The measuring principle, Figure 4, 10 the measuring principle – M&C TechGroup PMA 20 Operator's manual User Manual
Page 11
11
Gas sampling and gas conditioning technology
9-3.5.1-ME
10
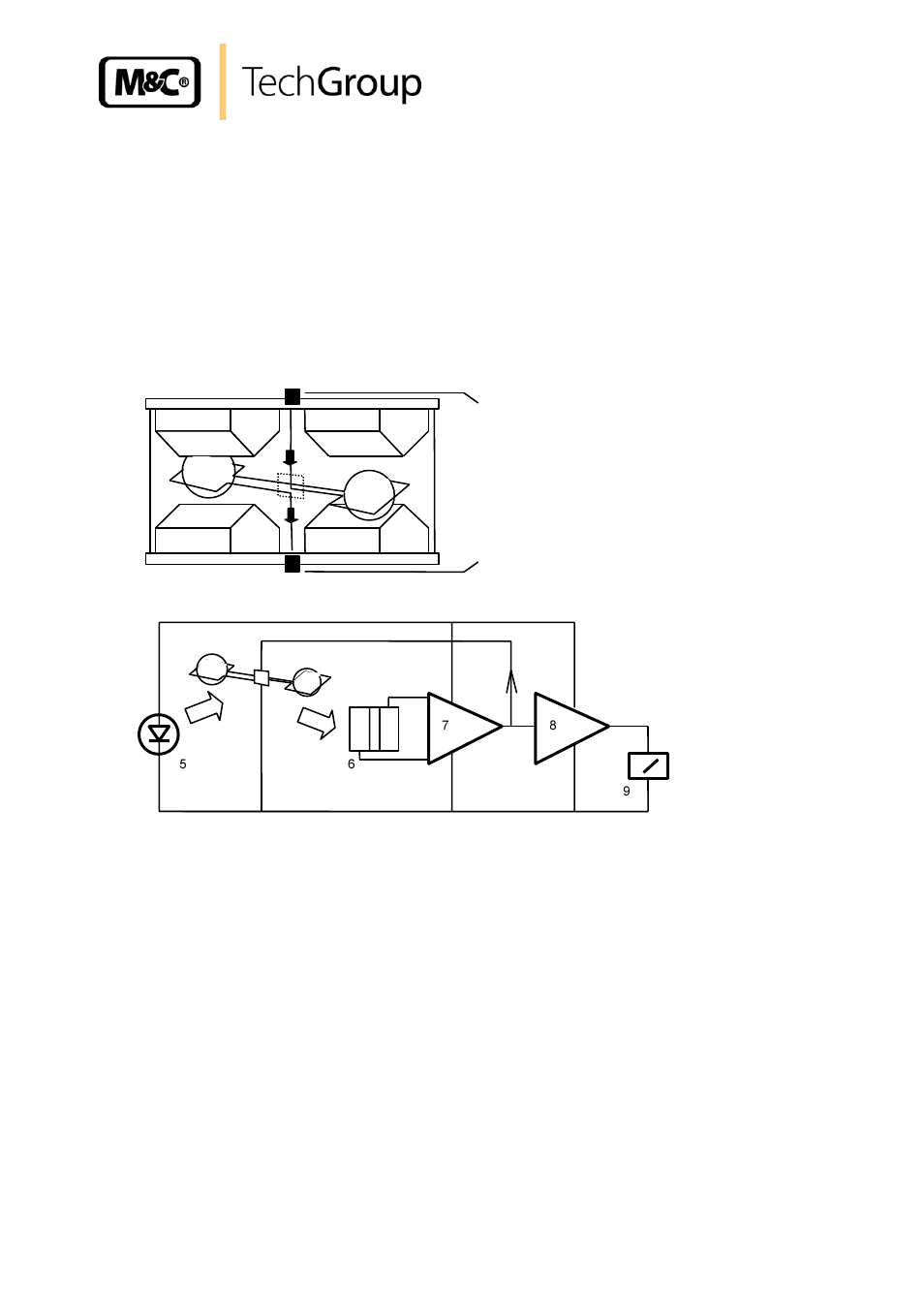
THE MEASURING PRINCIPLE
Oxygen is a gas with a significant paramagnetic susceptibility. The molecules of oxy gen are at-
tracted much more strongly by a magnetic field than the molecules of other gases.
The measuring principle shown in the following is benefitting from these characteristics of the
oxygen. The great advantage of the paramagnetic measuring principle is the highly reduced
cross sensitivity of the measurement to other components in the sample gas.
Figure 2 shows the diagram of the measuring cell as well as the optical system for the detection
of the dumbbell’s movement.
2
4
3
1
GAS INLET
GAS OUTLET
Figure 4
Scheme of the measuring cell and optical signal processing
The measuring cell consists of two nitrogen-filled spheres which are arranged in the form of
a dumbbell. In the dumbbell’s central point of rotation, a small mirror is placed. The dumbbell
is surrounded by a wire coil needed for the compensation procedure. The described system is
fixed rotationally symmetrical inside a glass tube via a tightening strap out of platinum and is
srewed up with two pole pieces .
Two permanent magnets are producing an inhomogeneous magnetic field. When oxygen is flo w-
ing in, the molecues of the oxygen are drawn into the magnetic field. In consequence, the lines of
electric flux on the cuneiform pole pieces are compressed. The nitrogen-filled diamagnetic
sheres are pushed out of the magnetic field. This causes a rotation of the dumbbell. The rotation
is detected via an optical system consisting of mirror , projection LED and photoelectric cell
.
In case the dumbbell is pushed out of the magnetic fieild, the tension of the photoelectric cell is
immediately changed. The measuring amplifiers and are producing a respective current
which develops via the wire coil on the dumbbell an electro-magnetic load moment. The load
moment is resetting the dumbbell into its zero position.
