Virtual forwarder, Creating a virtual forwarder, Vf weight and priority – H3C Technologies H3C SR8800 User Manual
Page 59: For example, as shown in, Figure 18, Host a regards th
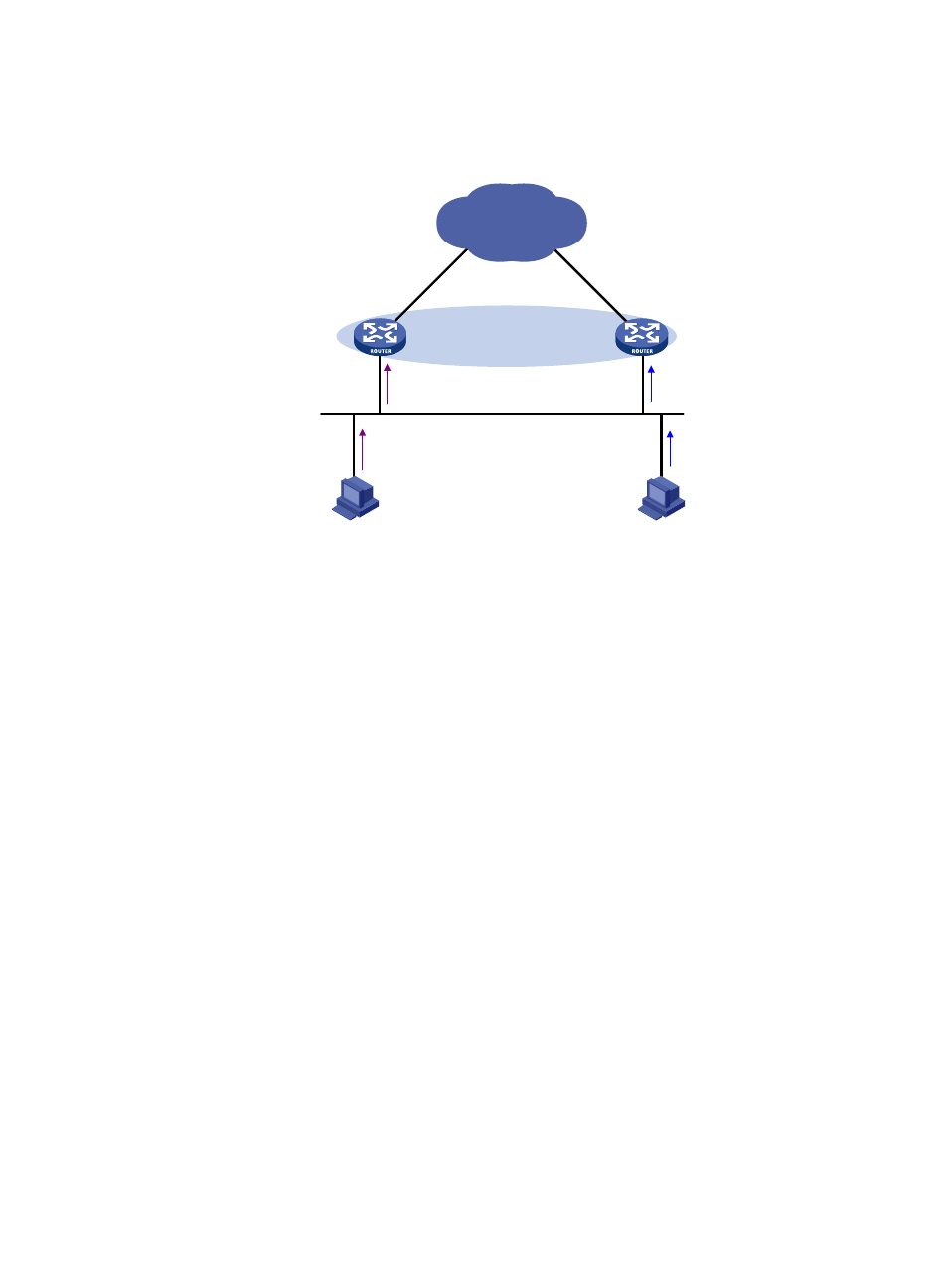
50
MAC address of Router B as the gateway MAC address, so it sends packets to Router B for
forwarding.
Figure 18 Sending packets to different routers for forwarding
Virtual forwarder
Creating a virtual forwarder
Virtual MAC addresses help different hosts transmit packets to different routers in a VRRP group. To
enable the routers in the VRRP group to forward the packets, be sure to create virtual forwarders (VFs) on
the routers. Each VF associates with a virtual MAC address in the VRRP group and forwards packets
destined to this virtual MAC address.
The following describes how VFs are created on the routers in a VRRP group:
1.
The master assigns virtual MAC addresses to all routers in the VRRP group. After learning its virtual
MAC address, a router in the VRRP group creates a VF that corresponds to this MAC address, and
becomes the owner of this VF.
2.
The router advertises the VF information to the other routers in the VRRP group.
3.
After receiving the VF advertisement, each of the other routers creates the advertised VF.
As described in the preceding steps, each router in the VRRP group creates not only a VF corresponding
to its virtual MAC address, but also VFs advertised by the other routes in the VRRP group..
VF weight and priority
The weight of a VF indicates the forwarding capability of a router. A higher weight indicates a higher
forwarding capability. When the weight is lower than the lower limit of failure, the router cannot be
capable of forwarding packets for the hosts.
The priority of a VF determines the VF state. Among the VFs that correspond to the same virtual MAC
address on different routers in the VRRP group, a VF with the highest priority is in the active state and is
known as the active virtual forwarder (AVF), which forwards packets; other VFs are in the listening state
and are known as the listening virtual forwarders (LVFs), which listen to the state of the AVF. The priority
value of a VF ranges from 0 to 255, where 255 is reserved for the VF owner. If the weight of a VF owner
Host A
Host B
Router A
Master
Router B
Backup
Virtual IP: 10.1.1.1/24
Network
Gateway IP: 10.1.1.1/24
Gateway MAC: 000f-e2ff-0011
Gateway IP: 10.1.1.1/24
Gateway MAC: 000f-e2ff-0012
Virtual MAC: 000f-e2ff-0011
Virtual MAC: 000f-e2ff-0012
