2 alternative modbus register organization, 1 input registers and outputs registers, 2 discrete bit-packed registers – Banner SureCross DX80 Wireless Networks User Manual
Page 5
2.2 Alternative Modbus Register Organization
The SureCross DX80 Alternative Modbus Register Organization registers are used for reordering data registers to allow
host systems to efficiently access all inputs or outputs using a single Modbus command. The register groups include the
input/output registers, bit-packed registers, and analog registers. This feature is only available with the Performance
models using version 3 or newer of the LCD firmware code.
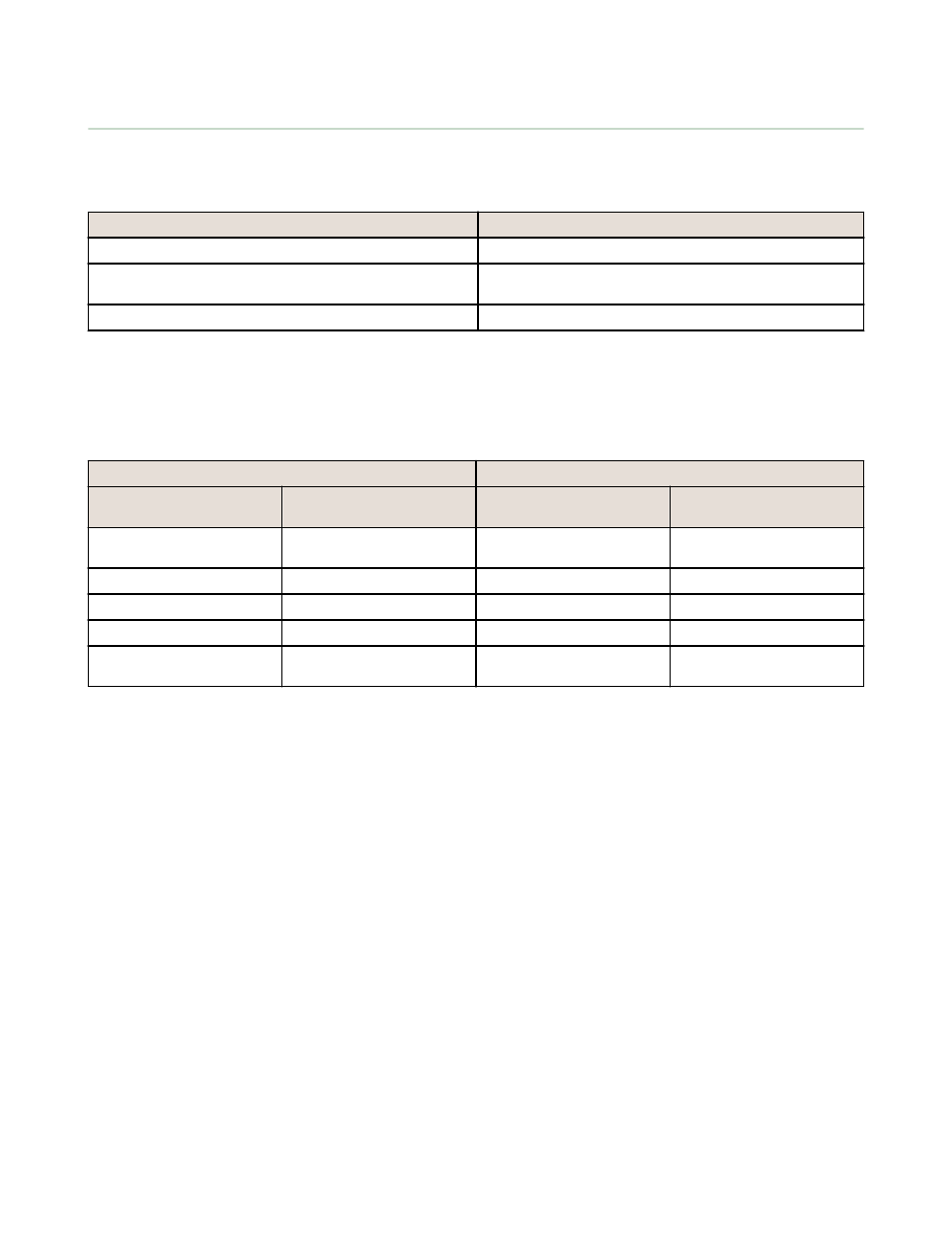
Name
Modbus Register Address (Dec.)
Inputs and Outputs, in order by device
2201 through 4784
Discrete Bit Packed (Status, Discrete Inputs, Discrete
Outputs)
6601 through 6753
Analog Inputs (1-8) and Analog Outputs (1-8)
6801 through 9098
2.2.1 Input Registers and Outputs Registers
Modbus registers 2201 through 2584 are used to organize all inputs together. In this format, users can sequentially read
all input registers using one Modbus message. Modbus registers 4401 through 4784 organize all outputs together to allow
users to sequentially write to all outputs registers using one Modbus message.
Inputs (2201–2584)
Outputs (4401–4784)
Modbus Register Address
(Dec)
16-bit Register Value
Modbus Register Address
(Dec)
16-bit Register Value
2201–2208
Gateway Inputs 1 through 8
4401–4408
Gateway Outputs 1 through
8
2209–2216
Node 1 Inputs 1 through 8
4409–4416
Node 1 Outputs 1 through 8
2217–2224
Node 2 Inputs 1 through 8
4417–4424
Node 2 Outputs 1 through 8
...
...
...
...
2577–2584
Node 47 Inputs 1 through 8
4777–4784
Node 47 Outputs 1 through
8
Refer to your device's datasheet for a list of the active inputs and outputs. Not all inputs or outputs listed in this table may
be active for your system.
2.2.2 Discrete Bit-Packed Registers
Discrete bit-packed registers include the discrete status registers, discrete inputs, and discrete outputs.
Bit packing involves using a single register, or range of contiguous registers, to represent I/O values.
When networks use similar Nodes to gather data using the same I/O registers for each Node, discrete data from multiple
Nodes can be bit packed into a single register on the Gateway. The bit-packed data is arranged by I/O point starting at
Modbus register 6601. For example, Discrete IN 1 for all the Nodes in the network is stored in three contiguous 16-bit
registers.
The most efficient way to read (or write) discrete data from a SureCross
®
DX80 Gateway is by using these bit-packed
registers because users can read or write registers for all devices using one Modbus message. The following registers
contain discrete bit-packed I/O values for the Gateway and all Nodes. Values are stored first for the Gateway, then for
each Node in order of Node address.
Host Controller Systems
5
