KROHNE BM 102 Handbook User Manual
Page 48
48
BM 102
3.4
BM 102 MICROFLEX T.D.R. meter characteristics
This subsection explains:
• the four principle configurations for setting up a measurement scale and what the user should
be aware of in each case;
• what happens when the tank is full or empty;
• what is the level threshold and how to modify it and
• what happens when level is measured when more than one product in the tank;
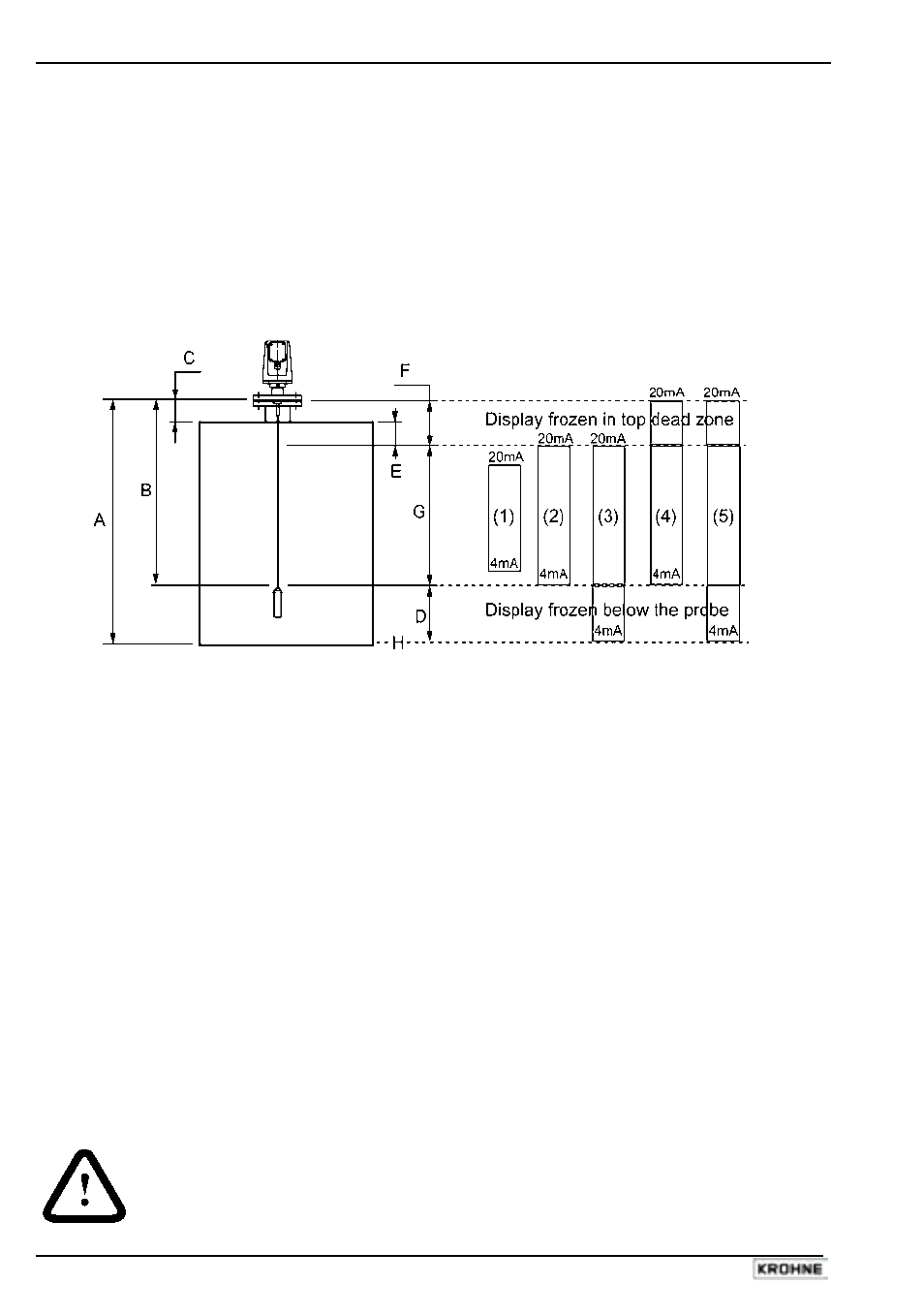
The measurement scale: five possible configurations for analogue current output – with
“Level” selected in PCSTAR 2 function 1.3.1: Current 1 Item
A Tank height (Fct. 1.1.1)
F Upper dead zone (Fct. 1.1.2)
B Probe length (Fct. 1.1.6)
G Optimal measuring range
C Detection delay (Fct. 1.5.1)
H Reference point at tank bottom
D Non-measurable zone
E Minimum distance between non-
measurable zone and dead zone
(Fct.: 1.1.2 – Fct.: 1.5.1)
Fct.: 1.3.1 = Level
The configurations described below are illustrated in the above diagram:
(1) The “current output” range is smaller than the optimal measuring range.
(2) The “current output” range is equal to the optimal measuring range:
Scale min.: 4 mA (Fct. 1.3.3) = tank height – probe length
Scale max.: 20 mA (Fct. 1.3.4) = tank height – dead zone
(3) The “current output” range is greater than the optimal measuring range:
Scale min.: 4 mA (Fct. 1.3.3) = 0.0
Scale max.: 20 mA (Fct. 1.3.4) = tank height – dead zone
(4) The “current output” range is greater than the optimal measuring range:
Scale min.: 4 mA (Fct. 1.3.3) = tank height – probe length
Scale max.: 20 mA (Fct. 1.3.4) = tank height
(5) The “current output” range is greater than the optimal measuring range:
Scale min.: 4 mA (Fct. 1.3.3) = 0.0
Scale max.: 20 mA (Fct. 1.3.4) = tank height
NOTE:
The reference point for distance measurements is the bottom of the flange face.
