User tab – Dolphin Peripherals 9500 User Manual
Page 121
Dolphin® 9500 Series User’s Guide
7 - 21
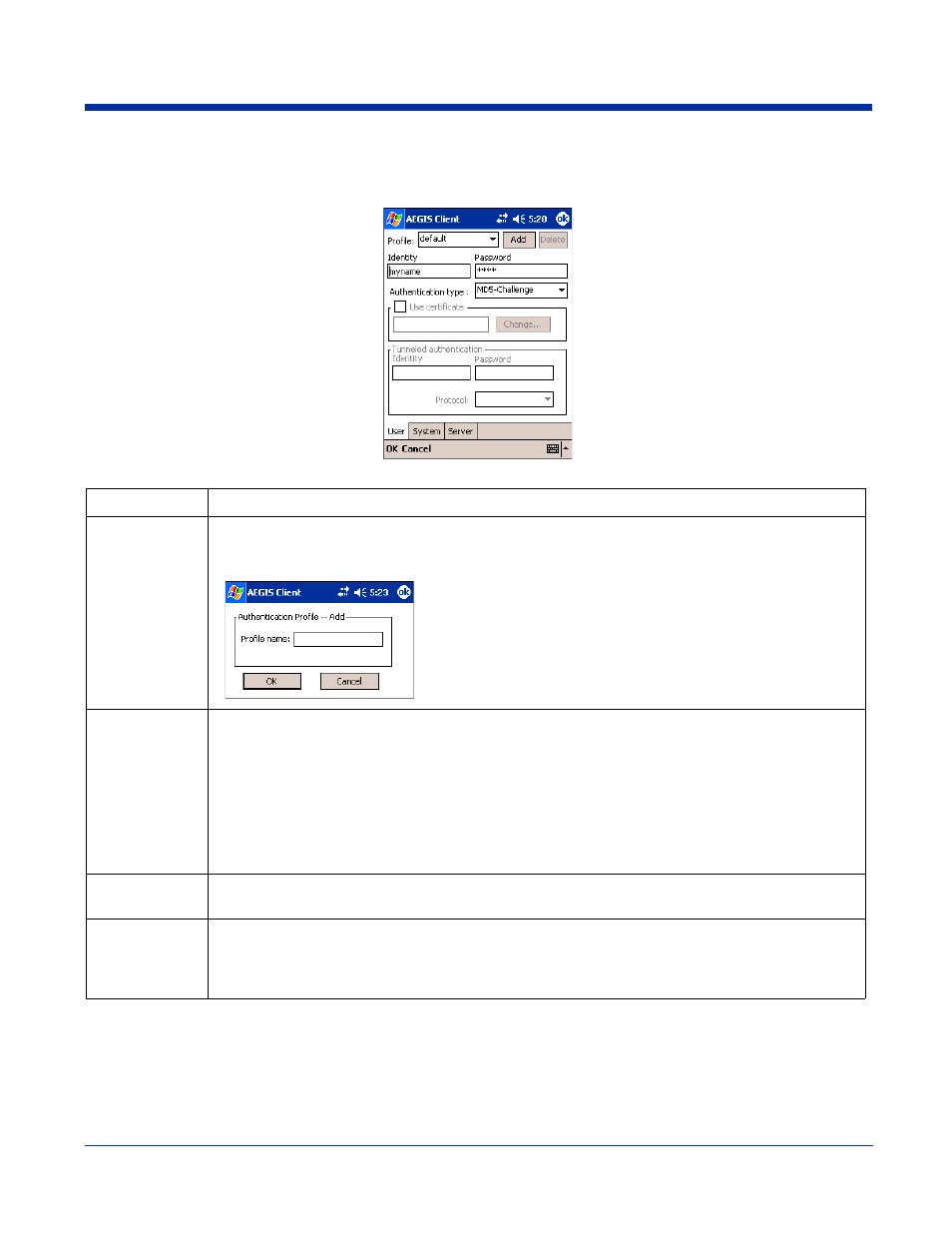
User Tab
The User settings tab defines the protocol and the credentials used to authenticate a user.
Field
Description
Profile
Multiple user credential profiles can be created for use when the user roams from one network to
another. The drop-down list contains existing authentication credential profiles. Select a profile from the
list to edit it in the fields that follow.
Tapping Add permits new profiles to be added to the list. A screen
appears where you can enter a name for the new profile.
Enter a Profile name and tap OK. The name entered appears in the
Profile drop-down list.
Tapping Delete deletes authentication profiles. To be deleted, a pro-
file cannot be assigned to a configured network.
Identity
This is the 802.1X identity supplied to the authenticator. The identity value can be up to 63 ASCII char-
acters and is case-sensitive.
For tunneled authentication protocols such as TTLS and PEAP, this identity (called the Phase 1 identity)
is sent outside the protection of the encrypted tunnel. Therefore, it is recommended that this field not
contain a true identity, but instead the identity “anonymous” and any desired realm (e.g. anony-
[email protected]). For TTLS and PEAP, true user credentials (Phase 2 identity) are entered in the
Tunneled authentication section.
When used with PEAP and the .NET Enterprise Server Version 5.2, this field must contain the identity
used in both Phase I and Phase II. The Phase II identity field is ignored.
Password
This is the password used for MD5-Challenge or LEAP authentication. It may contain up to 63 ASCII
characters and is case-sensitive. Asterisks appear instead of characters for enhanced security.
Authentication
type
This is the authentication method to be used - MD5-Challenge, LEAP, PEAP, TLS, or TTLS.
Your network administrator should let you know the protocols supported by the RADIUS server. The
RADIUS server sits on the network and acts as a central credential repository for Access Servers that
receive the radio signals and ultimately block or allow users to attach to the network.
