Protocol-specific information, 1 modbus – Toshiba XLTR-200 User Manual
Page 45
44
13. Protocol-Specific Information
This section will discuss topics that are specific to each of the available network
selections.
13.1 Modbus
The gateway supports Modbus slave and master functionality via Modbus RTU.
The slave implementations share common access methods, which is to say
they support the same functions and reference the internal points via a
common “Modbus Slave” holding register assignment. Other notes of interest
are:
•
Points are addressed by their assigned holding register (4X reference) via
Modbus slave protocols.
•
Points can access both holding registers (4X references) and input
registers (3X references) via Modbus master protocols.
•
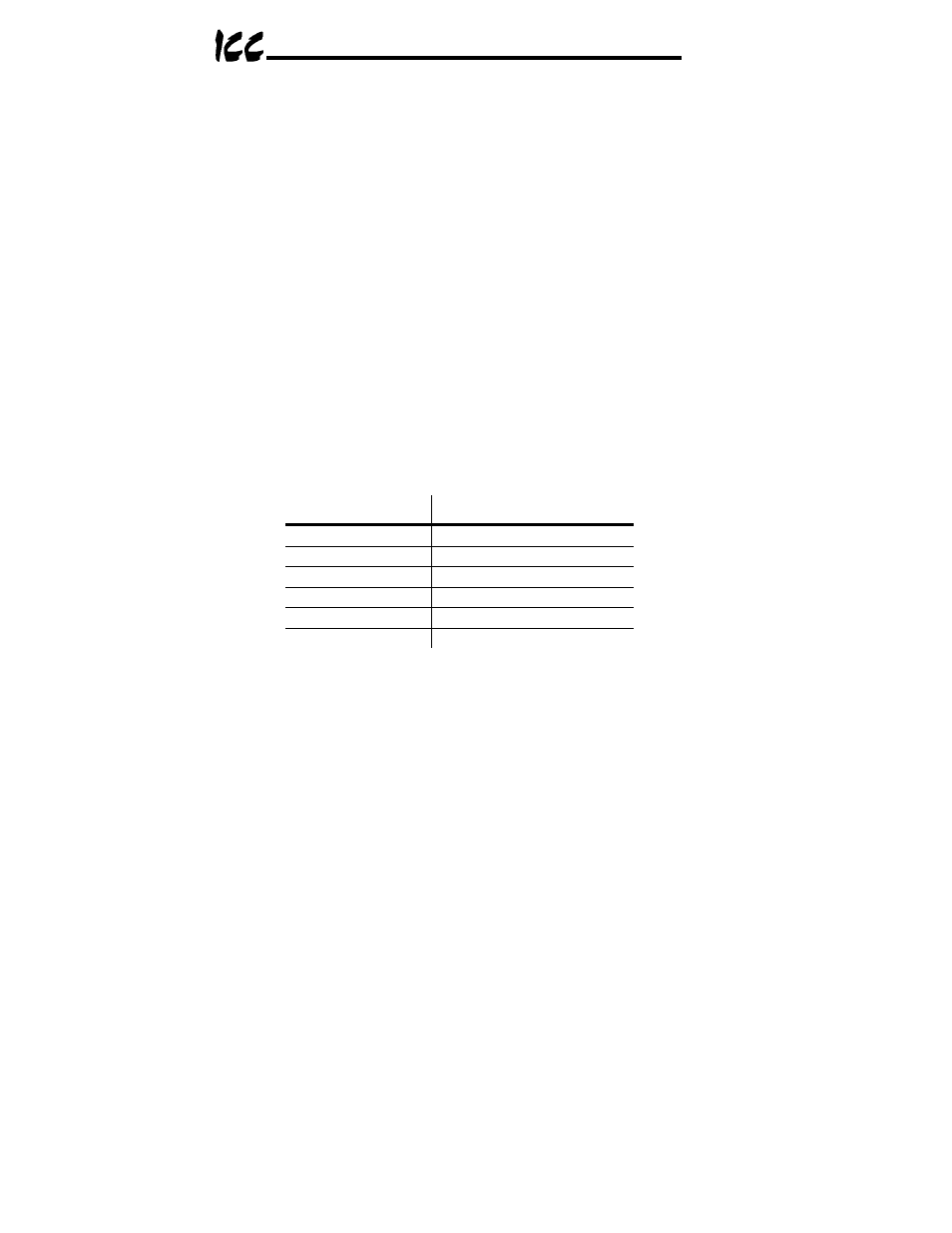
Supported Modbus slave functions are indicated in Table 1.
Table 1: Supported Modbus Slave Functions
Function Code
Function
1 Read
coils
3
Read multiple registers
5 Write
coil
6
Write single register
15
Force multiple coils
16
Write multiple registers
•
Register number entry radix is decimal (e.g. 10 = 10
10
)
•
Configuration tip: Improved network utilization may be obtained by
appropriately grouping points into blocks having contiguous holding
register assignments. In this way, the “read multiple registers” and “write
multiple registers” functions can be used to perform transfers of larger
blocks of registers using fewer Modbus transactions compared to a
situation where the read/write registers were arranged in an alternating or
scattered fashion.
•
Because the transaction is handled locally within the gateway, write data
checking is not available. For example, if a write is performed to a register
with a data value that is out-of-range of the corresponding “source port”
