Buffer i/o – Rockwell Automation Logix5000 Controllers I/O and Tag Data Programming Manual User Manual
Page 19
Communicate with I/O modules
Chapter 1
Where
Is
SubMember
Specific data related to a Member.
Bit
Specific point on a digital I/O module; depends on the size of the I/O module (0–31 for a
32-point module)
Buffering is a technique in which logic does not directly reference or manipulate
the tags of real I/O devices. Instead, the logic uses a copy of the I/O data. Buffer
I/O in the following situations:
• To prevent an input or output value from changing during the execution of
a program. (I/O updates asynchronous to the execution of logic.)
• To copy an input or output tag to a member of a structure or element of an
array.
Tip: Starting with Logix Designer version 24, you can use program parameters to buffer data in a program without
having to copy the data to a second tag. Input and Output program parameters automatically buffer data while the
program routines execute. For more information on program parameters, refer to th
publication
Follow these steps to buffer I/O.
1. On the rung before the logic for the function, copy or move the data from
the required input tags to their corresponding buffer tags.
2. In the logic of the function, reference the buffer tags.
3. On the rung after the function, copy the data from the buffer tags to the
corresponding output tags.
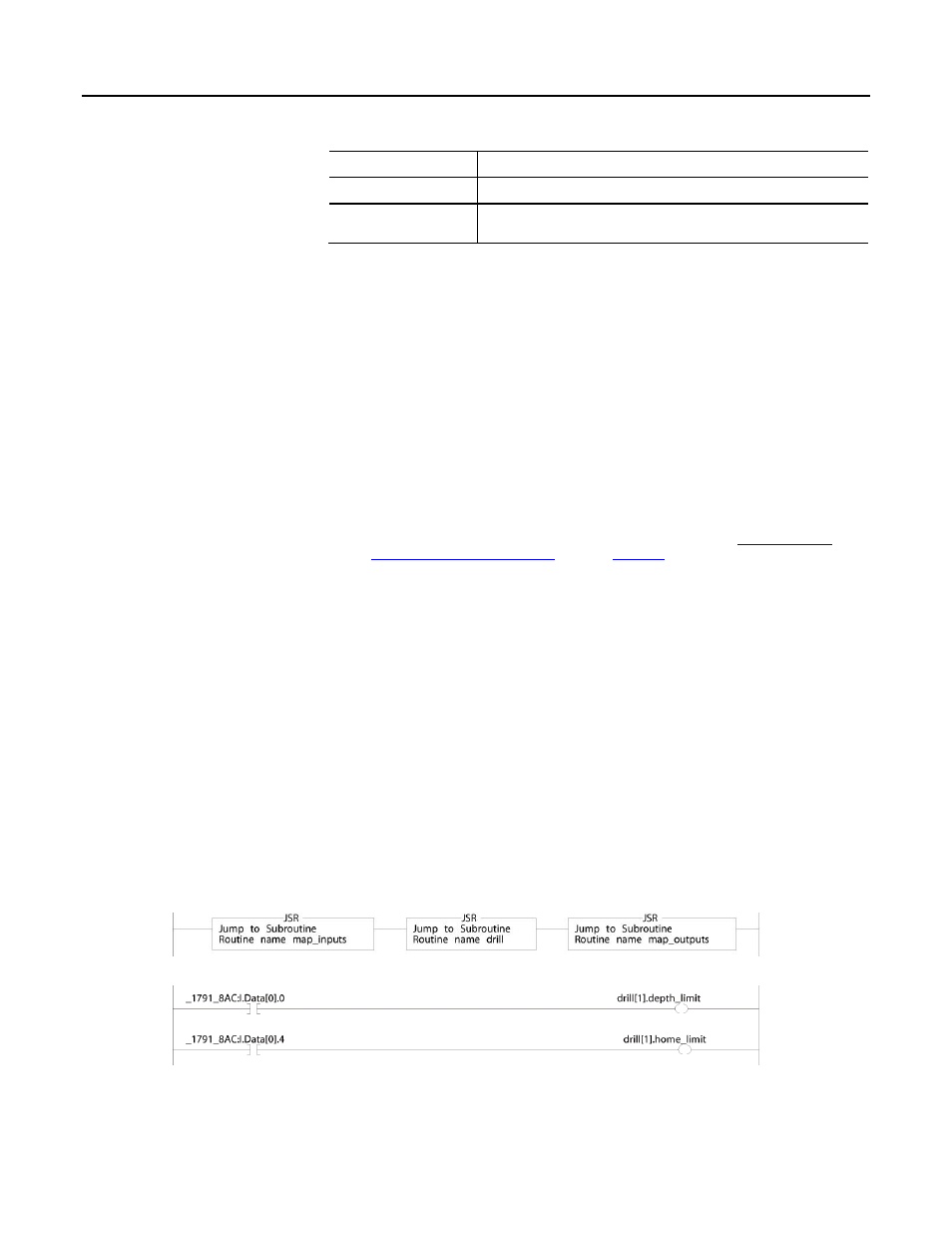
The following example copies inputs and outputs to the tags of a structure for a
drill machine.
Example:
Buffer I/O by mapping values to tags
The main routine of the program executes the following subroutines in this sequence.
The map_inputs routine copies the values of input devices to their corresponding tags that are used in the drill routine.
Buffer I/O
Rock well Automati on Publication 1756- PM004E -EN-P - October 2014
19
