Ubiquiti Networks PowerBridgM User Manual
Page 53
50
Chapter 6: Advanced Tab
airOS
™
v5.5.4 User Guide
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
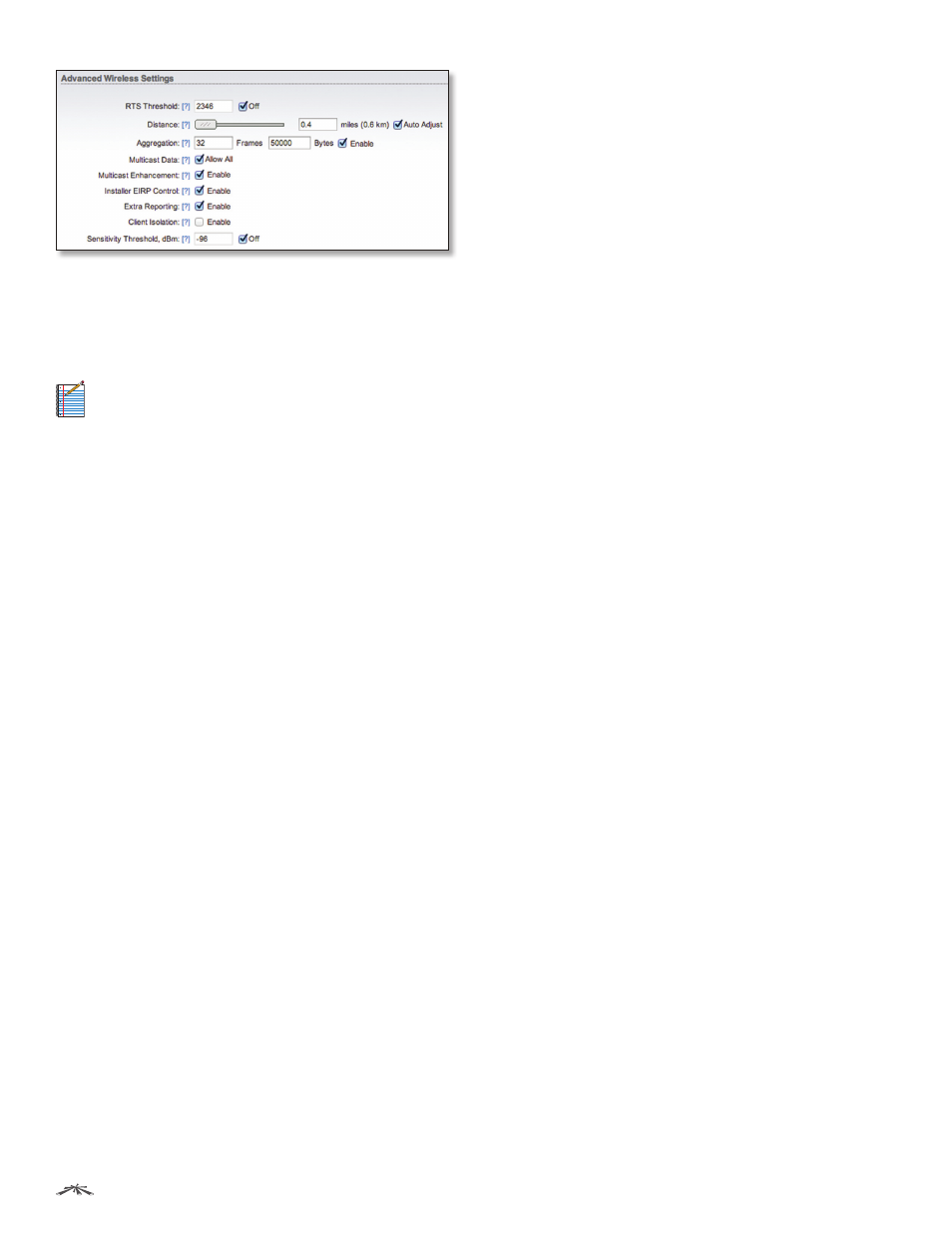
RTS Threshold
(If airMAX is enabled, RTS Threshold is not
required.) Determines the packet size of a transmission
and, through the use of an AP, helps control traffic flow.
The range is 0-2346 bytes. The default setting is the value
2346; this means that RTS is disabled.
Note:
As an alternative, you can select Off to
disable this option.
The 802.11 wireless networking protocol uses the 802.11
wireless networking Request to Send (RTS)/Clear to Send
(CTS) mechanisms to reduce frame collisions introduced
by the hidden terminal problem. The RTS/CTS packet size
threshold is 0-2346 bytes. If the packet size that the device
wants to transmit is larger than the threshold, then the
RTS/CTS handshake is triggered. If the packet size is equal
to or less than the threshold, then the data frame is sent
immediately.
The system uses RTS/CTS frames for the handshake;
this reduces collisions for APs with hidden stations. The
station sends an RTS frame first; the AP responds with a
CTS frame. After the handshake with the AP is completed,
the station sends data. CTS collision control management
has a time interval defined; during this interval, all other
stations do not transmit and wait until the requesting
station finishes transmission.
Distance
To specify the distance value in miles (or
kilometers), use the slider or manually enter the value.
The signal strength and throughput fall off with range.
Changing the distance value will change the ACK
(Acknowledgement) timeout value accordingly.
Auto Adjust
We recommend enabling the Auto Adjust
option. Every time the station receives a data frame, it
sends an ACK frame to the AP (if transmission errors are
absent). If the station does not receive an ACK frame
from the AP within the set timeout, then it re-sends the
frame. If too many data frames are re-sent (whether the
ACK timeout is too short or too long), then there is a poor
connection, and throughput performance drops.
The device has a new auto-acknowledgement
timeout algorithm, which dynamically optimizes the
frame acknowledgement timeout value without user
intervention. This critical feature is required for stabilizing
long-distance 802.11n outdoor links.
If two or more stations are located at considerably
different distances from the AP they are associated with,
the distance to the farthest station should be set on the
AP side.
Aggregation
A part of the 802.11n standard that allows
sending multiple frames per single access to the medium
by combining frames together into one larger frame. It
creates the larger frame by combining smaller frames with
the same physical source, destination end points, and
traffic class (QoS) into one large frame with a common
MAC header.
•
Frames
Determines the number of frames combined in
the new larger frame.
•
Bytes
Determines the size (in bytes) of the larger frame.
•
Enable
Check the box to use the Aggregation option.
Multicast Data
Allows multicast packets to pass through.
By default this option is enabled.
Multicast Enhancement
(Available in Access Point or
AP‑Repeater mode only.) If clients do not send IGMP
(Internet Group Management Protocol) messages, then
they are not registered as receivers of your multicast
traffic. Using IGMP snooping, the Multicast Enhancement
option isolates multicast traffic from unregistered
clients and allows the device to send multicast traffic to
registered clients using higher data rates. This lessens the
risk of traffic overload on PtMP links and increases the
reliability of multicast traffic since packets are transmitted
again if the first tranmission fails. If clients do not send
IGMP messages but should receive multicast traffic, then
you may need to disable the Multicast Enhancement
option. By default this option is enabled.
Installer EIRP Control
Allows you to control the Auto
Adjust to EIRP Limit setting on the Wireless tab.
Extra Reporting
Reports additional information, such
as device name, in the 802.11 management frames. This
information is commonly used for system identification
and status reporting in discovery utilities and router
operating systems.
Client Isolation
(Available in Access Point or AP‑Repeater
mode only.) Allows packets to be sent only from the
external network to the CPE and vice versa. If Client
Isolation is enabled, wireless stations connected to the
same AP will not be able to interconnect on both the Layer
2 (MAC) and Layer 3 (IP) levels. This also affects associated
stations and WDS peers as well.
Sensitivity Threshold, dBm
Defines the minimum client
signal level accepted by the AP for the client to connect.
If the client signal level subsequently drops, the client
remains connected to the AP.
