Lead / lag operation, 3 or 4 boilers – LAARS NeoTherm NTV (Sizes 150–850 MBTU/h) - Install and Operating Manual User Manual
Page 48
Page 44
LAARS Heating Systems
Caution
You should set the Modbus addresses before you
connect the Modbus wiring. If the wiring is attached
before the Modbus addresses on the controls are
changed, there will be multiple controls with the
same address, and the system will not work.
WARNING
If the Modbus addresses are not assigned properly,
the system could fail to operate correctly, or it might
operate in an unsafe manner. This could lead to
property damage, personal injury or death.
How to get there: On each boiler: From the “Home” screen,
press “I” to go to “Info/Install.” screen. Choose “Advanced
Setup,” then select “System Configuration”. Then select
“System ID & Access,” and select “MB1 Modbus Address.”
Change it to its new unique Modbus address ( 1-8), then
select “MB2 Modbus Address” and change it to the same
address as the changed “MB1 Modbus Address” DO NOT
CHANGE THE MENU LINE “ModBus Address”. It will
automatically change when you change the “MB1 Modbus
Address”
4. The next job is to identify each boiler as a Lead/Lag
Master or Slave.
• On the boiler that will be used as the Lead/Lag Master,
identify the unit that will operate as the master by turning
on “Master Enable.”
How to get there: From the “Home” screen, press “I” to
go to “Info/Install.” Choose “Advanced Setup,” then go
to “Lead/ Lag Configuration.” Select “Lead Lag Master
Configuration.” On the line for “Master Enable,” select
“Enable.”
• On all of the boilers (including the Lead/Lag Master),
identify each unit as a slave by turning on “Slave Enable.”
How to get there: From the “Home” screen, press “I” to
go to “Info/Install.” Choose “Advanced Setup,” then go
to “Lead/ Lag Configuration”. Select “Lead Lag Slave
Configuration.” On the line for “Slave Enable” select
“Enable.” When you select Slave Enable these options will
be displayed
“Enable via Modbus Master” or
“Enable via Sola Master”.
Choose “Enable via Sola Master”.
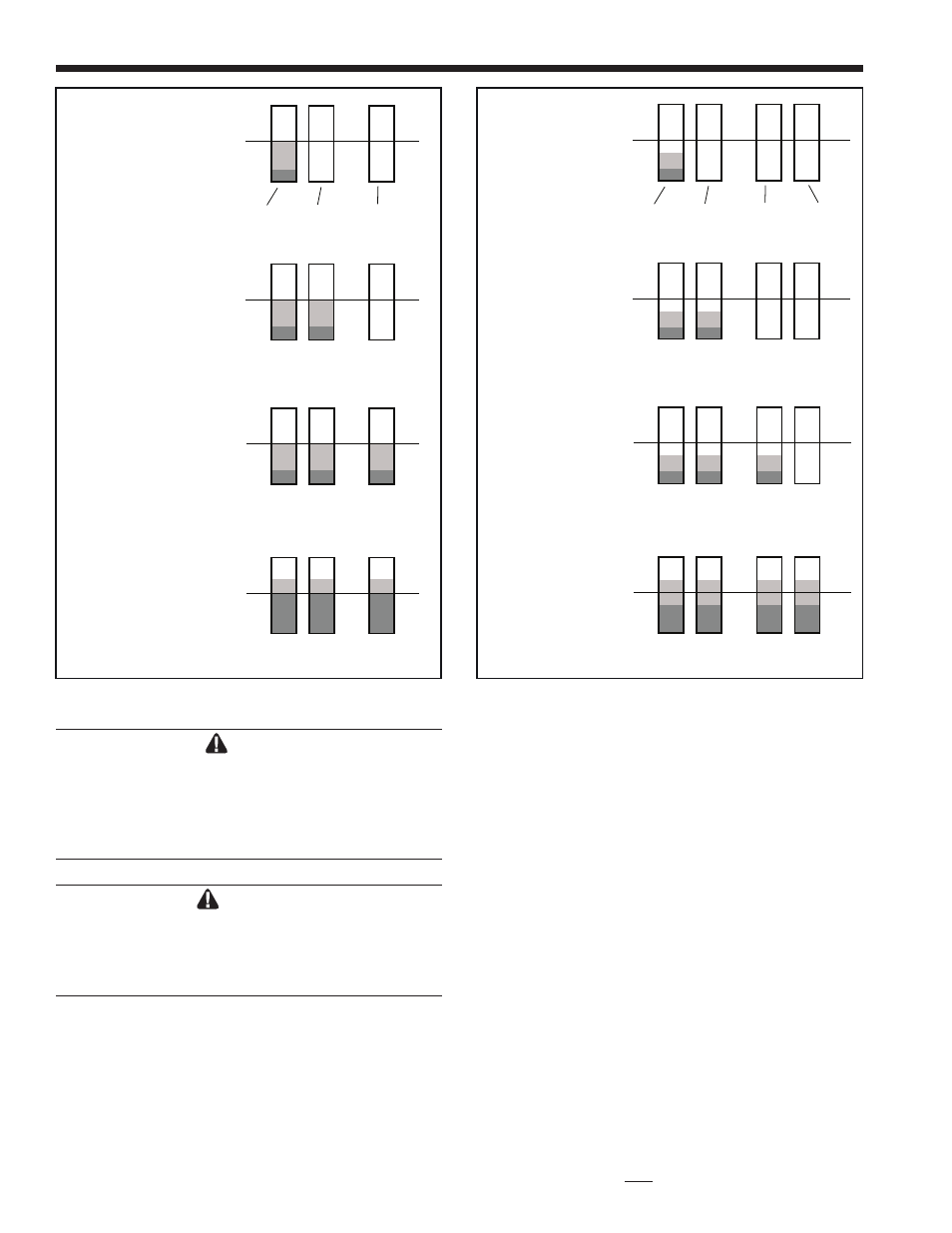
Fig. 39B - Lead / Lag Operation, 3 boilers.
Fig. 39C - Lead / Lag Operation, 4 or more boilers.
Low demand -
The first boiler in
sequence fires at
less than 35%
First
boiler
Second
boiler
Third
boiler
Fourth
boiler
Demand increases -
Once the first boiler
reaches 35%,
the second boiler
switches on, and
both modulate
together between 20%
and 35%
Demand increases -
Once the first two
boilers reach 35%,
the third boiler
switches on, and all
three modulate together
between 20% and 35%
Nearing max. demand -
The fourth boiler is
active. Once all four
reach 35%, all are
allowed to go over
35%
* - The Lead/Lag controller will change the firing order of the boilers,
based on the run time of each burner.
Low demand -
The first boiler in
sequence fires at
less than 50%
First
boiler
Second
boiler
Third
boiler
Demand increases -
Once the first boiler
reaches 50%,
the second boiler
switches on, and
both modulate
together between 20%
and 50%
Demand increases -
Once the first two
boilers reach 50%,
the third boiler
switches on, and all
three modulate together
between 20% and 50%
Nearing max. demand -
Once all three reach
50%, then all three
are allowed to go over
50%
* - The Lead/Lag controller will change the firing order of the boilers,
based on the run time of each burner.
