Texas Instruments MSP50C6xx User Manual
Page 369
Mechanical Information
7-3
Customer Information
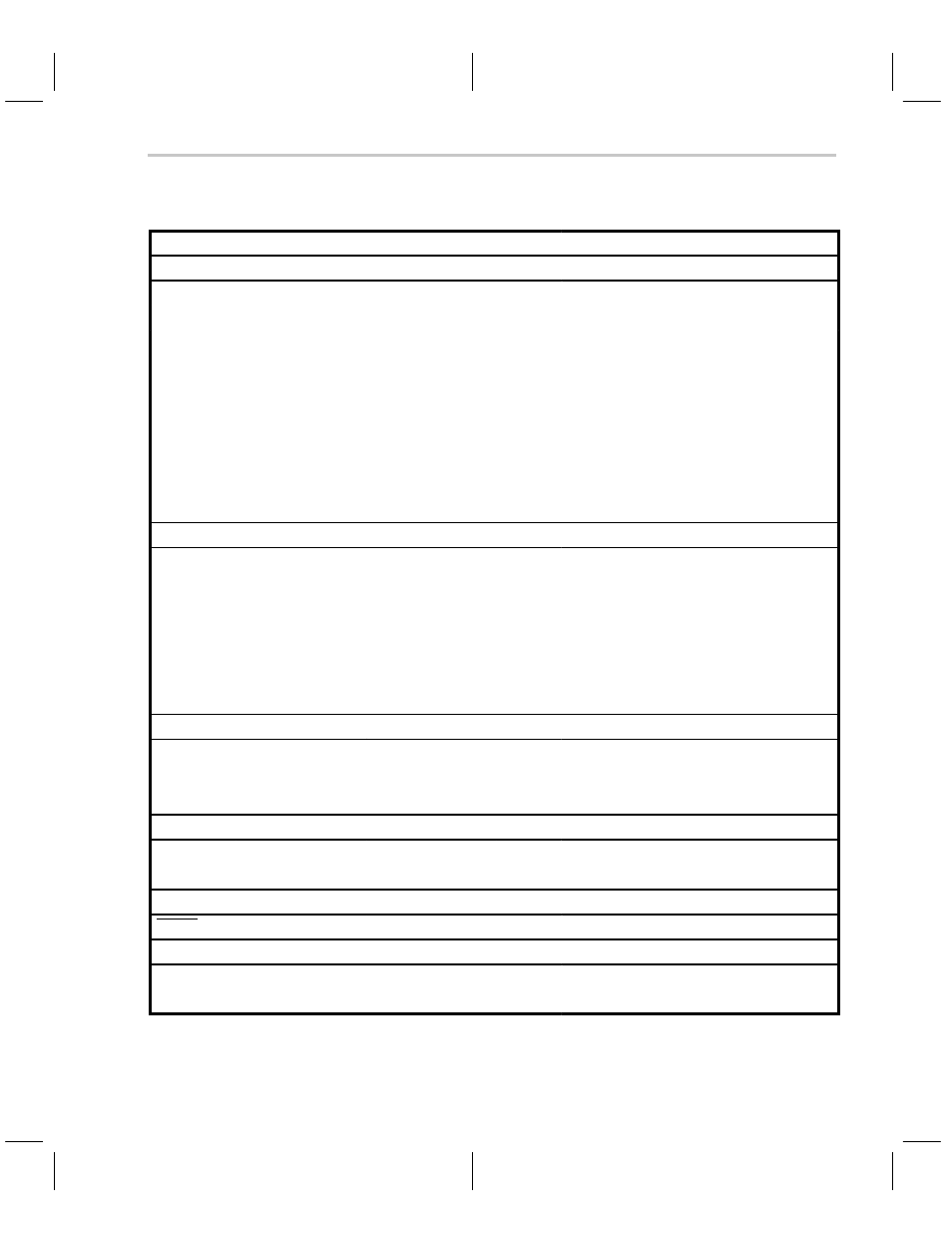
Table 7–1. Signal and Pad Descriptions for the MSP50C614
SIGNAL
PIN NUMBER
PAD NUMBER
I/O
DESCRIPTION
Input/Output Ports
PA0 – PA7
66 – 59
75 – 68
I/O
Port A general-purpose I/O
(1 Byte)
PB0 – PB7
76 – 69
85 – 78
I/O
Port B general-purpose I/O
(1 Byte)
PC0 – PC7
90 – 83
8 – 1
I/O
Port C general-purpose I/O
(1 Byte)
PD0 – PD7
100 – 93
18 – 11
I/O
Port D general-purpose I/O
(1 Byte)
PE0 – PE7
51 – 44
63 – 56
I/O
Port E general-purpose I/O
(1 Byte)
PF0 – PF7
16 – 9
31 – 24
I
Port F dedicated input
(1 Byte)
PG0 – PG7
37 – 30
49 – 42
O
Port G dedicated output
(1 Byte)
PG8 – PG15
25 – 18
39 – 32
O
Port G dedicated output
(1 Byte)
Pins PD4 and PD5 may be dedicated to the comparator function, if the comparator enable bit is set.
Refer to Section 3.3, Comparator, for details.
Scan Port Control Signals
SCANIN
42
54
I
Scan port data input
SCANOUT
38
50
O
Scan port data output
SCANCLK
41
53
I
Scan port clock
SYNC
40
52
I
Scan port synchronization
TEST
39
51
I
MSP50C6xx: test modes
The scan port pins must be bonded out on any MSP50C6xx production board.
Consult the “Important Note regarding Scan Port Bond Out”.
Reference Oscillator Signals
OSCOUT
56
65
O
Resistor/crystal reference out
OSCIN
57
66
I
Resistor/crystal reference in
PLL
58
67
O
Phase-lock-loop filter
Digital-to-Analog Sound Outputs
DACP
7
22
O
Digital-to-analog plus output (+)
DACM
5
20
O
Digital-to-analog minus output (–)
Initialization
RESET
43
55
I
Initialization
Power Signals
VSS
1†, 26, 52, 67, 91
9, 19†, 40, 64, 76
Ground
VDD
6†, 8, 27, 68, 92
10, 21†, 23, 41, 77
Processor power (+)
† The VSS and VDD connections service the DAC circuitry. Their pins tend to sustain a higher current draw. A dedicated decoupling
capacitor across these pins is therefore required.
