Layer 3 multicast protocols – H3C Technologies H3C SecPath F1000-E User Manual
Page 11
10
NOTE:
•
Generally, we refer to IP multicast working at the network layer as Layer 3 multicast and the
corresponding multicast protocols as Layer 3 multicast protocols, which include IGMP/MLD, PIM/IPv6
PIM, MSDP, and MBGP/IPv6 MBGP; we refer to IP multicast working at the data link layer as Layer 2
multicast and the corresponding multicast protocols as Layer 2 multicast protocols, which include IGMP
Snooping/MLD Snooping, and multicast VLAN/IPv6 multicast VLAN.
•
IGMP Snooping, IGMP, multicast VLAN, PIM, MSDP, and MBGP are for IPv4, MLD Snooping, MLD, IPv6
multicast VLAN, IPv6 PIM, and IPv6 MBGP are for IPv6.
•
Currently, H3C SecPath F5000-A5 and H3C SecPath F1000-E support only Layer 3 multicast protocols.
•
This section provides only general descriptions about applications and functions of the Layer 2 and
Layer 3 multicast protocols in a network.
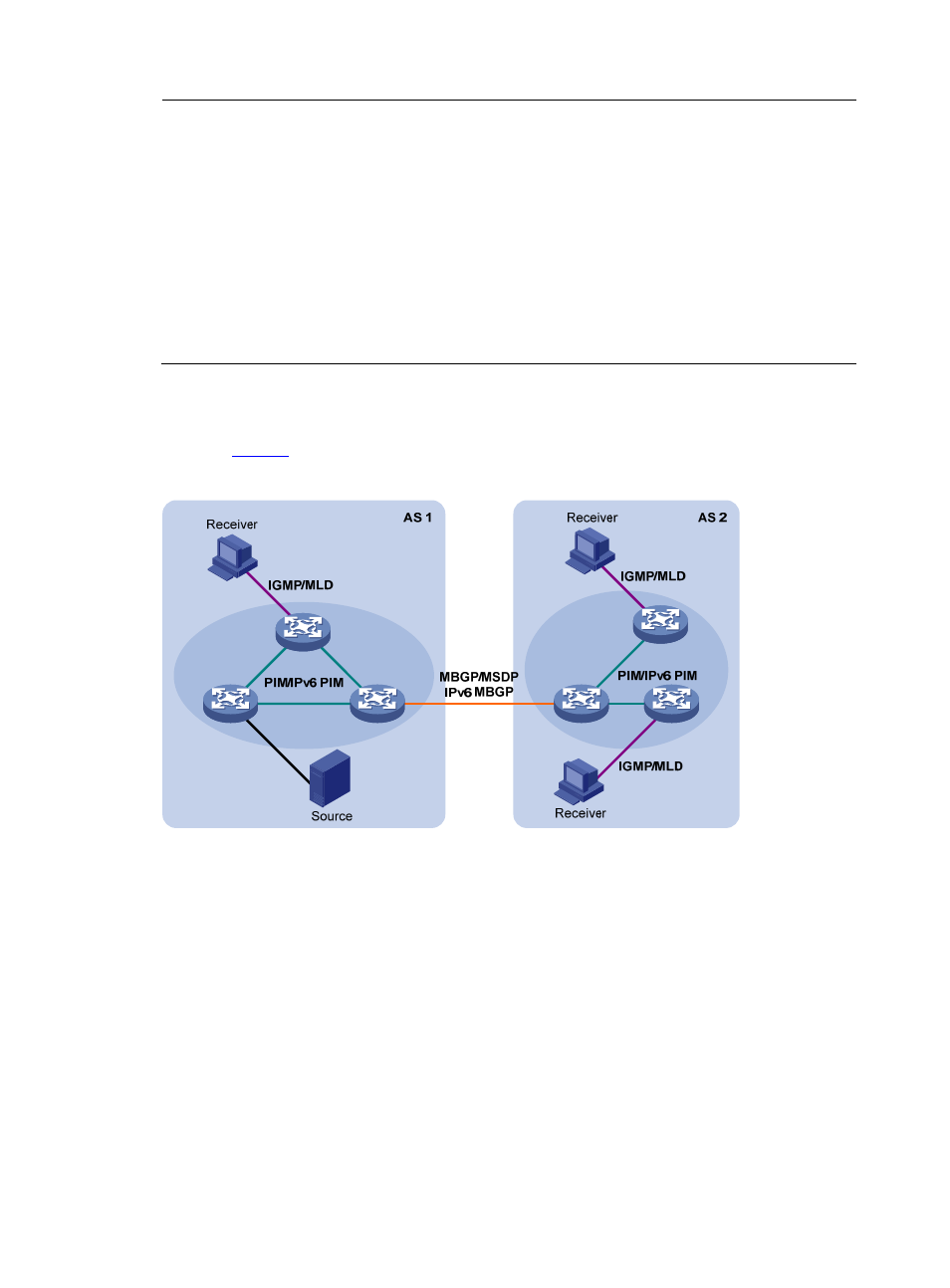
Layer 3 multicast protocols
Layer 3 multicast protocols include multicast group management protocols and multicast routing
describes where these multicast protocols are in a network.
Figure 8 Positions of Layer 3 multicast protocols
1.
Multicast group management protocols
Typically, the internet group management protocol (IGMP) or multicast listener discovery protocol (MLD)
is used between hosts and Layer 3 multicast devices directly connected with the hosts. These protocols
define the mechanism of establishing and maintaining group memberships between hosts and Layer 3
multicast devices.
2.
Multicast routing protocols
A multicast routing protocol runs on Layer 3 multicast devices to establish and maintain multicast routes
and forward multicast packets correctly and efficiently. Multicast routes constitute loop-free data
transmission paths from a data source to multiple receivers, namely, a multicast distribution tree.
In the ASM model, multicast routes include intra-domain routes and inter-domain routes.
•
An intra-domain multicast routing protocol is used to discover multicast sources and build multicast
distribution trees within an AS so as to deliver multicast data to receivers. Among a variety of mature
intra-domain multicast routing protocols, protocol independent multicast (PIM) is most widely used.
