Cabling the network synchronization port, Cabling the clock ports on the bits chassis, Cabling the network synchronization port -10 – Carrier Access BROADway System 770-0125-AB User Manual
Page 26: Cabling the clock ports on the bits chassis -10, Installation
2-10
BROADway - Release 4.00
Installation
Cabling the Network Synchronization Port
Cabling the Network Synchronization Port
There are two chassis types, BITS and ITU; the difference is in the number and type of network
synchronization ports. The network synchronization ports (CKIN-1 and CKIN-2) can be connected to
an external synchronization source that is typically traceable to a Stratum 1 level primary reference
source. In the U.S. and Canada the BITS chassis expects to see a D4 or ESF framed T1 signal at this
input. In countries that utilize an E1 network hierarchy, the ITU chassis expects to see a ITU-T G.703
2.048 MHz square wave signal. These connections are optional and should only be used when external
timing is required. If a single external input only is available, it should always be connected to CKIN-1
rather than CKIN-2. For more information about network synchronization, refer to Timing and
Synchronization in the online help.
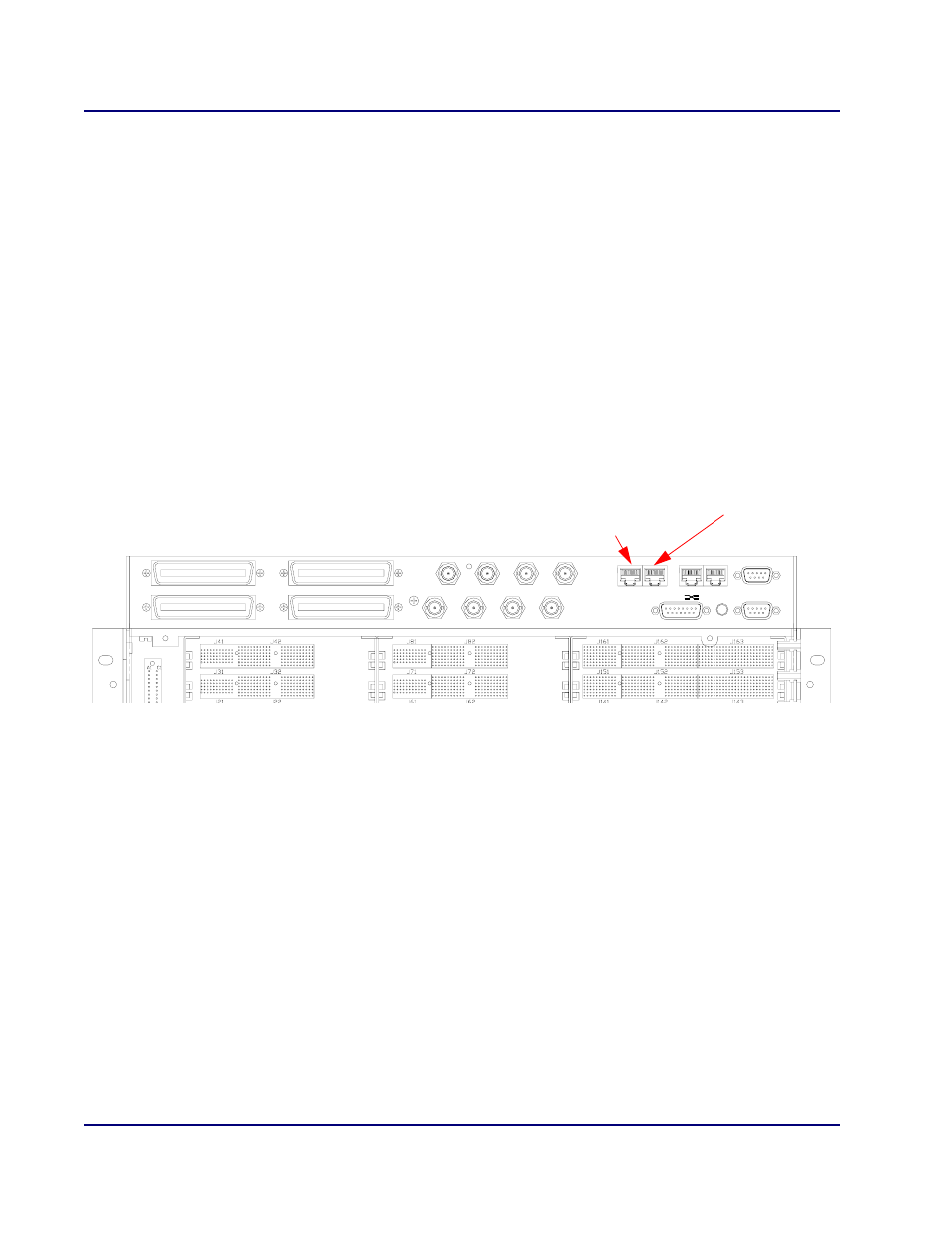
Cabling the Clock Ports on the BITS Chassis
On the front panel of the chassis are two synchronization clock ports: CKIN-1 and CKIN-2 (one is
redundant for the other). CKIN-1 connects to NSP-1, and CKIN-2 connects to NSP-2.
The CKIN-1 and CKIN-2 ports are female, RJ45 connectors. For pinout information on CKIN-1 and
CKIN-2, see CKIN-1 and CKIN-2 Connector Pinouts (BITS Only) on page A-4.
CKIN-1
NIP TX1
NIP TX2
TX2
TX1
TX3
TX4
NIP RX1
NIP RX2
RX3
RX1
RX2
RX4
ALARMS
ACO
SCP-2
ETH-1
CKIN-2
ETH-2
SCP-1
Connect a clock source
Connect a second clock source
