Multiple vrrp groups configuration example, Network requirements, Configuration procedure – H3C Technologies H3C SR8800 User Manual
Page 98
89
The output shows that when interface GigabitEthernet 4/1/2 on Router A is not available, the
priority of Router A reduces to 80 and it becomes the backup. Router B becomes the master and
packets sent from Host A to Host B are forwarded by Router B.
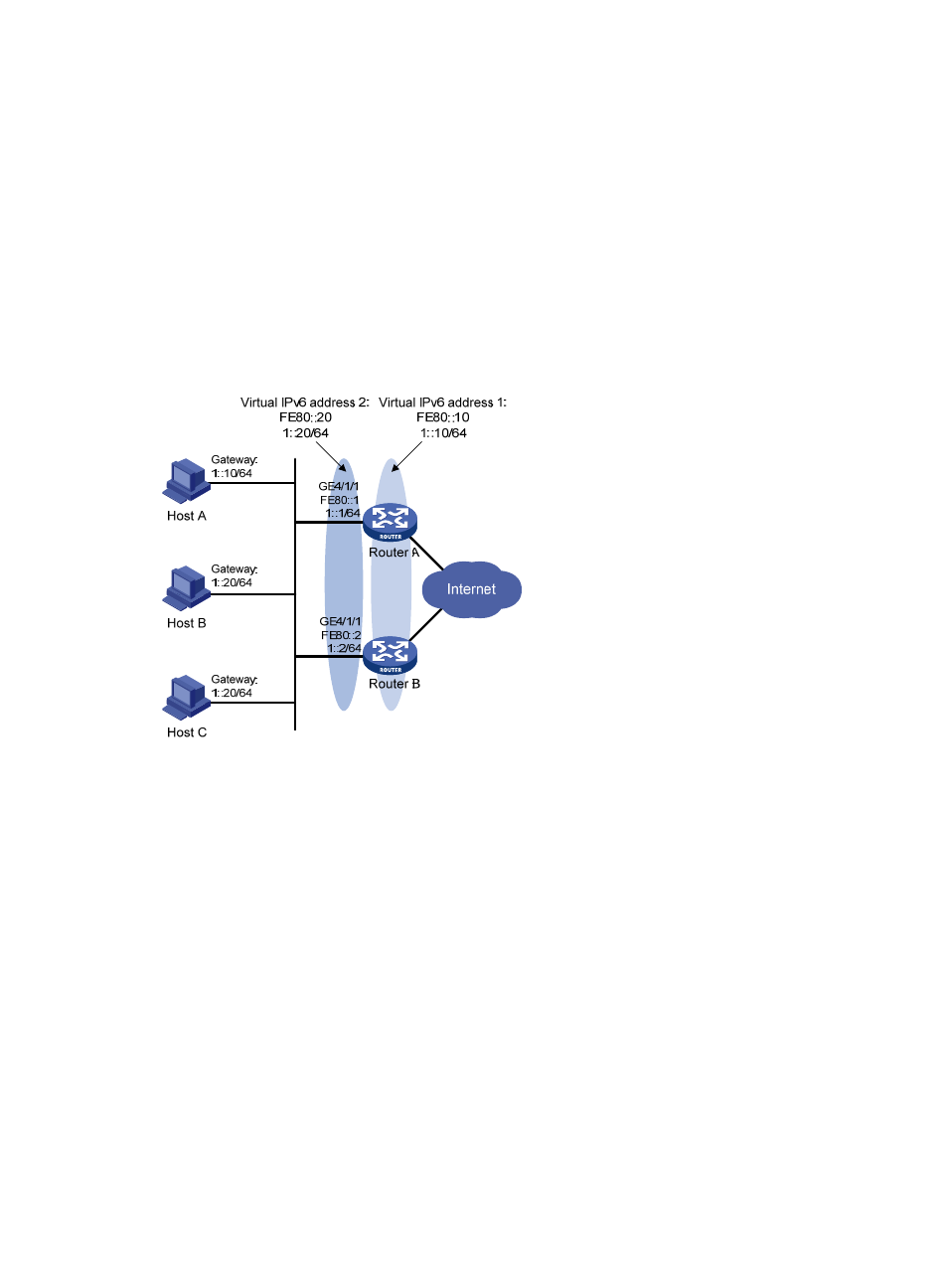
Multiple VRRP groups configuration example
Network requirements
•
In the network, some hosts use 1::10/64 as their default gateway and some hosts use 1::20/64 as
their default gateway.
•
Load sharing and mutual backup between default gateways can be implemented by using VRRP
groups.
Figure 27 Network diagram
Configuration procedure
1.
Configure Router A:
[RouterA] ipv6
[RouterA] interface GigabitEthernet 4/1/1
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet4/1/1] ipv6 address fe80::1 link-local
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet4/1/1] ipv6 address 1::1 64
# Create VRRP group 1 and set its virtual IPv6 addresses to FE80::10 and 1::10.
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet4/1/1] vrrp ipv6 vrid 1 virtual-ip fe80::10 link-local
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet4/1/1] vrrp ipv6 vrid 1 virtual-ip 1::10
# Set the priority of Router A in VRRP group 1 to 110, which is higher than that of Router B (100),
so that Router A can become the master in VRRP group 1.
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet4/1/1] vrrp ipv6 vrid 1 priority 110
# Create VRRP group 2 set its virtual IPv6 addresses to FE80::20 and 1::20.
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet4/1/1] vrrp ipv6 vrid 2 virtual-ip fe80::20 link-local
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet4/1/1] vrrp ipv6 vrid 2 virtual-ip 1::20
# Enable Router A to send RA messages.
