Single vrrp group configuration example, Network requirements, Configuration procedure – H3C Technologies H3C SR8800 User Manual
Page 92
83
Single VRRP group configuration example
Network requirements
•
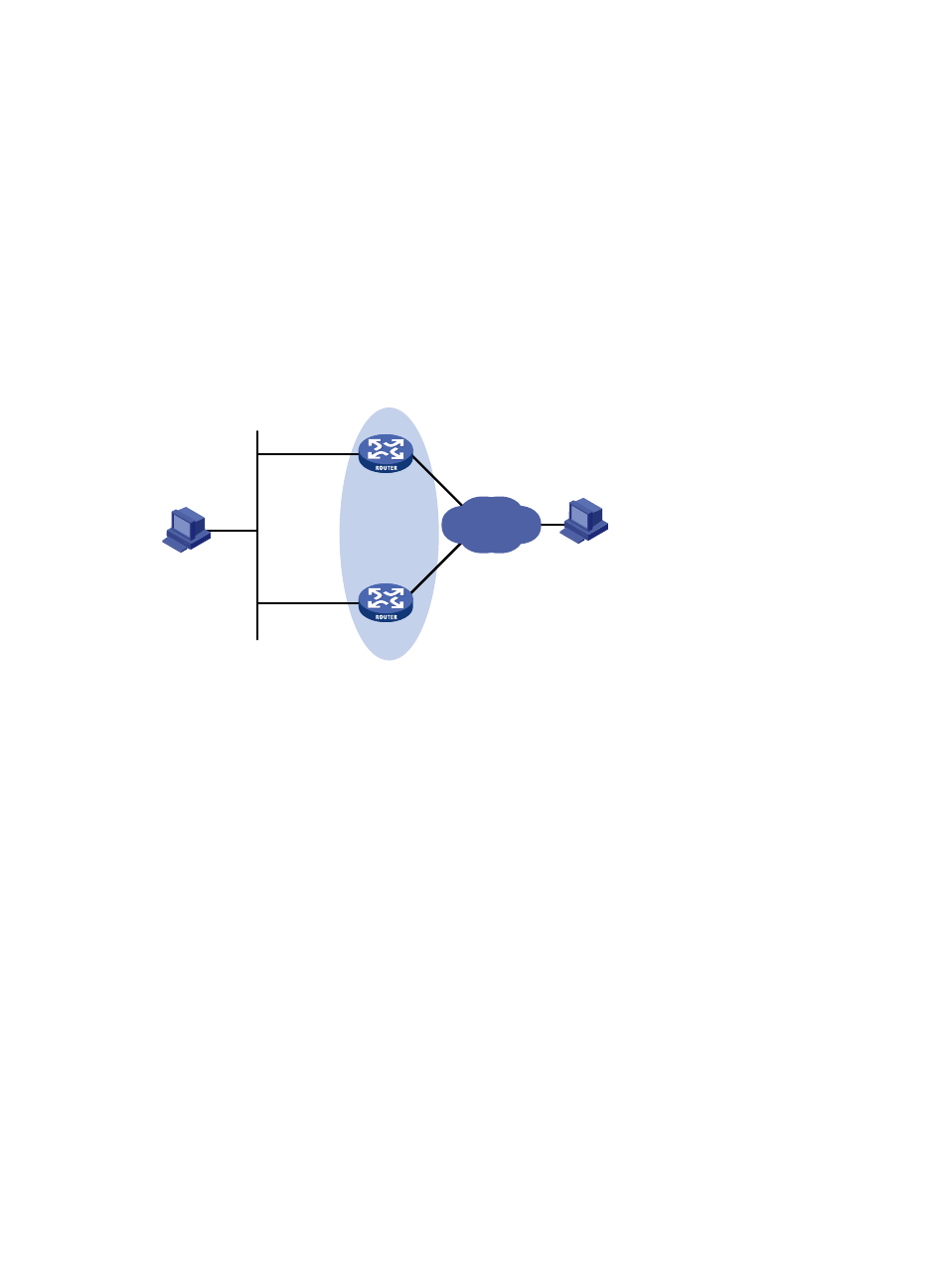
Router A and Router B belong to VRRP group 1 with the virtual IPv6 addresses of 1::10/64 and
FE80::10.
•
Host A wants to access Host B on the Internet. Host A learns 1::10/64 as its default gateway through
the RA messages sent by the routers.
•
When Router A operates normally, packets sent from Host A to Host B are forwarded by Router A;
when Router A fails, packets sent from Host A to Host B are forwarded by Router B.
Figure 25 Network diagram
Configuration procedure
1.
Configure Router A:
[RouterA] ipv6
[RouterA] interface GigabitEthernet 4/1/1
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet4/1/1] ipv6 address fe80::1 link-local
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet4/1/1] ipv6 address 1::1 64
# Create a VRRP group 1 and set its virtual IPv6 addresses to FE80::10 and 1::10.
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet4/1/1] vrrp ipv6 vrid 1 virtual-ip fe80::10 link-local
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet4/1/1] vrrp ipv6 vrid 1 virtual-ip 1::10
# Configure the priority of Router A in VRRP group 1 as 110, which is higher than that of Router
B (100), so that Router A can become the master.
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet4/1/1] vrrp ipv6 vrid 1 priority 110
# Configure Router A to work in preemptive mode so that it can become the master whenever it
works normally; configure the preemption delay as five seconds to avoid frequent status
switchover.
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet4/1/1] vrrp ipv6 vrid 1 preempt-mode timer delay 5
# Enable Router A to send RA messages, so that Host A can learn the default gateway address.
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet4/1/1] undo ipv6 nd ra halt
2.
Configure Router B:
Host A
Router A
Router B
Virtual IPv6 address:
FE80::10
1::10/64
GE4/1/1
FE80::1
1::1/64
GE4/1/1
FE80::2
1::2/64
Host B
Gateway:
1::10/64
Internet
