Static – Ubiquiti Networks PowerBridgM User Manual
Page 36
33
Chapter 5: Network Tab
airOS
™
v5.5.4 User Guide
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
•
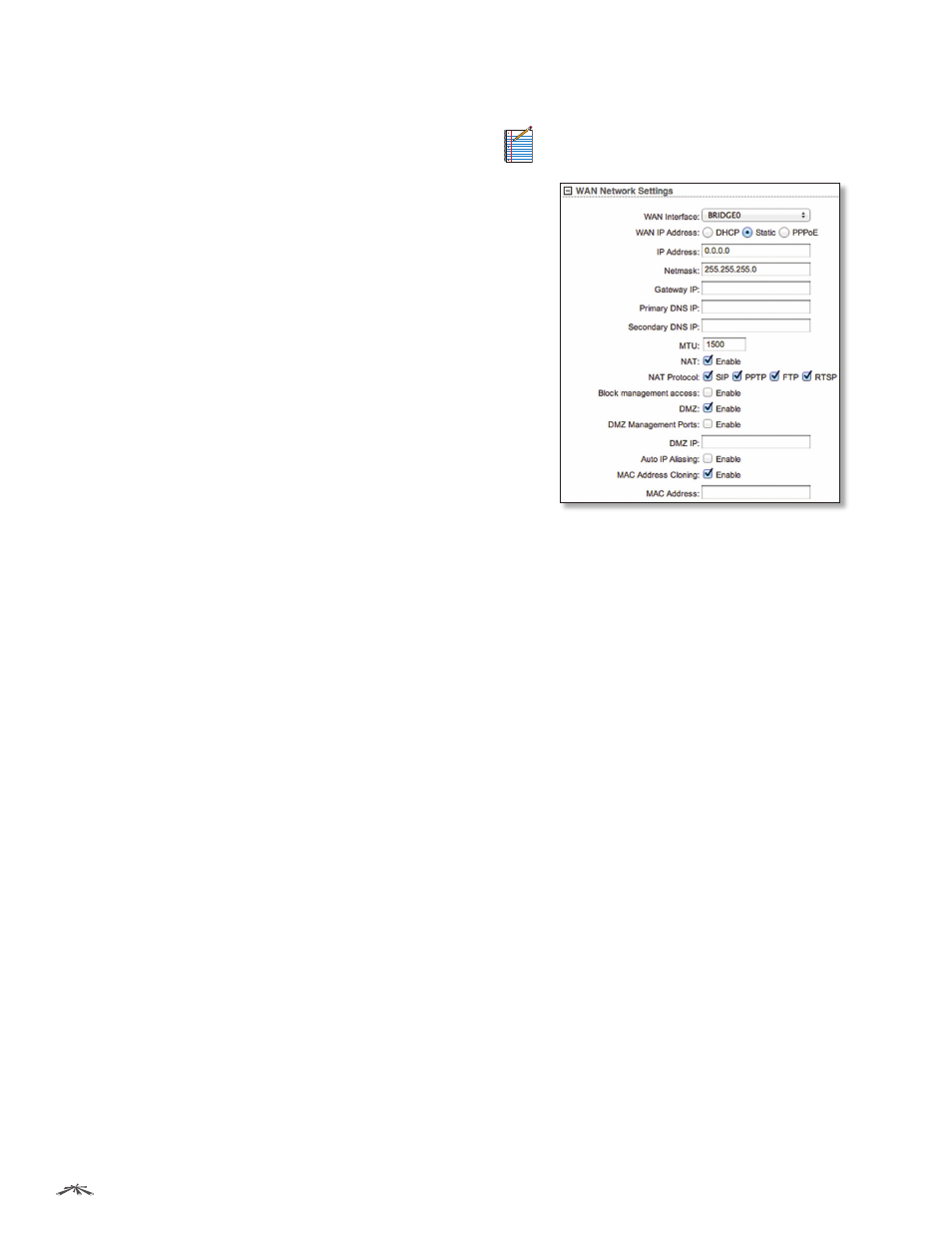
DMZ Management Ports
The web management port
(TCP/IP port 80 by default) of the airOS device will be
used for the host device. The airOS device responds to
requests from the external network as if it were the host
device that is specified with the DMZ IP address. DMZ
Management Ports is disabled by default; the device is
accessible from the WAN port. If DMZ Management Ports
is enabled, all management ports will be forwarded to
the device, so you’ll only be able to access the device
from the LAN side.
•
DMZ IP
Specify the IP address of the local host network
device. The DMZ host device will be completely exposed
to the external network.
Auto IP Aliasing
If enabled, automatically generates an
IP address for the corresponding WLAN/LAN interface.
The generated IP address is a unique Class B IP address
from the 169.254.X.Y range (netmask 255.255.0.0), which
is intended for use within the same network segment only.
The Auto IP always starts with 169.254.X.Y, with X and Y
as the last two octets from the MAC address of the device.
For example, if the MAC is 00:15:6D:A3:04:FB, then the
generated unique Auto IP will be 169.254.4.251.
The Auto IP Aliasing setting can be useful because you
can still access and manage devices even if you lose,
misconfigure, or forget their IP addresses. Because an
Auto IP address is based on the last two octets of the MAC
address, you can determine the IP address of a device if
you know its MAC address.
MAC Address Cloning
When enabled, you can change
the MAC address of the respective interface. This is
especially useful if your ISP only assigns one valid IP
address and it is associated to a specific MAC address. This
is usually used by cable operators or some WISPs.
•
MAC Address
Enter the MAC address you want to clone
to the respective interface. This becomes the new MAC
address of the interface.
Static
Assign static IP settings to the device.
Note:
IP settings should be consistent with the
address space of the device’s network segment.
IP Address
Specify the IP address of the device. This IP
will be used for device management purposes.
Netmask
When the netmask is expanded into its
binary form, it provides a mapping to define which
portions of the IP address range are used for the network
devices and which portions are used for host devices.
The netmask defines the address space of the device’s
network segment. The 255.255.255.0 (or “/24”) netmask is
commonly used on many Class C IP networks.
Gateway IP
Typically, this is the IP address of the host
router, which provides the point of connection to the
Internet. This can be a DSL modem, cable modem, or
WISP gateway router. The device directs data packets to
the gateway if the destination host is not within the local
network.
Primary DNS IP
Specify the IP address of the primary DNS
(Domain Name System) server.
Secondary DNS IP
Specify the IP address of the
secondary DNS server. This entry is optional and used only
if the primary DNS server is not responding.
MTU
(Available in Simple view.) The Maximum
Transmission Unit (MTU) is the maximum packet size (in
bytes) that a network can transmit. The default is 1500.
NAT
Network Address Translation (NAT) enables packets
to be sent from the external network (WAN) to the local
interface IP address and then sub-routed to other client
devices on its local network while the airOS device is
operating in Access Point or AP‑Repeater mode. Packets are
routed in the reverse direction in Station mode.
NAT is implemented using the masquerade type firewall
rules. NAT firewall entries are stored in the iptables
nat table. Specify static routes to allow packets to pass
through the airOS device if NAT is disabled.
