1 range of application, 2 mode of operation and system structure, 1 operating principle (fmcw-radar) – KROHNE BM 70 A_P EN User Manual
Page 6
Installation and operating instructions BM 70 A/P
Page: 6
11/00
1 Range of application
The BM 70 A/P Level-Radar level gauging system is designed to measure the distance, level, volume
and reflection of liquids, pastes, slurries, solids and particulate materials. It can be operated on
storage and process tanks and also on stilling wells.
BM 70 P is specially designed for applications on storage tanks with highest precision requirements.
BM 70 A/P Ex hazardous-duty versions are suitable for use in Ex-Zone 0, 1 and 2.
In Germany (and, depending on the respective radio approval, in some other countries as well) its use
is restricted to closed tanks or containers made of metal or concrete. Because of the low output
involved, however, the microwaves are not harmful to human beings.
2 Mode of operation and system structure
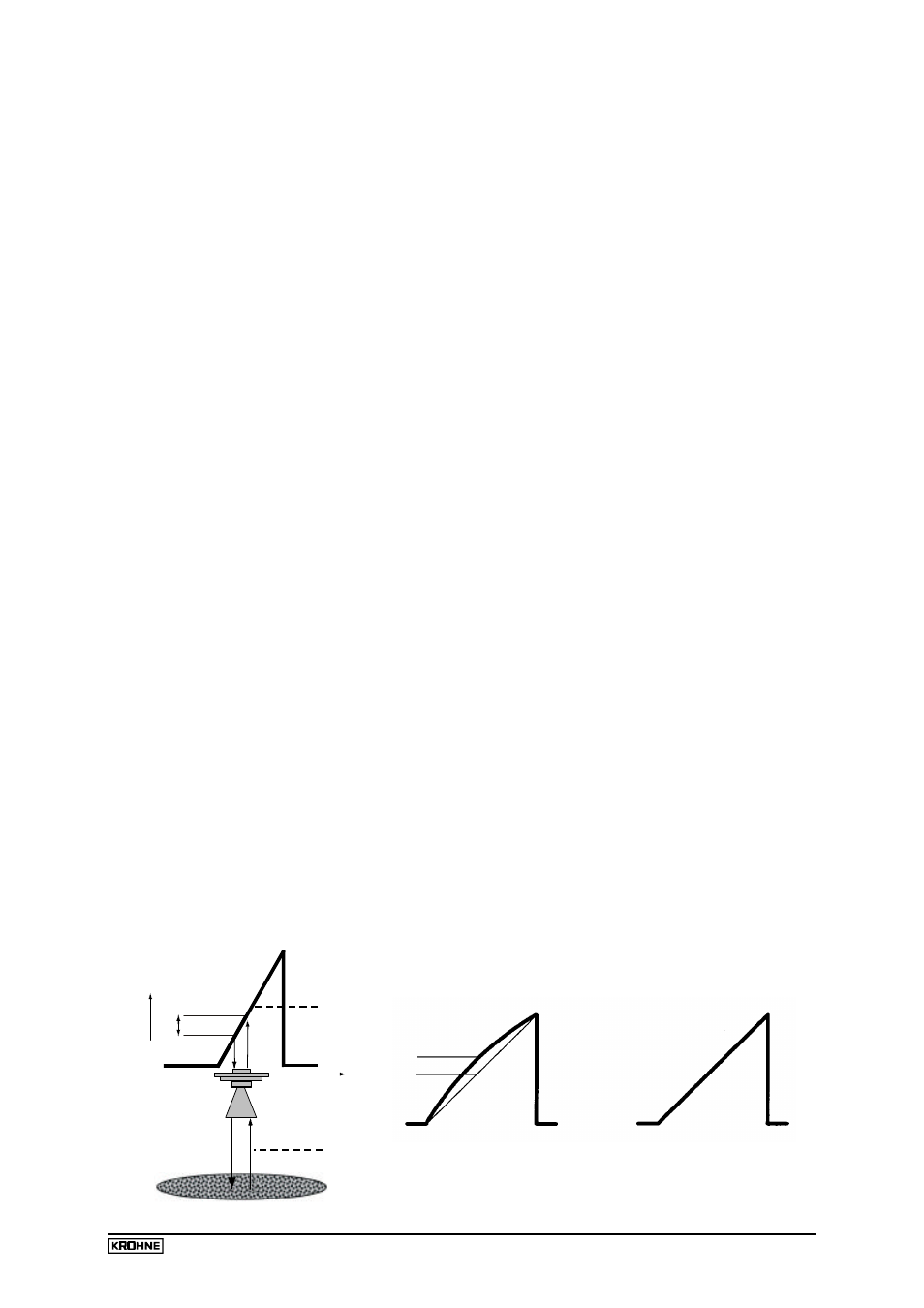
2.1 Operating principle (FMCW-Radar)
A radar signal is given via an antenna, reflected on the measuring surface and received after a delay
time t.
FMCW: Frequency Modulated Continuous Wave
The FMCW-radar uses a high frequency signal (~10 GHz) which transmit frequency increasing
linearly 1 GHz during the measurement (frequency sweep) (1). The signal is emitted, reflected on the
measuring surface and received time-delayed (2).
For further signal processing the difference
∆
f is calculated from the actual transmit frequency and
the receive frequency (3). The difference is directly proportional to the distance i.e. a large frequency
difference correspond to a large distance and vice versa.
The frequency difference is transformed via a Fourier transformation (FFT) into a frequency spectrum
and then the distance is calculated from the spectrum. The level results from the difference between
tank height and distance.
Linearity of frequency sweeps
The measuring accuracy of a FMCW radar is determined from the linearity of the frequency sweeps
and their reproducibility. The linearity correction is deduced via reference measurement of the
oscillator.
The non-linearity is corrected up to 98% (BM 700/BM 70 A).
An immediate frequency regulation is necessary with the BM 70 P device because of the higher
demand on the measuring accuracy.
With the PLL technology (Phase Locked Loop) the signal frequency is directly recorded as a digital
data and the converter oscillator locks automatically on the right frequency.
3) differential frequency
formed
1) radar frequency
linearly changed
2) delay time due to wave
propagation
f
∆∆
f
t
antenna
∆∆
f
non-linear sweep
linear sweep
f
Start
f
Stop
