Maximum power point tracking, Weather conditions, Applications – Outback Power Systems FLEXmax Extreme Owners Manual User Manual
Page 72: Figure 62 maximum power point tracking
Applications
70
900-0150-01-00 Rev A
Weather Conditions
Cooler climates can cause the V
oc
to rise above the array’s rated V
oc
. In climates that observe temperatures less
than approximately -15°C (5°F), a V
oc
greater than 125 Vdc is not recommended.
Hot weather: lower V
oc
and lower V
mp
Cold weather: higher V
oc
and higher V
mp
If the specific voltage temperature correction factor is not known for a particular module, allow for ambient
temperature correction using the following information:
25° to 10°C (77° to 50°F)
multiply V
oc
by 1.06
9° to 0°C (49° to 32°F)
multiply V
oc
by 1.10
-1° to -10°C (31° to 14°F)
multiply V
oc
by 1.13
-11° to -20°C (13° to -4°F)
multiply V
oc
by 1.17
-21° to -40°C (-5° to -40°F)
multiply V
oc
by 1.25
Maximum Power Point Tracking
Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) is the technology used by FLEXmax charge controllers to optimize the
harvest of power from PV arrays.
PV modules do not have a defined operating voltage. Their voltage is defined strictly by the load connected to
them. With no load (disconnected), a module displays “open-circuit” voltage (V
oc
), and delivers no current. At
full load (shorted), a module has no voltage, although it delivers the maximum “short-circuit” current (I
sc
). In
neither case does it produce usable wattage.
When partially loaded, a PV module delivers partial current and voltage. These numbers can be multiplied to see
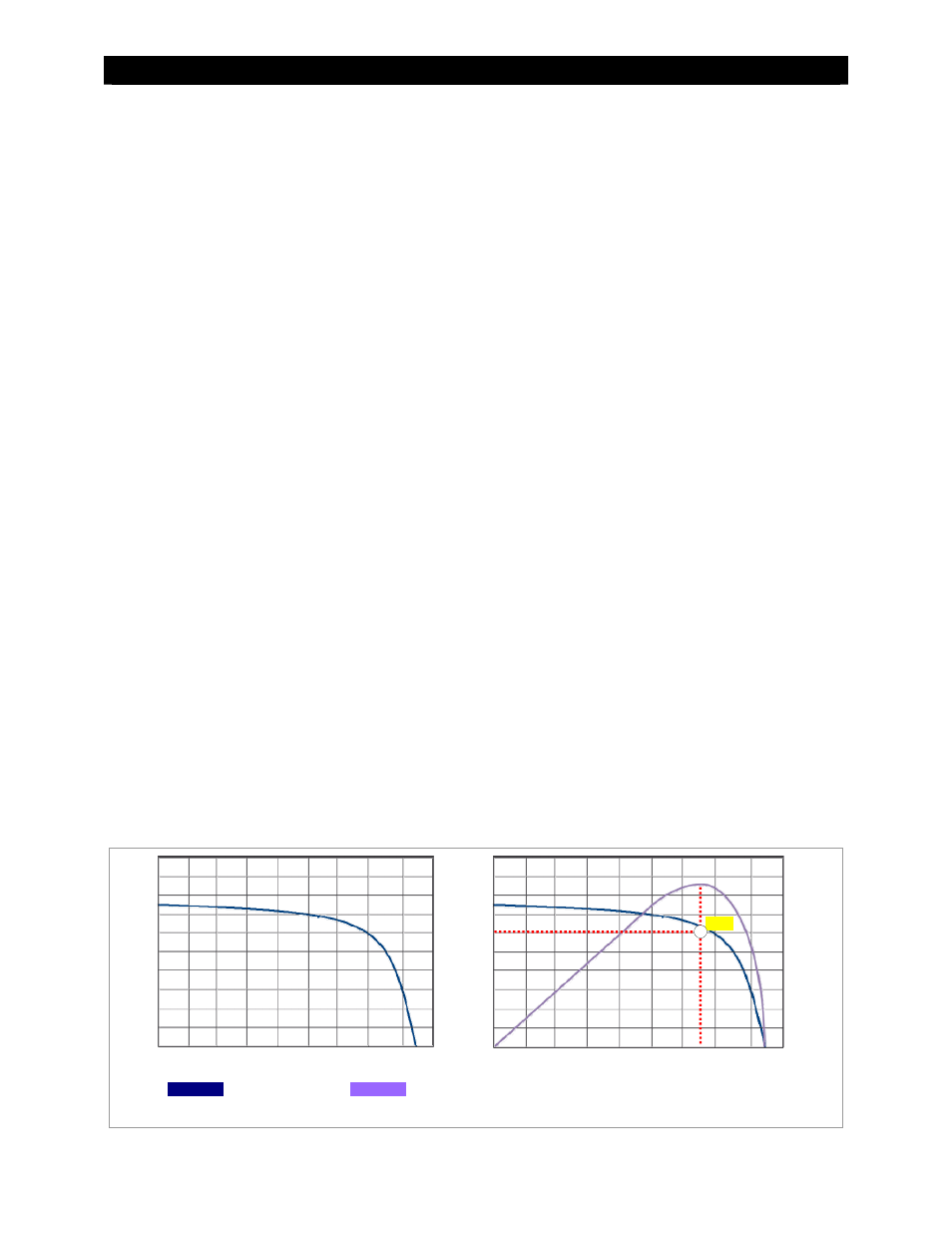
the available wattage. However, the delivery of wattage is not linear. The current and voltage delivered at a
given load will change with the load, along a curve such as that shown in the drawing to the left in Figure 62.
This is known as the V-I curve. The wattage is different at every point along the curve. (The V-I curve also varies
with module type and manufacturer.) Only one point on the V-I curve represents the delivery of the module’s
maximum (rated) wattage. This is known as the maximum power point, or MPP. The current at this point, Imp, is
the highest that can be drawn while still maintaining the highest voltage, V
mp
.
The FLEXmax controller places a variable load on the PV array and tracks the result to determine the maximum
power point. This process, MPPT, is maintained so that the FLEXmax can deliver the maximum PV power
regardless of any change in conditions. The drawing to the right in Figure 62
shows the MPP and compares the
V-I curve against the available wattage.
Figure 62
Maximum Power Point Tracking
I
sc
I
sc
V
oc
V
oc
V
mp
I
mp
MPP
VOLTAGE
VOLTAGE
CURRENT
CURRENT
V-I curve
Available wattage
