4 operation, 1 measuring principle, measuring behavior – INFICON BCG450 ATM to Ultra-High Vacuum Triple Gauge User Manual
Page 25
tina40e1-b (2011-04)
25
4 Operation
The BCG450 vacuum gauges consist of three separate measuring systems (hot
cathode Bayard-Alpert (BA) Pirani sensor and capacitance diaphragm sensor).
The BA measuring system uses an electrode system according to Bayard-Alpert
which is designed for a low x-ray limit.
The measuring principle of this measuring system is based on gas ionization. Elec-
trons emitted by the hot cathode (F) ionize a number of molecules proportional to
the pressure in the measuring chamber. The ion collector (IC) collects the thus
generated ion current I
+
and feeds it to the electrometer amplifier of the measure-
ment instrument. The ion current is dependent upon the emission current I
e
, the
gas type, and the gas pressure p according to the following relationship:
I
+
= I
e
× p × C
Factor C represents the sensitivity of the gauge head. It is generally specified for
N
2
.
The lower measurement limit is 5×10
-10
mbar (gauge metal sealed).
To usefully cover the whole range of 5×10
-10
mbar … 10
-2
mbar, a low emission
current is used in the high pressure range (fine vacuum) and a high emission cur-
rent is used in the low pressure range (high vacuum). The switching of the emis-
sion current takes place at decreasing pressure at approx. 7.2×10
-6
mbar, at in-
creasing pressure at approx. 3.2×10
-5
mbar. At the switching threshold, the
BCG450 can temporarily (<2 s) deviate from the specified accuracy.
IC
200V
40V
+
–
+
–
(Degas 250V)
EC
F
F
EC
IC
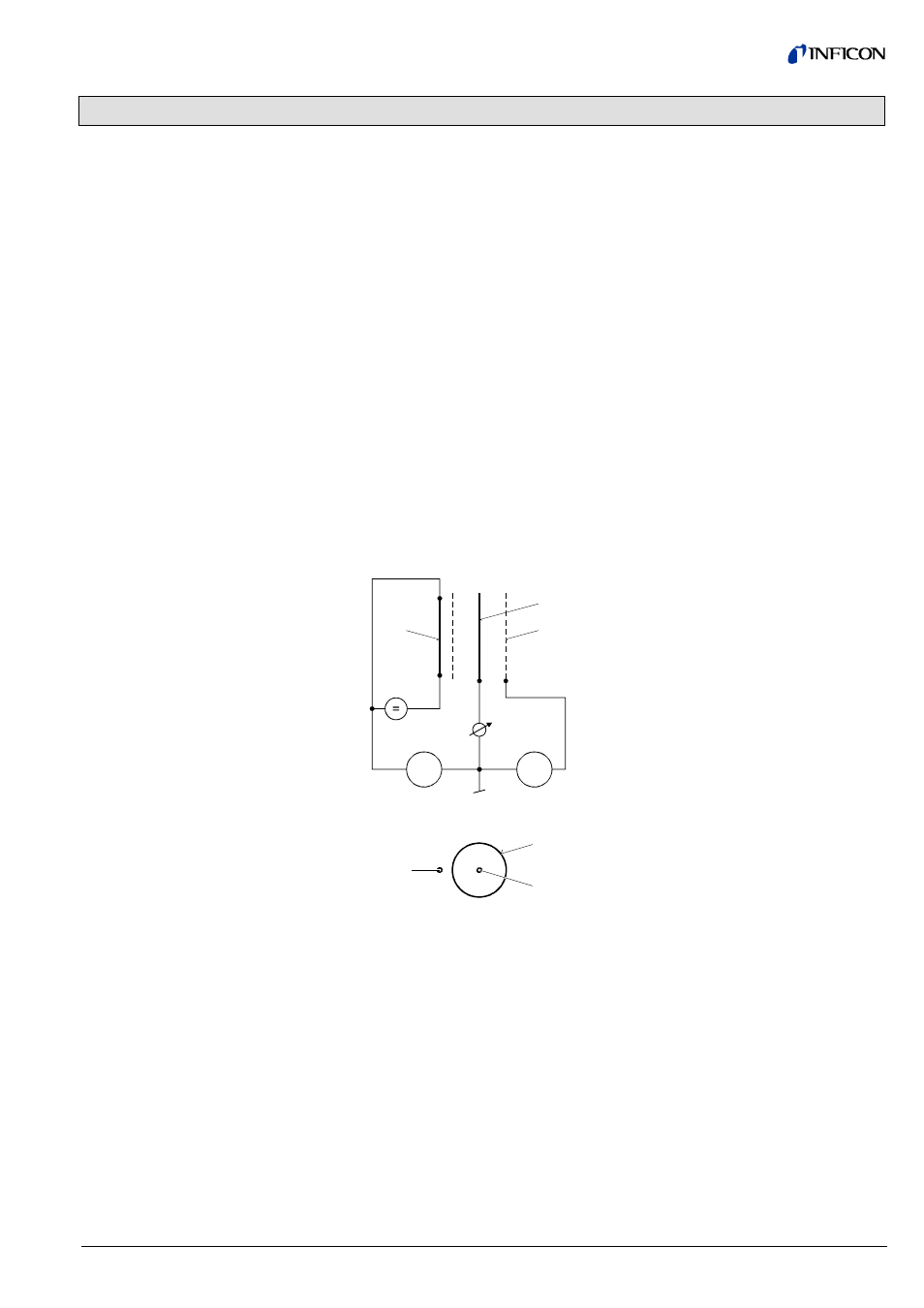
Diagram of the BA measuring system
F
hot cathode (filament)
IC ion
collector
EC anode (electron collector)
Within certain limits, the thermal conductibility of gases is pressure dependent. This
physical phenomenon is used for pressure measurement in the thermal conduc-
tance vacuum meter according to Pirani. A self-adjusting bridge is used as meas-
uring circuit (
→ schematic). A thin tungsten wire forms the sensor element. Wire
resistance and thus temperature are kept constant through a suitable control cir-
cuit. The electric power supplied to the wire is a measure for the thermal conduc-
tance and thus the gas pressure. The basic principle of the self-adjusting bridge
circuit is shown in the following schematic.
4.1 Measuring Principle,
Measuring Behavior
Bayard-Alpert (BA)
Pirani
