GF Signet 3719 pH_ORP Wet-Tap User Manual
Page 7
7
Signet 3719 pH/ORP Wet-Tap
Offset in pH Electrodes
Electrode offsets occur due to:
•
Clogged reference junction
•
Aged or contaminated reference solution/wire
•
A constant output near 0 mV in all buffer solutions indicates a shorted electrode that must
be replaced.
Check offsets in a pH 7 buffer @ 25 °C. The theoretical output is 0 mV. Any deviation from 0
mV is the pH electrode offset. The mV offset will track across the entire pH range. The slope is
usually not affected by offset changes. (i.e., pH 7= +10 mV, pH 4= +187 mV); slope = 59 mV.
pH Electrode Offset pH 7 buffer @ 25 °C
Theoretical:
pH 7.0 (0.0 mV)
New electrode:
pH 7 ± 0.25 pH (±15 mV)
Reliable:
pH 7 ± 0.85 pH (± 50 mV)
Electrode offsets greater than 0.85 pH (50 mV) indicate the electrode requires cleaning
or replacement. See Maintenance and Cleaning section.
Offset in ORP Electrodes
•
ORP electrode offsets are usually caused by clogged reference junctions or by an aged or contaminated reference solution/wire.
•
Offsets should be checked in pH 7 buffer saturated with quinhydrone @ 25 °C. The theoretical output is +86 mV.
Any deviation from +86 mV is the ORP electrode offset (e.g., +90 mV).
•
Quinhydrone is the oxidizer measured by the ORP electrode and is required for calibration.
To measure ORP electrode offset, saturate 50 mL of pH 4 and pH 7 buffers with ⅛ g quinhydrone.
A new ORP electrode measures these values ±15 mV. The electrode continues to be functional until the offset from these values
exceeds 50 mV. Electrodes with offset greater than 50 mV should be cleaned and replaced if necessary.
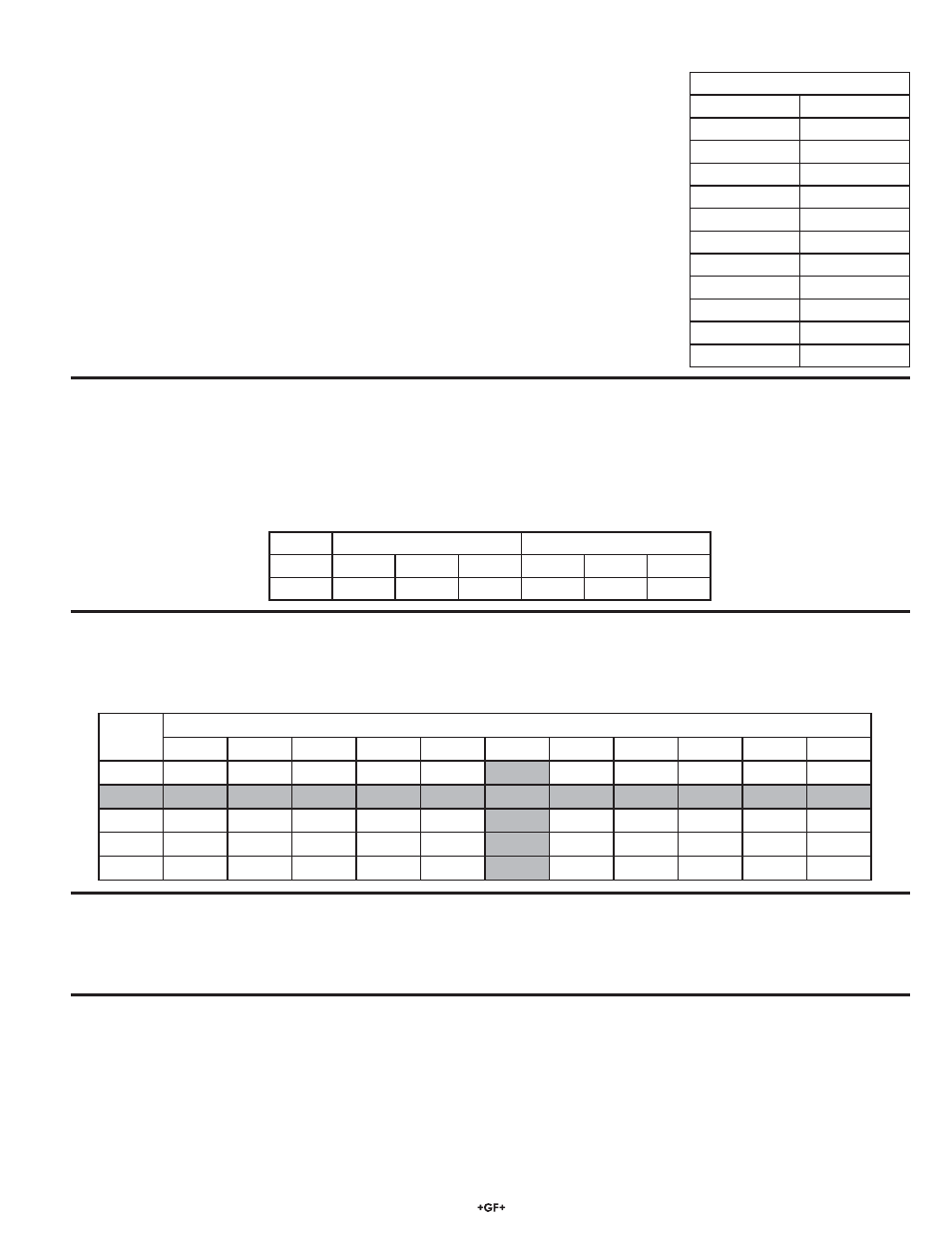
Theoretical mV Values @ 25 °C
pH
mV
2
+296 mV
3
+237 mV
4
+177 mV
5
+118 mV
6
+59 mV
7
0 mV
8
-59 mV
9
-118 mV
10
-177 mV
11
-237 mV
12
-296 mV
°C
pH
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
15
0.15
0.12
0.09
0.06
0.03
0
0.03
0.06
0.09
0.12
0.15
25
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
35
0.15
0.12
0.09
0.06
0.03
0
0.03
0.06
0.09
0.12
0.15
45
0.3
0.24
0.18
0.12
0.06
0
0.06
0.12
0.18
0.24
0.3
55
0.45
0.36
0.27
0.18
0.09
0
0.09
0.18
0.27
0.36
0.45
4 pH w/Quinhydrone
7 pH w/Quinhydrone
Temp:
20 °C
25 °C
30 °C
20 °C
25 °C
30 °C
ORP:
268 mV 263 mV 258 mV
92 mV
86 mV
79 mV
Slope in ORP electrodes
ORP slope errors are caused by contamination of the platinum electrode surface. Cleaning the electrode surface will usually restore
proper values, response time, and stability. Many systems require both pH and ORP calibration. To conserve calibration reference
solutions, use pH 7 and 4 buffers for pH calibration fi rst. ORP calibration can be performed with the same buffers after adding
quinhydrone.
Slope in pH electrodes
Electrode slope is the mV output per pH unit. At 25
C the theoretical slope is 59.16 mV per pH. The graph below illustrates potential
pH error when a temperature-compensated instrument is not used.
•
Coatings on the glass may affect sensor slopes. See Maintenance and Cleaning section.
•
Temperature affects electrode slope. Calibrate temperature before calibrating the standard and slope.
Response Time/Stability
Response time and stability are affected by the condition of the glass surface (ORP electrode - Platinum surface), reference junction,
and reference solution. Restoration to acceptable levels can often be accomplished by cleaning the electrode's glass surface (ORP
electrode - platinum surface) and reference junction.
7. Troubleshooting
pH and ORP electrodes are similar to batteries; they age with time and usage.
The following information will help maximize electrode life:
•
High temperatures or concentrated acids/caustics will accelerate electrode aging.
•
Never store the electrode tip in deionized (DI) water.
•
Never expose electrode to temperatures below –12 °C (10 °F) or allow it to dehydrate. These conditions will damage the electrode.
