Det-Tronics EQP Fire and Gas Detection/Releasing System SAFETY MANUAL User Manual
Page 15
5.1
95-8599
13
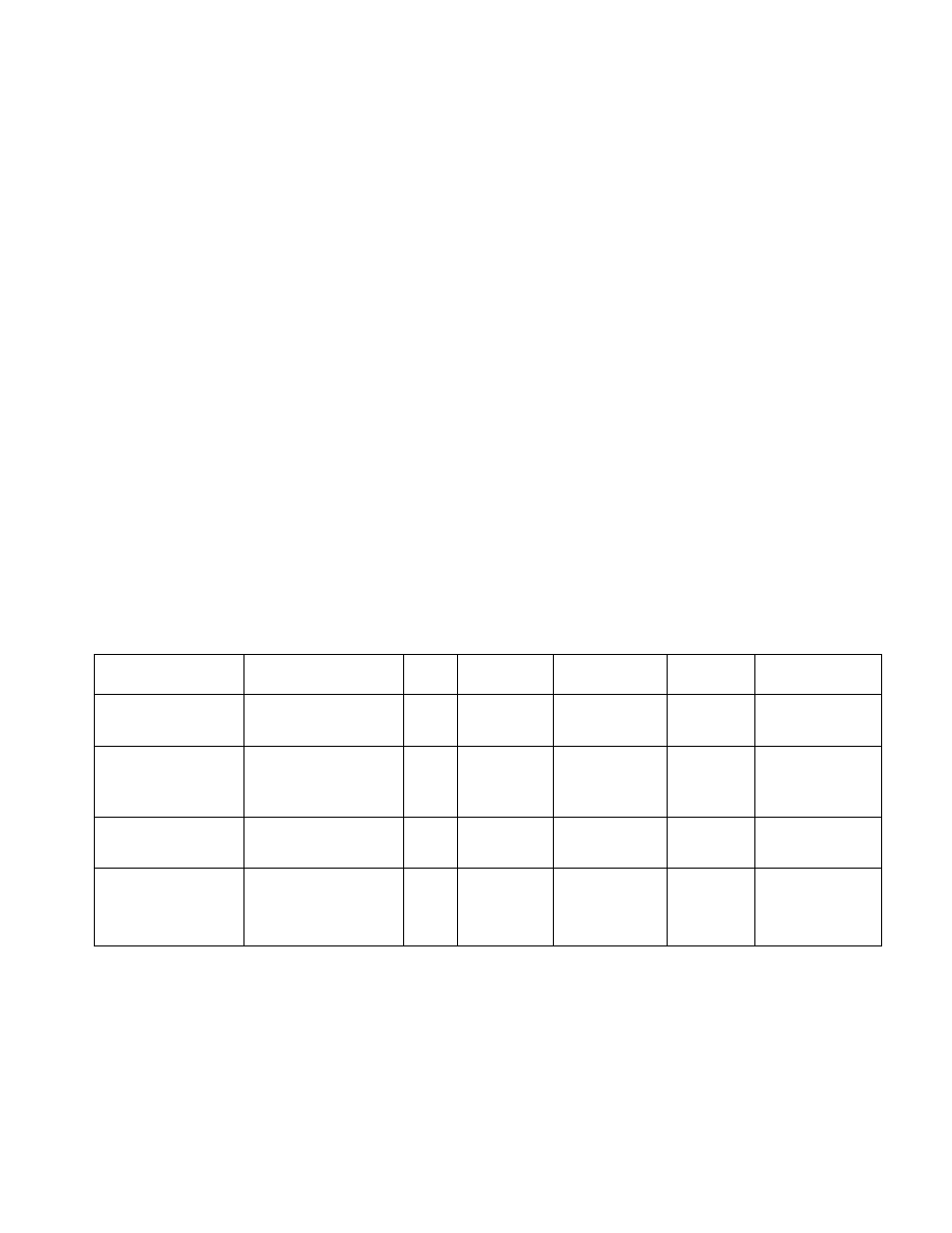
Table 1 provides the low demand EQP SIL 2 Safety
Function model and recommendations for complex
modeling (see Note 3).
PFDavg for each element is calculated according
to the equation above, where
l
DU
is the undetected
dangerous failure rate per 10
9
hours and T1 is the proof
test interval. (In this example, T1 is chosen as 1 year
(8760 hours) for all components of the safety function).
The value of PFDavg for the system is the sum of
PFDavg for the individual elements.
Note
the eQP system is an energize to trip system.
the power supply to the output device should
be monitored and annunciated when lost. this is
counted as a Dangerous Detected (DD) fault. If the
power supply is not monitored, it must be counted
as a Dangerous Undetected (DU) fault.
Example 1 (figure 3A)
Fire input from an X3301 and output to an EDIO.
PfDavg
= 0.58 x 10
-3
+ (0.38 x 10
-3
+ 0.1 x 10
-3
) +
0.1 x 10
-3
+ valve & supply = 1.16 x 10
-3
+ valve & supply
Example 2 (figure 3B)
Gas alarm from a PIRECL and output to an EDIO.
PfDavg
= 0.58 x 10
-3
+ (0.38 x 10
-3
+ 0.1 x 10
-3
) +
0.1 x 10
-3
+ valve & supply = 1.16 x 10
-3
+ valve & supply
Example 3 (figure 3C)
Input from an EDIO and output to the same EDIO.
PfDavg
= 0.003 x 10
-3
+ (0.38 x 10
-3
+ 0.1 x 10
-3
) +
0.1 x 10
-3
+ valve & supply = 0.58 x 10
-3
+ valve & supply
Using the table given in the standard, this value would
be suitable for a low demand SIL 2 safety function.
Other conditions (hardware fault tolerance and safe
failure fraction) also allow its use in a SIL 2 application.
See IEC 61508-6 for a more comprehensive guide to the
calculation of PFDavg.
Safety function
INPUT
Safety function
OUTPUT
Sff
Total failure
Rate
DU
(failure to Trip)
SU
(false Trip)
DD
(Detected fault)
X3301 FIRE InPUT
EDIO OUTPUT
(OPEn MOnITORInG) 96.6%
7,070 FIT
242 FIT
226 FIT
2,980 FIT
EDIO FIRE InPUT
(OPEn & SHORT
MOnITORInG)
EDIO OUTPUT
(OPEn MOnITORInG) 96.9%
3,580 FIT
110 FIT
130 FIT
2,020 FIT
PIRECL GAS InPUT
EDIO OUTPUT
(OPEn MOnITORInG) 96.2%
6,420 FIT
242 FIT
316 FIT
3,920 FIT
EDIO GAS InPUT
(OPEn & SHORT
MOnITORInG)
EDIO OUTPUT
(OPEn MOnITORInG) 96.9%
3,580 FIT
110 FIT
130 FIT
2,020 FIT
nOTE 1: The table includes consideration to a 246 node system with 6 network Extenders, 14 Physical Layer Repeaters, maximum
cable distance, and a 1-year Proof Test Interval (nFPA 72 requirement) with usage of less than 65% of the SIL 2 budget.
nOTE 2: One EDIO provides both the input channel and the output channel.
nOTE 3: For complex modeling of the EQP System, reference the exida
®
tool at www.exida.com.
Table 1—EQP SIL 2 Safety Function Model - Example
