Cabletron Systems DMS-100 User Manual
Page 156
156 Appendix E: Understanding IP and IP addressing
297-8991-910 Standard 03.01 August 1999
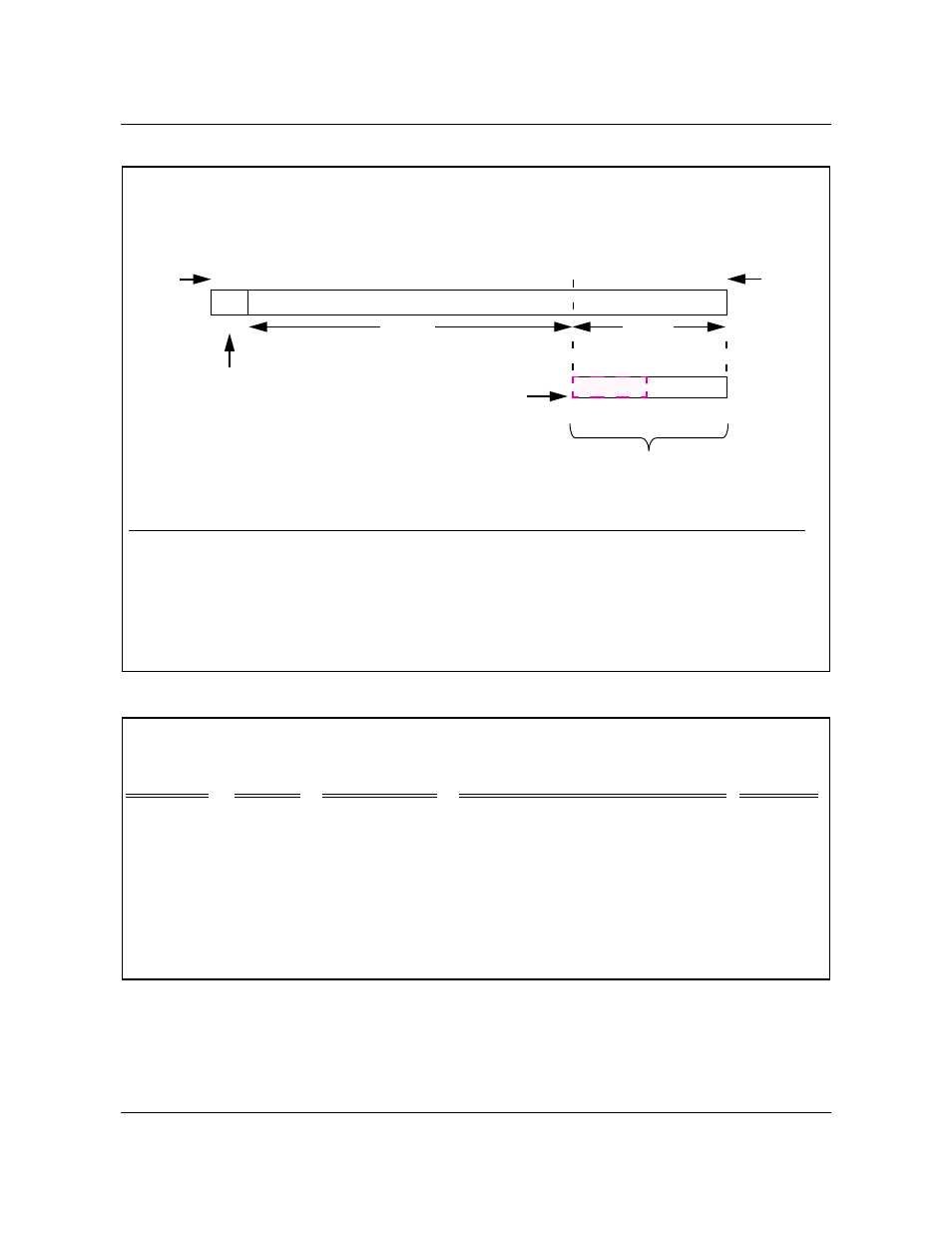
Figure 33
IP addressing: class C
Figure 34
Subnet mask: class C
|
|
21
32
networkid
hostid
bits
|
hostid
bits
3 bit
2 to 6 bits
Class C indicator
|
|
|
subnet id
|
|
|
2 to 6 bits
110
therefore, we can have 16384-2 class C networks each with 65536-2 hosts (if no subnets).
Class C addresses range from 192.0.0.X to 223.255.255.X (standard network mask is 255.255.255.0),
Note 1: Network ids and host ids which are comprised of all 1’s or all 0’s are reserved,
therefore, subtract 2 from the subnet id and hostid to get the actual count.
Note 2: There are also special addresses that are reserved for ‘unconnected’ networks
(networks that use IP but are not connected to the Internet). Class C networks
have 256 of these special addresses ranging from 192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.0.
Base_Tel-13
For any class, the hostid can be split into a subnet id and a hostid depending on custom-
er requirements. This helps simplify routing to areas. For class C network, the subnet id
can range from 2 to 6 bits.
8 bits
Field subnet in table IPNETWRK
Base_Tel-14
CLASS C subnet masks
IPNETWRK
No. subnets
No. hosts
netmask
Netmask in binary format
subnet size
2 62 255.255.255.192 (11111111.11111111.11111111.11000000) 2
6 30 255.255.255.224 (11111111.11111111.11111111.11100000) 3
14 14 255.255.255.240 (11111111.11111111.11111111.11110000) 4
30 6 255.255.255.248 (11111111.11111111.11111111.11111000) 5
62 2 255.255.255.252 (11111111.11111111.11111111.11111100) 6
Host/Router DMS
