Other relevant documentation or manuals, Condensed power monitor – Goulds Pumps 3296 EZMAG - IOM User Manual
Page 91
Other Relevant Documentation or Manuals
Other Relevant Documentation or Manuals
Condensed power monitor
Description
ITT offers various power-monitoring devices for specific pump sizes, speeds, and impeller
diameters. Power-monitoring devices are designed to protect pumps from:
• Dry-running
• Running against a closed discharge valve
• Running outside of the recommended operating region
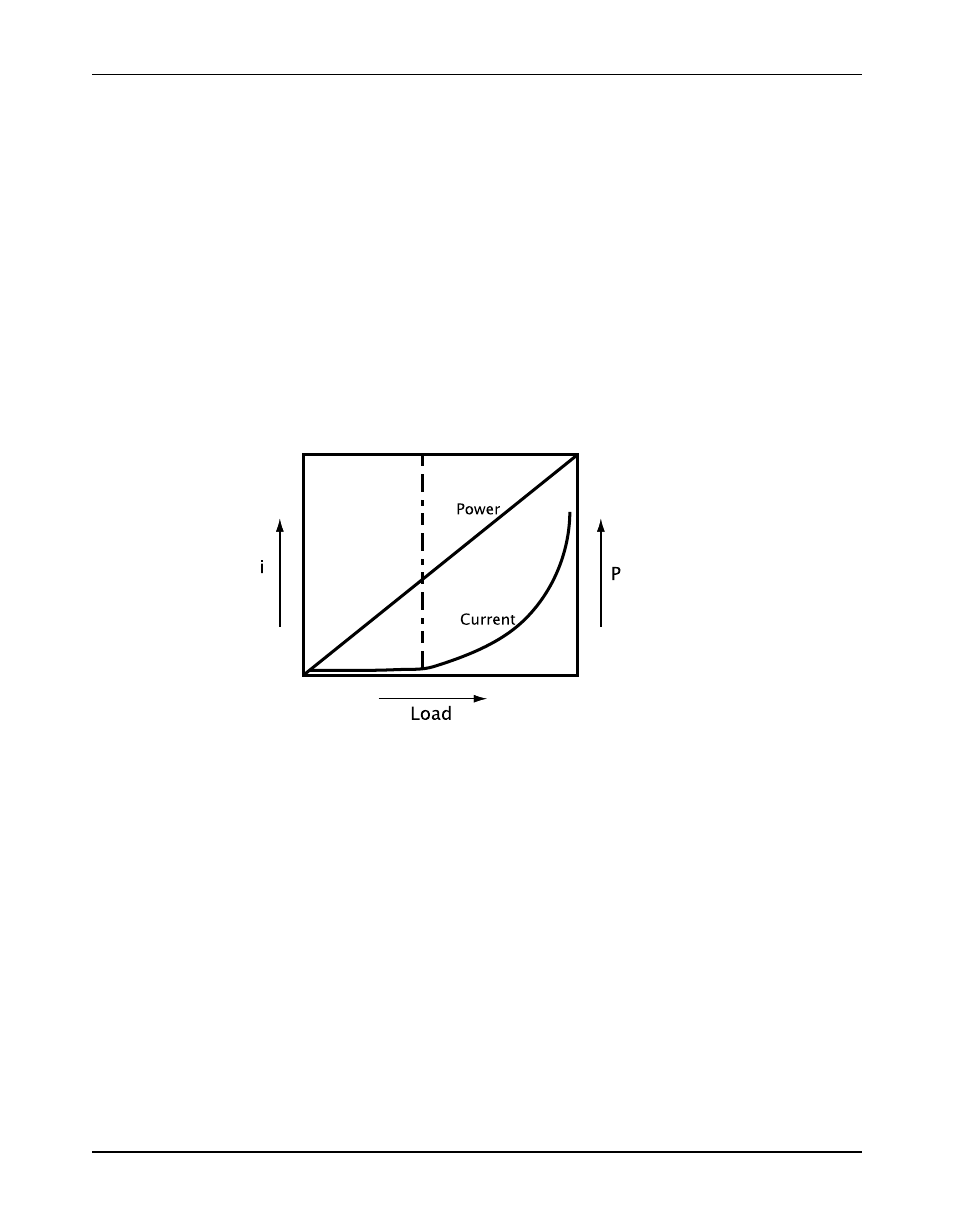
Power monitors were designed to detect power relative to load, which is a linear function, as
opposed to measuring amperage relative to load, which is a parabolic function. The linear
characteristic of measuring power vs. load enhances sensitivity at low-power conditions where
increments in power are critical. This figure shows a comparison of power measurements vs.
amperage measurements. A properly adjusted and installed power monitor is an insurance
policy for securing extended pump life.
Figure 15: Power vs. amperage measurements
Since the current curve is so flat, load changes are difficult to detect when you measure only
the current in this range. If you misread these changes, then nuisance tripping or a dry running
pump can result. If you measure power as well, then this problem is eliminated.
Power draw measuring
Power monitors can be strategically calibrated to protect your pump by measuring the power
draw from any of these conditions:
• Dry running
• Closed discharge valve
• No prime
• Inadequate suction conditions/plugged suction
• Cavitation
• Air lock
• Decoupled magnets
• Solidified, plugged, or frozen discharge line
• Fluctuating viscosities, precipitation, or coagulation
• Broken or damaged shaft
Model 3296 EZMAG Installation, Operation, and Maintenance Manual
89
