HP XP Continuous Access Software User Manual
Page 33
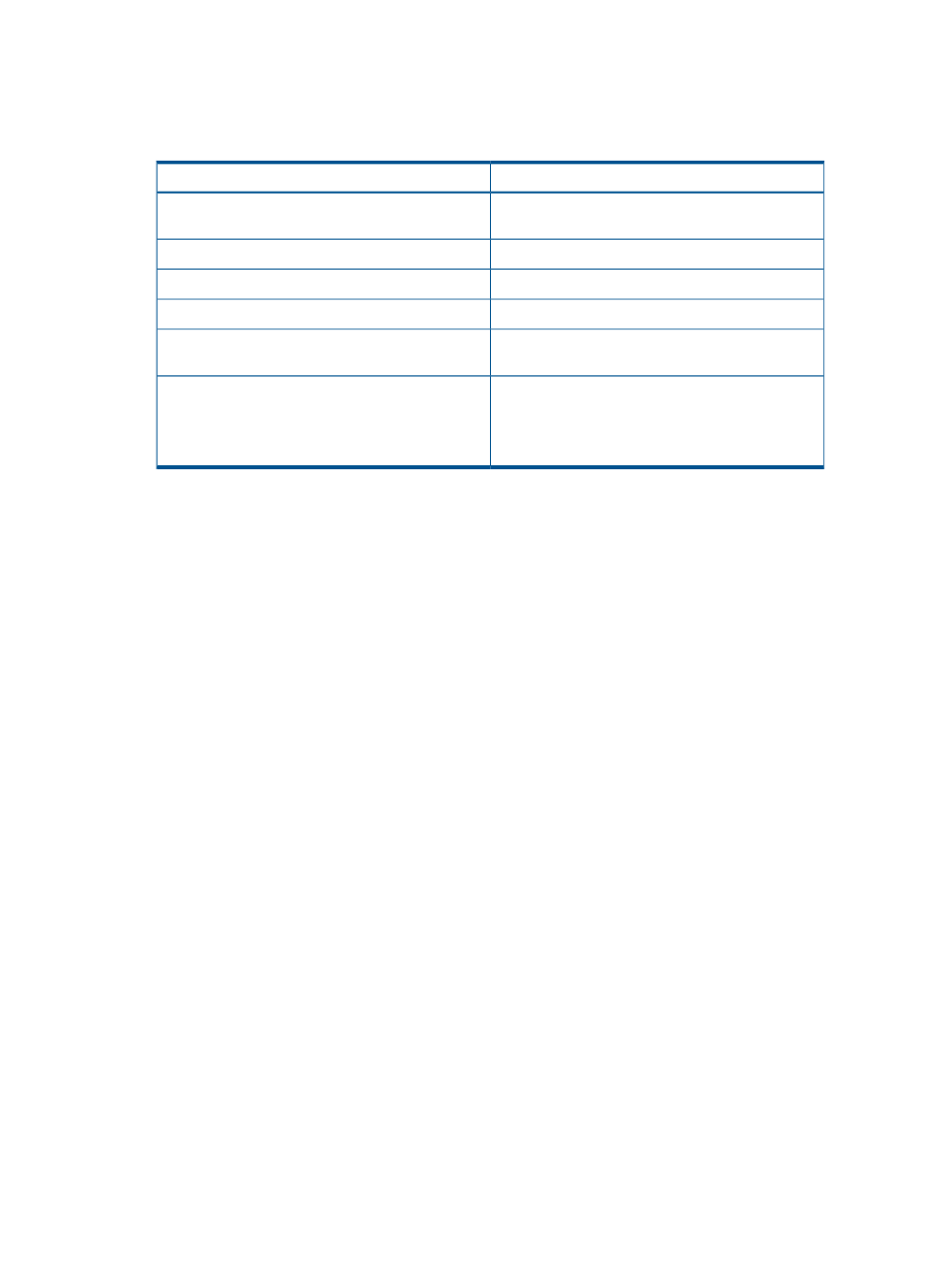
You can view the detailed pair status information at the Remote Web Console computer (XP
Continuous Access Journal Detailed Information window) or at the UNIX/Computer server host
(RAID Manager Pairdisplay command).
shows the relationships.
Table 4 Relationship Between the Operations and Pair Status
Pair Status
Operations or Processing
SMPL
Unassigned volume (no XP Continuous Access Journal
data volume pair exists)
COPY
Pair creation started (initial copy)
PAIR
Initial copy operation completed
PSUE
Pair suspended due to error
PSUS
User initiates XP Continuous Access Journal pair split
(pairsplit-r)*
SMPL
Pair released*
(If you released the pair from the secondary storage
system, the status of the primary data volume will be
PSUS.)
* When you split or release a pair on the secondary storage system, the status of the secondary
data volume changes. Then, if the path status is normal, the primary storage system detects the
change of the status of the secondary data volume, and then changes the status of the primary
data volume.
Assigning a volume status
•
Status SMPL: A volume that is not assigned to an XP Continuous Access Journal data volume
pair has the status SMPL.
•
Status Copy: When an XP Continuous Access Journal data volume pair is started, the primary
storage system changes the status of the primary data volume and secondary data volume to
COPY.
•
Status PAIR: When the initial copy operation is complete, the primary storage system changes
the status of both data volumes to PAIR.
•
Status PSUE: When a pair is suspended due to an error condition, the primary storage system
changes the primary data volume and secondary data volume status to PSUE (if the path status
is normal).
Status PSUS
•
When an XP Continuous Access Journal pair is split by the user (pairsplit-r), the primary storage
system or secondary storage system changes the status of the primary data volume and
secondary data volume to PSUS (if the path status is normal).
•
When a pair is split from the secondary storage system, the secondary storage system changes
the secondary data volume status to PSUS, and the primary storage system detects the pair
deletion (if the path status is normal) and changes the primary data volume status to PSUS.
Mixed Status
•
When a pair is released from the primary storage system, the primary storage system changes
the status of both data volumes to SMPL.
•
When a pair is released from the secondary storage system, the secondary storage system
changes the secondary data volume status to SMPL, and the primary storage system detects
the pair release (if the path status is normal) and changes the primary data volume status to
PSUS.
Service Information Messages and Status
Pair Status
33
