Reflection experiments – Ocean Optics S1024DW Install User Manual
Page 57
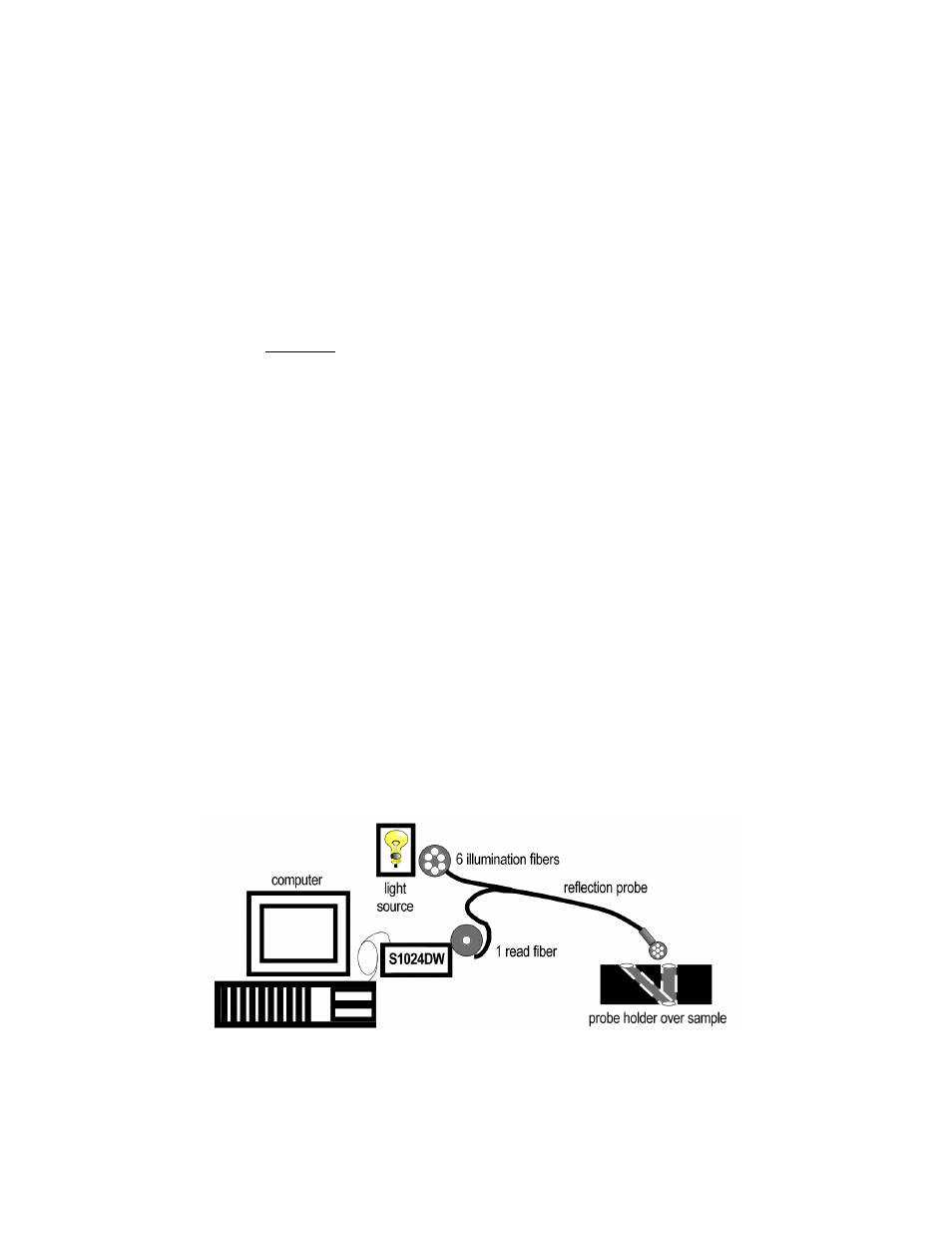
54
Reflection Experiments
Reflection is the return of radiation by a surface, without a change in wavelength. The reflection may be:
•
Specular, in which the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
•
Diffuse, in which the angle of incidence is not equal to the angle of reflection.
Every surface returns both specular and diffuse reflections. Some surfaces may return mostly specular
reflection, others more diffuse reflection. The glossier the surface, the more specular the reflection.
Reflection is expressed as a percentage (
%R
λ
) relative to the reflection from a standard substance (such as
our WS-1 white reference for a diffuse reflection measurement):
S
λ
- D
λ
%R
λ
=
R
λ
- D
λ
x 100%
where S is the sample intensity at wavelength
λ
, D is the dark intensity at wavelength
λ
, R is the
reference intensity at wavelength
λ
.
Common applications include measuring the reflection properties of mirrors, anti-reflection coatings, and
measuring the visual properties of the color in paints, graphic arts, plastics, and food products. To take a
reflection measurement:
1. Make sure you are in scope mode, by either clicking the scope mode icon on the toolbar, or selecting
Spectrum | Scope Mode from the menu. Make sure the signal is on scale. The peak intensity of the
reference signal should be about 3500 counts. Take a reference spectrum by first making sure nothing
is blocking the light path going to your sample. The analyte you want to measure must be absent while
taking a reference spectrum. Take the reference reading by clicking the store reference spectrum icon
on the toolbar or selecting Spectrum | Store Reference from the menu.
2. While still in scope mode, take a dark spectrum by first completely blocking the light path going to
your sample. If possible, do not turn off the light source. Take the dark reading by clicking the store
dark spectrum icon on the toolbar or selecting Spectrum | Store Dark from the menu.
3. Begin a reflection measurement by first making sure the sample is in place and nothing is blocking the
light going to your sample. Then choose the transmission mode icon on the toolbar or select
Spectrum | Transmission Mode from the menu. The mathematics required to calculate reflection
measurements are identical to those necessary to compute a transmission spectrum. To save the
spectrum, click the save icon on the toolbar or select File | Save | Processed from the menu.
"
"
"
"
If at any time any sampling variable changes -- including integration time, averaging,
boxcar smoothing, distance from light source to sample, etc. -- you must store a new
reference and dark spectrum.
A typical configuration for a reflection experiment.
