Rockwell Automation 5370-CMPK Color CVIM Module MATH-PAK User Manual
Page 42
Chapter 4
Defining Formulas
4–27
Results: Inverse trigonometric function results imply an angle or angular
measurement. The result of an arcsine or arctangent operation is always
given as being between –90
°
and 90
°
(see Figure 4.10, page 4–26).
The result of an arccosine operation is always given as being between 0
°
and
180
°
(see Figure 4.11).
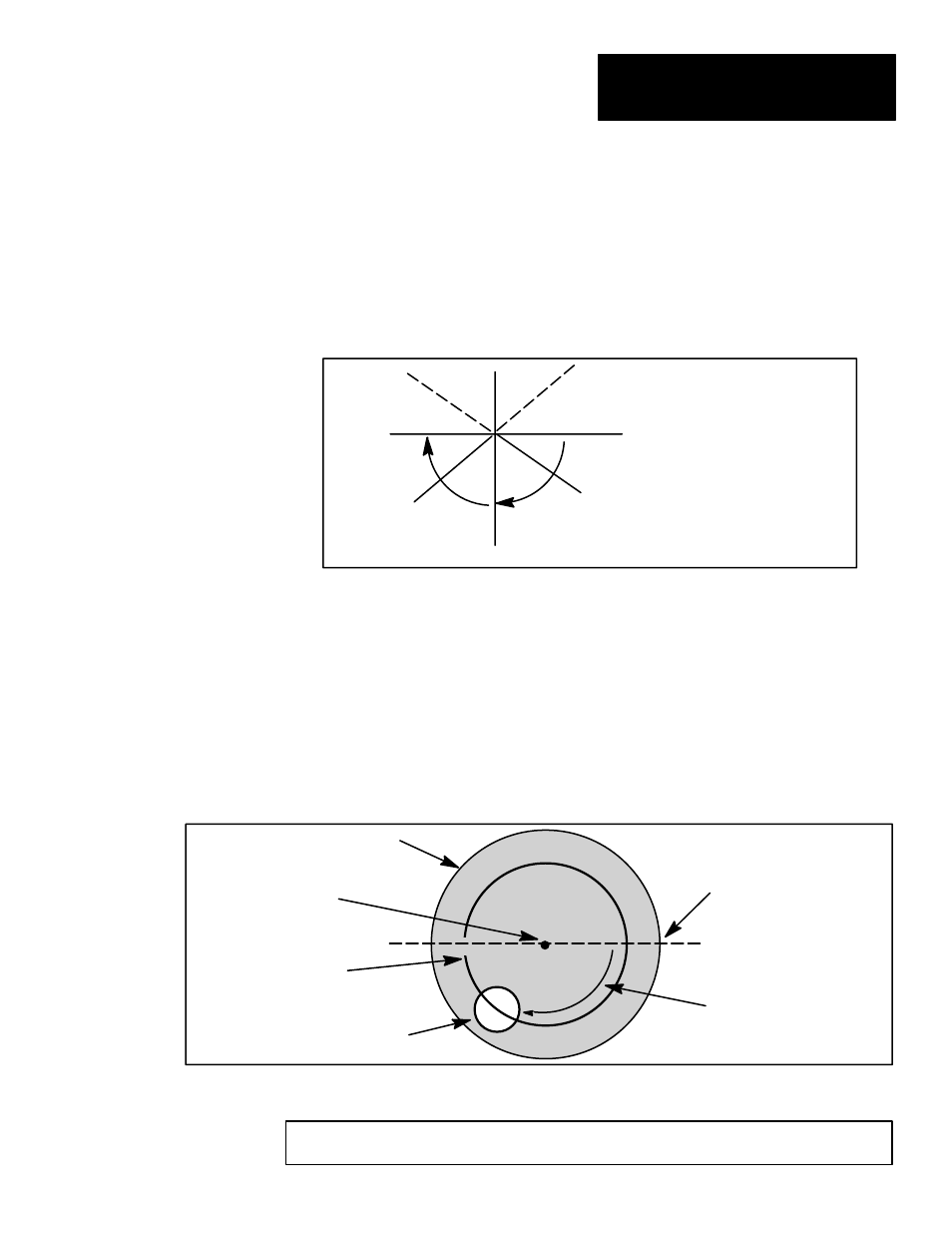
Figure 4.11 Arccosine operation results
90
d
45
d
0
d
Result (implied angle) is
always given as a value
between 0
°
and 180
°
180
d
135
d
( 0 to 90
d
if cosine > 0 )
( 90 to 180
d
if cosine < 0 )
Example arctangent usage: One objective of an inspection is to measure the
angle, clockwise, of an object on a workpiece, relative to an imaginary
horizontal line through the workpiece center (see Figure 4.12).
In this case, gage 2, a circular gage, is set to the
Y Position
operation, with
the feature offset defined to locate of the center of the object (see
Figure 4.12) on a circular workpiece. The
Y Position
operation for a
circular gage finds directional vertical distance from the defined feature to
the implied center of the gage. It is assumed here that the implied center of
the gage is aligned with the center of the workpiece.
Figure 4.12 Example application: Using the arctangent to calculate an angle
q
X
Gage 2 (circular)
finds the position of
the center of the
object on the
workpiece
Workpiece
Implied center of
circular gage,
aligned with
workpiece center
Object
Formula finds the angle of
the object, relative to a
horizontal line drawn
through workpiece center
Horizontal line drawn
through workpiece center
This formula provides the required angular measure:
ARC TAN (GAGE2 / GAGE2.3) + 180 * (GAGE2.3 < 0)
