Rung 2:22, Rung 2:23, Rung 2:24 – Rockwell Automation 1403-NENET Ethernet Communication Card Installation Instructions User Manual
Page 74: Rung 2:25, Command msg write, Configuration msg write
Publication 1403-IN005A-EN-P
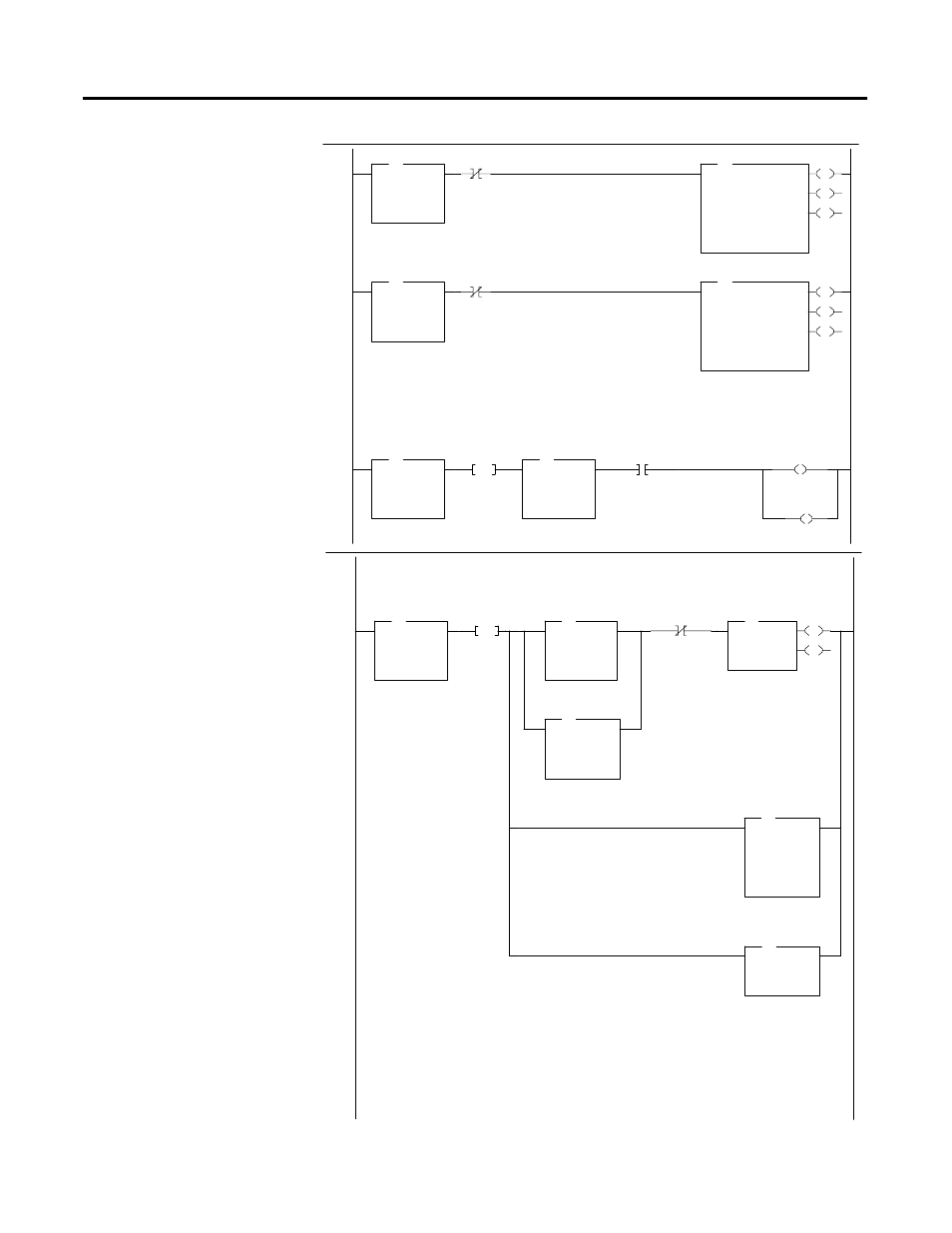
C-14 Sample Ladder Listing
Rung 2:22
Command MSG Write.
Rung 2:23
Configuration MSG Write.
Rung 2:24
If the setpoint counter done bit is set, the
last setpoint MSG Write has occurred and
was followed by a diagnostic MSG Read.
If the diagnostic table indicates a
successful setpoint MSG Write, setpoint
mode is done. The setpoint mode bit is
unlatched, and the run mode bit is
latched.
0022
EQU
Equal
Source A
N9:0
40<
Source B
54
54<
N54:0
15
EN
DN
ER
MSG
Read/WriteMessage
Type
Peer-To-Peer
Read/Write
Write
Target Device
500CPU
Local/Remote
Local
Control Block
N54:0
Control Block Length
14
Setup Screen
Command
0023
EQU
Equal
Source A
N9:0
40<
Source B
55
55<
N55:0
15
EN
DN
ER
MSG
Read/Write Message
Type
Peer-To-Peer
Read/Write
Write
Target Device
500CPU
Local/Remote
Local
Control Block
N55:0
Control Block Length
14
Setup Screen
Config
Begin runmode once all setpoint block transfers are complete
0024
EQU
Equal
Source A
N9:0
40 <
Source B
56
56<
OSR
B3:18
15
One-shot 4
EQU
Equal
Source A
N82:36
0<
Source B
0
0<
Status -
Bad table check
C5:0
DN
Setpoint counter
done bit
B3:0
1
Setpoint mode
B3:0
2
Run mode
Rung 2:25
This rung is activated once when the
sequencer output file changes to setpoint
MSG Write. Its purpose is to determine
the address of the next setpoint data and to
copy the data residing at this address into
the setpoint MSG Write data location.
This is accomplished by first adding an
address offset to a base address to
determine the location of the next setpoint
data. The data residing at the resulting
address is then transferred to the setpoint
MSG Write data location. A counter is
used to determine the address offset. Prior
to the first setpoint MSG Write, the
counter is automatically incremented. For
subsequent setpoint MSG Writes, the
counter is incremented when the
diagnostic table MSG Read for the
previous setpoint MSG Write is successful.
For example, the 3rd setpoint resides at
base address 24. In this case, a counter
value of 3 is added to the base address 21.
The data residing at location 24 is then
transferred into the setpoint MSG Write
data location N86:1.
Load next setpoint into setpoint write data
0025
EQU
Equal
Source A
N9:0
40<
Source B
56
56<
OSR
B3:19
0
One-shot 5
EQU
Equal
Source A
N82:36
0<
Source B
0
0<
EQU
Status
-
Bad table check
EQU
Equal
Source A
C5:0.ACC
3<
Source B
3
3<
Prepareinitial
setpoint write
C5:0
DN
Setpoint counter
done bit
CU
DN
CTU
Count Up
Counter
C5:0
Preset
3<
Accum
3<
Setpoint number
ADD
Add
Source A
21
21<
Source B C5:0.ACC
3<
Dest
N20:1
23<
Setpoint data
address
COP
Copy File
Source #N[N20:1]:1
Dest
#N86:1
Length
20
COP
Move current
setpoint data into
MSG write table
