source-side RP; otherwise it will not be able to
advertise the multicast source information out of the PIM-SM domain.
•
Receiver-side MSDP peer: the MSDP peer nearest to the receivers, typically the receiver-side RP, like
RP 3. Upon receiving an SA message, the receiver-side MSDP peer resolves the multicast source
information carried in the message and joins the SPT rooted at the source across the PIM-SM
domain. When multicast data from the multicast source arrives, the receiver-side MSDP peer
forwards the data to the receivers along the RPT.
•
Intermediate MSDP peer: an MSDP peer with multicast remote MSDP peers, like RP 2. An
intermediate MSDP peer forwards SA messages received from one remote MSDP peer to other
remote MSDP peers, functioning as a relay of multicast source information.
2.
MSDP peers created on common PIM-SM routers (other than RPs)
Router A and Router B are MSDP peers on common multicast routers. Such MSDP peers just forward
received SA messages.
