Over-speed monitoring applications – Banner Safe Speed Monitoring Modules User Manual
Page 11
Configuration for Zero Speed Detection
These directions illustrate only one setup method, which may be not as accurate as using an rpm meter or an oscilloscope to set the
switching frequency to a precise value. This example should set the switch point very close to Standstill.
1. Turn OFF power to the Module and the machine.
2. Pry open the Module's front plate with a small flat-blade screwdriver.
3. Select the range with the slowest ipm values using the DIP switches (5-40 ipm range for model SSM-FM-11A10 and 10-80 ipm range
for model SSM-FM-11A20).
4. Set the simultaneity potentiometer to the middle position (0).
5. Use the fine-tuning potentiometer to set the switch point to the lowest possible value (fully counter-clockwise, to the 1 setting).
6. If the sensors are not yet installed, install them now so that they can detect the rotation of the motor.
7. Connect the sensor outputs to the Module.
8. Disconnect the wires from the Module safety output contacts 13-14 and 23-24.
9. Connect power to the Module; the Motor should still be OFF.
The Module Power LED must come ON immediately. The safety output contacts (13-14 and 23-24) and indicators should come ON
after no more than a 3-second time delay.
10. Start the motor.
The safety output contacts and indicators should turn OFF (safety contacts open), as soon as the motor speed passes the switch
point for standstill.
11. Stop the motor.
After the motor speed drops below the minimum switch point value (less than 5 ipm or 10 ipm, depending on model) and after the
selected delay time, the N.C. safety output contacts and indicators should turn ON.
12. If the motor speed does not drop below the minimum switch point value, or if only one of the two channels detects a standstill condi-
tion, restart the motor, and increase the switch point for standstill slightly, by turning the fine-tune potentiometer a few degrees clock-
wise. Repeat this procedure until both channels detect standstill and turn OFF both internal relays simultaneously.
13. Connect safety outputs 13-14 and 23-24 to the monitoring circuit and verify that the system works according to the requirements.
Over-speed Monitoring Applications
For over-speed monitoring applications, the sensor setup is similar to standstill monitoring applications, except for the setting of the
switch point value. The safety output contacts are ON (closed) when the motor speed is below the set standstill switch point value; the
safety output contacts open when the motor speed exceeds the set over-speed value.
Setup
Safety Outputs
Motor Max.
Speed (2,000 rpm)
Set Switch Point Value
(300 rpm)
Set Switch Point Value
(2,000 rpm)
Output contacts
turn OFF again,
signaling overspeed
Motor speed increased above max.
speed of 2,000 rpm
Normal
Operation
Speed
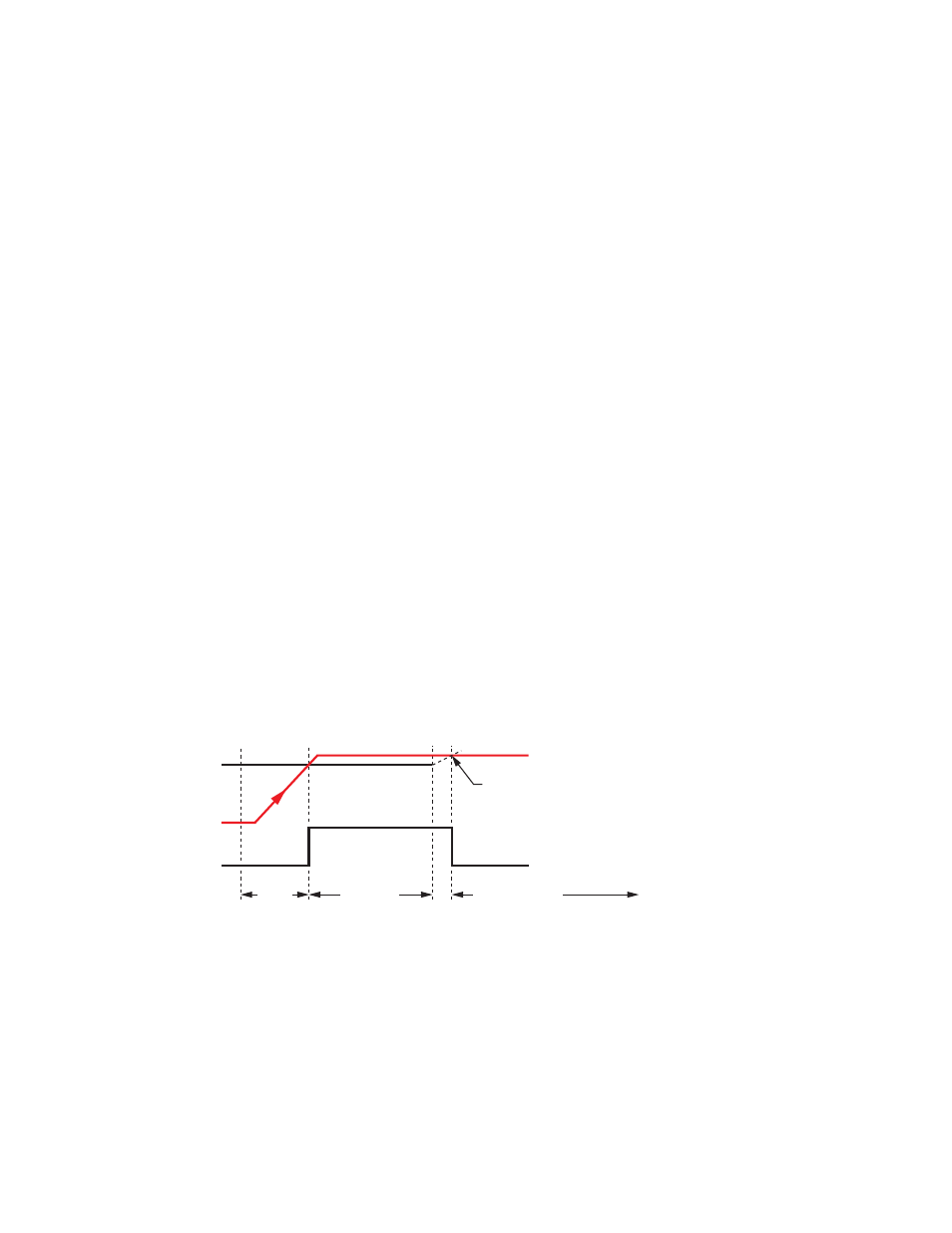
Figure 9. Over-speed Timing
For over-speed monitoring, it is important to adjust the two input channels sothey switch simultaneously. If one of the channels detects
the over-speed signal first, its internal relays will drop out and switch the safety output contacts OFF, dropping the motor speed immedi-
ately; the second input's internal relay would then remain ON, preventing the Module and the motor from restarting. (To restart in this
situation, cycle power to the Module.) The input channels are factory pre-adjusted, use the simultaneity potentiometer (behind the Module
front cover) to further synchronize the input channel timing.
The switch point has some hysteresis, so turn the potentiometer back a degree or so, but not to the point where the safety output indica-
tors turn OFF again. This is now your switch point to detect motor speeds above 2,000 rpm.
Configuring for Over-Speed Detection
Over-speed detection is detecting a high speed anywhere within the set range of the Module. For this example, we are using 2,000 ipm.
SSM-FM-11A... Safe Speed Monitoring Modules
P/N 140782_web
rev. C
www.bannerengineering.com - tel: 763-544-3164
11
