Port configuration – Amer Networks SS2GD8I User Manual
Page 25
19
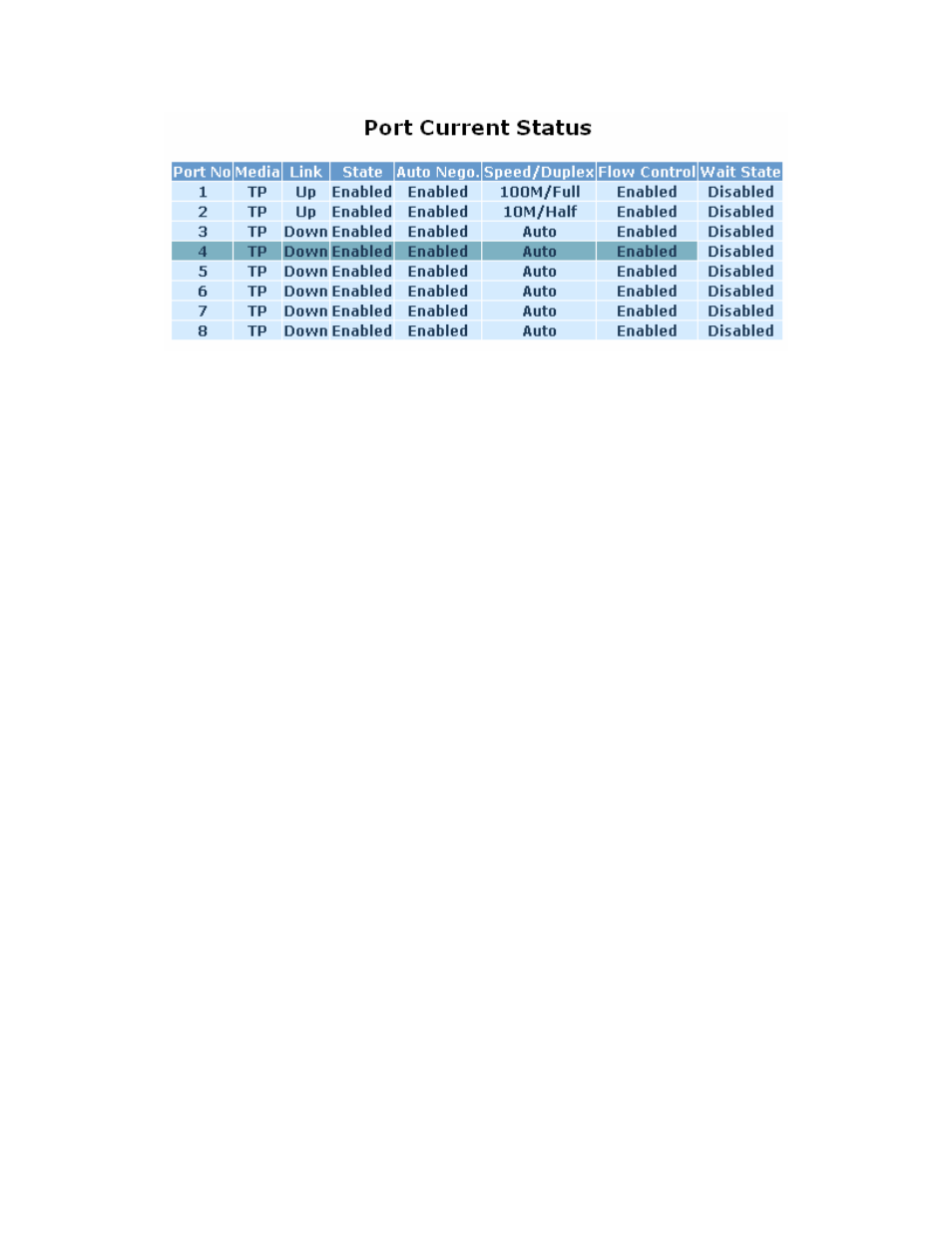
Figure 3-9: Port Status Page
Port No: The port number, ranging from 1-8. Both ports 7 and 8 are optional modules.
Media: Shows the media type of the port. Ports 1-6 are twisted pair (TP) or copper, while ports 7 and 8
could be twisted pair or fiber.
Link: Shows if the link is active or not. If the link is connected to a working device, the Link will be “Up”;
otherwise, it will be “Down”.
State: Shows whether the port is “Enabled” or “Disabled”. When it is enabled, traffic can be transmitted
and received via this port. When it is disabled, no traffic can be transmitted through this port. Port State is
configured by the user.
Auto Negotiation: Shows whether the port has speed and duplex auto-negotiation enabled on or not.
When “Enabled”, the switch will automatically negotiation the best speed and duplex supported by both
devices. If “Disabled”, it must be set manually by the user. This option is set by the user.
Speed / Duplex Mode: Displays the speed and duplex of the port. There are three speeds 10Mbps,
100Mbps and 1000Mbps supported for TP media, and the duplex supported is half duplex and full duplex.
If the media is 1Gbps fiber, it can be 1000Mbps only.
Flow Control: Shows the port’s flow control status.
Wait State: For 10/100M ports, this value is irrelevant. For Gigabit ports, setting of Wait State will remove
the issue with ignored pause frames but result in the minimum interframe gap being at least 14 bytes
instead of the usual 12 bytes. This applies to non-congested traffic as well. The larger interframe gap will
result in throughput rates less than 100%. For example, for a stream of 64-byte frames and a stream of
1518-byte frames, their maximum throughput is 97.7% and 99.9% respectively.
3.2.2 Port
Configuration
The Port Configuration page (Figure 3-10) is used to change the settings of each of the ports.
