Acronis True Image 9.1 Server for Windows - User Guide User Manual
Page 42
screen. Then your settings will be saved as default. See
for more
information.
12. Click Next.
13. Set filters for the specific types of files that are not to be restored. For example, you may
want hidden and system files and folders, as well as files with .~, .tmp and .bak
extensions, not to be restored from the archive.
You can also apply custom filters, using the common Windows masking rules. For example,
to exclude all files with extension .exe, add *.exe mask. My???.exe mask will reject all .exe
files with names consisting of five symbols and starting with “my”.
All of these settings will take effect for the current task. How to set the default filters that
will be called each time you restore data, see
14. Click Next.
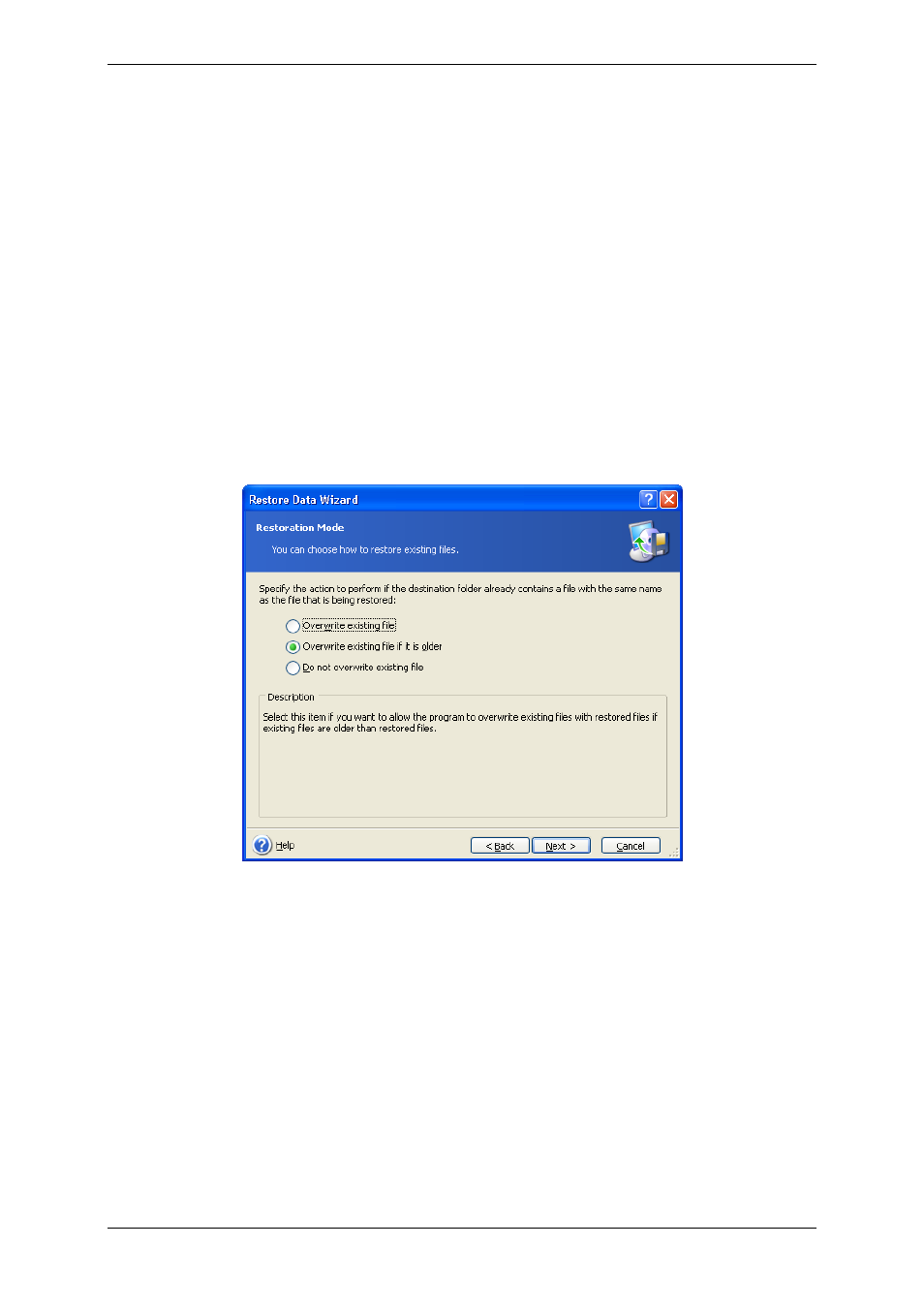
15. The next selection allows you to keep useful data changes made since the selected
backup was created. Choose what to do if the program finds in the target folder a file with
the same name as in the archive.
Overwrite existing file – this will give the archived file unconditional priority over the file
on the hard disk.
Overwrite existing file if it is older – this will give the priority to the most recent file
modification, whether it be in the archive or on the disk
Do not overwrite existing file – this will give the file on the hard disk unconditional
priority over the archived file.
16. At the final step, the restoration summary is displayed. Up to this point, you can click
Back to make changes in the created task. Clicking Proceed will launch the task execution.
17. The task will appear on the Active tasks pane of the main window. The task progress
will be shown in a special window. You can stop the procedure by clicking Cancel. Please
keep in mind that the aborted procedure still may cause changes in the destination folder.
42 Copyright © Acronis, Inc., 2000-2006
