Tektronix AFG3000 User Manual
Page 79
Syntax and Commands
AFG3000 Series Arbitrary/Function Generators Reference Manual
3-5
Creating Commands
SCPI commands are created by stringing together the nodes of a subsystem hier-
archy and separating each node by a colon.
In Figure 3-2, TRIGger is the root node and SEQuence, SLOPe, SOURce, and TIMer
are lower level nodes. To create an SCPI command, start with the root node
TRIGger and move down the tree structure adding nodes until you reach the end of
a branch. Most commands and some queries have parameters; you must include a
value for these parameters. The command descriptions, which begin on page 3-15,
list the valid values for all parameters.
For example, TRIGger:SEQuence:SOURce EXTernal is a valid SCPI command
created from the hierarchy tree in Figure 3-2.
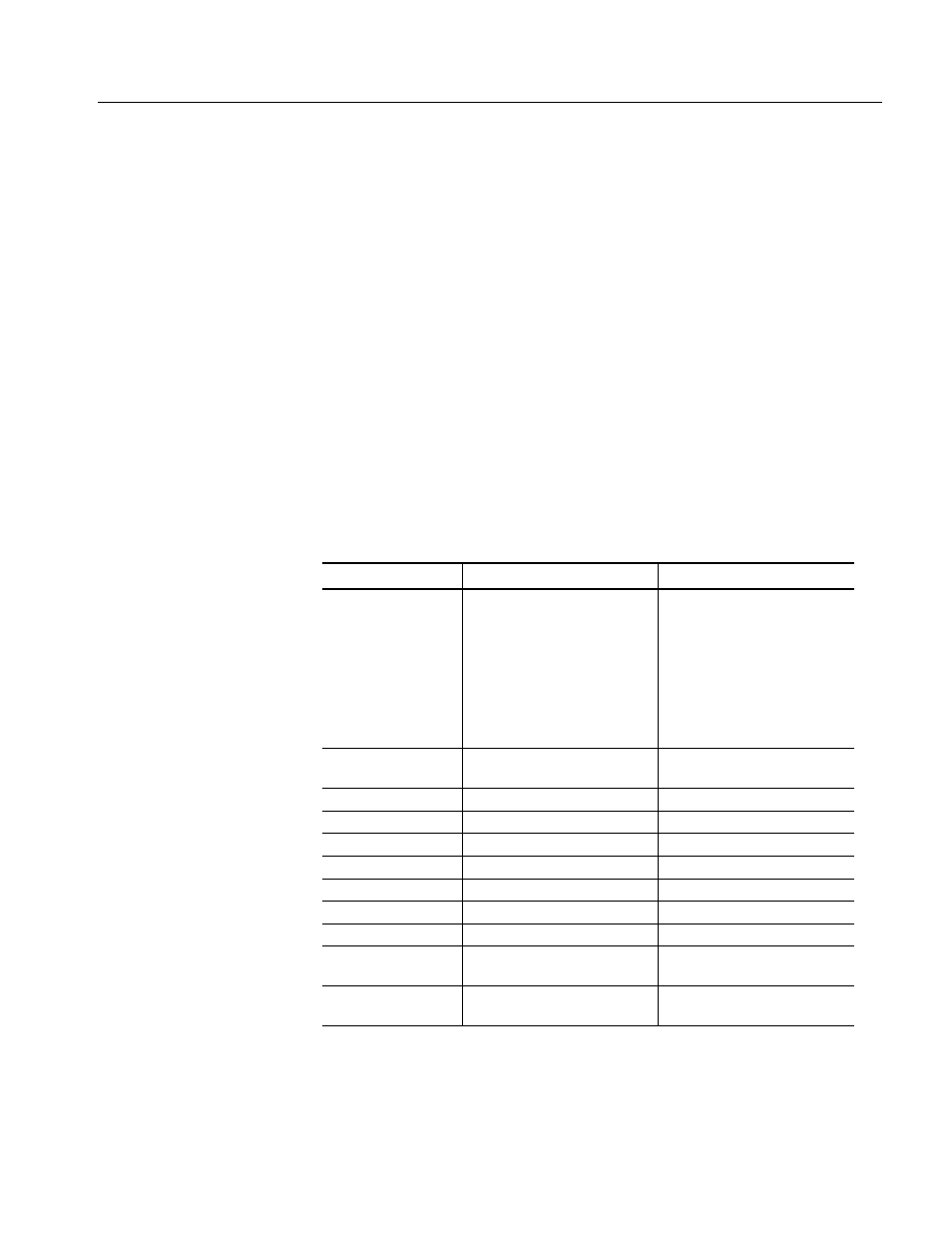
Parameter Types
Parameters are indicated by angle brackets, such as
different types of parameters, as listed in Table 3-4. The parameter type is listed
after the parameter. Some parameter types are defined specifically for
the
arbi-
trary/function generator
command set and some are defined by SCPI.
Table 3-4: Parameter types used in syntax descriptions
Parameter type
Description
Example
arbitrary block
A block of data bytes
#512234xxxxx...
where 5 indicates that the follow-
ing 5 digits (12234) specify the
length of the data in bytes;
xxxxx... indicates the data
or
#0xxxxx...
boolean
Boolean numbers or values
ON or
≠ 0
OFF or 0
discrete
A list of specific values
MIN, MAX
binary
Binary numbers
#B0110
octal
Octal numbers
#Q75, #Q3
hexadecimal
Hexadecimal numbers (0-9, A-F) #HAA, #H1
NR1 numeric
Integers
0, 1, 15, -1
NR2 numeric
Decimal numbers
1.2, 3.141516, -6.5
NR3 numeric
Floating point numbers
3.1415E-9, -16.1E5
NRf numeric
Flexible decimal number that
may be type NR1, NR2, or NR3
See NR1, NR2, NR3 examples
in this table
string
Alphanumeric characters (must
be within quotation marks)
“Testing 1, 2, 3”
