Electrical circuits – Texas Instruments TI-86 User Manual
Page 260
248
Chapter 19: Applications
19APPS.DOC TI-86, Chap 19, US English Bob Fedorisko Revised: 02/13/01 2:41 PM Printed: 02/13/01 3:05 PM Page 248 of 18
19APPS.DOC TI-86, Chap 19, US English Bob Fedorisko Revised: 02/13/01 2:41 PM Printed: 02/13/01 3:05 PM Page 248 of 18
Electrical Circuits
A measurement device has measured the DC current (C) in milliamperes and voltage (V) in
volts on an unknown circuit. From these measurements, you can calculate power (P) in
milliwatts using the equation
CV=P
. What is the average of the measured power?
With the TI
-86, you can estimate the power in milliwatts at a current of 125 milliamperes
using the trace cursor, the interpolate
àextrapolate editor, and a regression forecast.
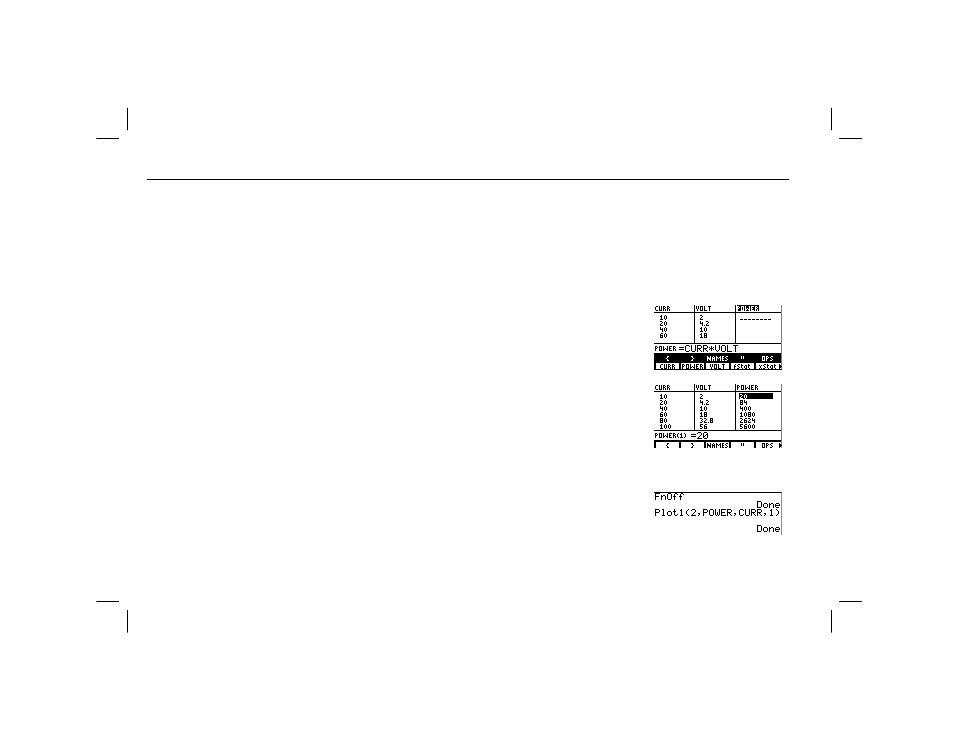
ᕡ In two consecutive columns of the list editor, store the current
measurements shown below to the list name
CURR
and the
voltage measurements shown below to the list name
VOLT
.
{10,20,40,60,80,100,120,140,160}¶CURR
{2,4.2,10,18,32.8,56,73.2,98,136}¶VOLT
ᕢ In the next column of the list editor, enter the list name
POWER
.
ᕣ Enter the formula
CURR
¹
VOLT
in the list editor entry line for
POWER
. Press b to calculate the values for power and store
the answers to the list name
POWER
.
ᕤ Select
WIND
from the
GRAPH
menu and set the window variable values as shown.
xMin=0
xMax=max(POWER) xScl=1000
yMin= 0
yMax=max(CURR) yScl=10
xRes=4
ᕥ From the home screen, select
FnOff
from the
CATALOG
and
press b to deselect all functions in the equation editor.
Select
Plot1(
from the
CATALOG
and set up a stat plot with
POWER
on the x-axis and
CURR
on the y-axis.
