Second derivative, Σ calculation, A syntax and input – Casio fx-5800P User Manual
Page 47: A remarks, E-46
E-46
differential calculation result that approaches zero can cause poor precision or error.
• You can interrupt an ongoing differential calculation operation by pressing
o.
k
Second Derivative
Your calculator lets you calculate the second derivative coeffi cient (
d
2
/
dx
2
(
f
(
x
))|
x
=
a
) for
f
(
x
)
where
x
=
a
. Your calculator uses approximation based on the second order value differential
equation of the Newton interpolation polynomial. Calculation is performed using the function
shown below.
d
2
/
dx
2
(
A Syntax and Input
d
2
/
dx
2
(
f
(
x
),
a
,
tol
)
f
(
x
): Function of
x
(Input the function used by variable X.)
• All variables other than X are viewed as constants.
a
:
Value of point (second derivative point) of desired second derivative
coeffi cient
tol
: Error tolerance range (Can be input only when linear display is being used.)
• This parameter can be omitted. In that case, a tolerance of 1 × 10
–10
is used.
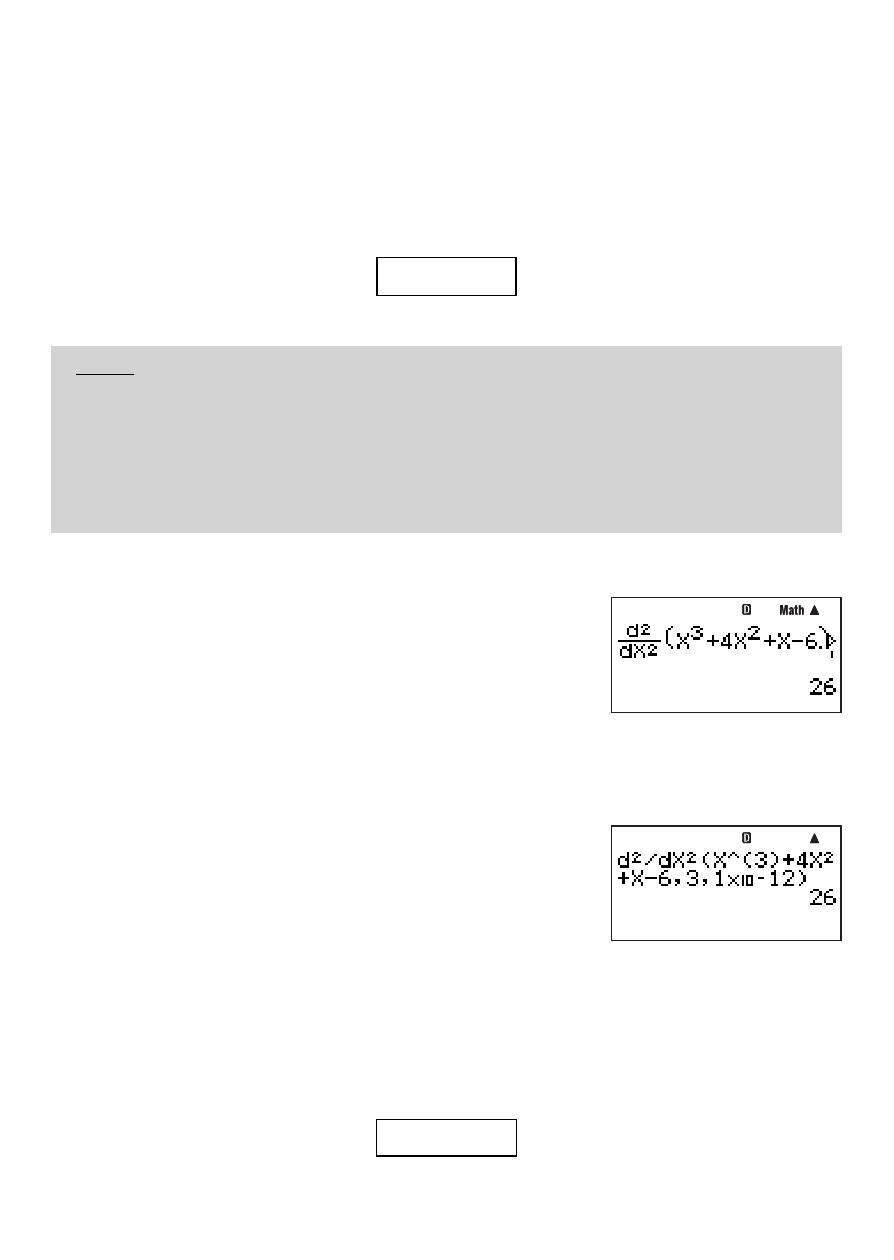
Example 1: To obtain the second derivative coeffi cient for the function
y
=
x
3
+ 4
x
2
+
x
– 6
when
x
= 3
B
z – {MATH} 3(d
2
/dX
2
)
S0(X)63e
+4S0(X)x+S0(X)-6e3E
Example 2: To perform the same procedure as Example 1, specifying
tol
= 1 × 10
–12
Since you want to specify a value for
tol
, you will need to perform this calculation using
linear display.
b
z – {MATH} 3(d
2
/dX
2
)
S0(X)63)+4
S0(X)x+S0(X)-6,3,1Z-
12)E
A Remarks
See the remarks for derivative on page 45.
k
Σ Calculation
This function determines the sum of an input
f
(
x
) for a specifi ed range. Calculation is
performed using the function shown below.
Σ (
