Storing odd-split repeater frequencies – Kenwood TM-G707 User Manual
Page 34
28
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
STORING SIMPLEX FREQUENCIES OR STANDARD
REPEATER FREQUENCIES
1 Press [VFO] to select VFO mode.
2 Press [BAND] to select the desired band.
3 Turn the Tuning control, or press Mic [UP]/ [DWN], to
select the desired frequency.
• You can also enter digits directly from the microphone
keypad (MC-53DM only). See page 54.
4 If storing a standard repeater frequency, select the
following data:
Offset direction {page 23}
Tone ON, if necessary {page 24}
Tone frequency, if necessary {page 24}
• If storing a simplex frequency, you may select other
related data (CTCSS ON, CTCSS freq. etc.).
5 Press [F].
• A memory channel number appears.
• A triangle icon appears above the memory channel
number if the channel already contained data.
6 Turn the Tuning control, or press Mic [UP]/ [DWN], to
select the desired memory channel (within approx.
10 seconds).
7 Press [MR].
• The selected frequency and related data are stored in
the memory channel.
STORING ODD-SPLIT REPEATER FREQUENCIES
Some repeaters use a receive and transmit frequency
pair with a non-standard offset. To access those
repeaters, store two separate frequencies in a memory
channel. You then can operate on those repeaters
without changing the offset programming in the Menu.
1 Select the appropriate receive frequency by using
steps 1 to 6 (not 7) given for simplex or standard
repeater frequencies.
• If necessary, select Tone ON {page 24} and tone
frequency {page 24}.
2 Press [MR] (1 s).
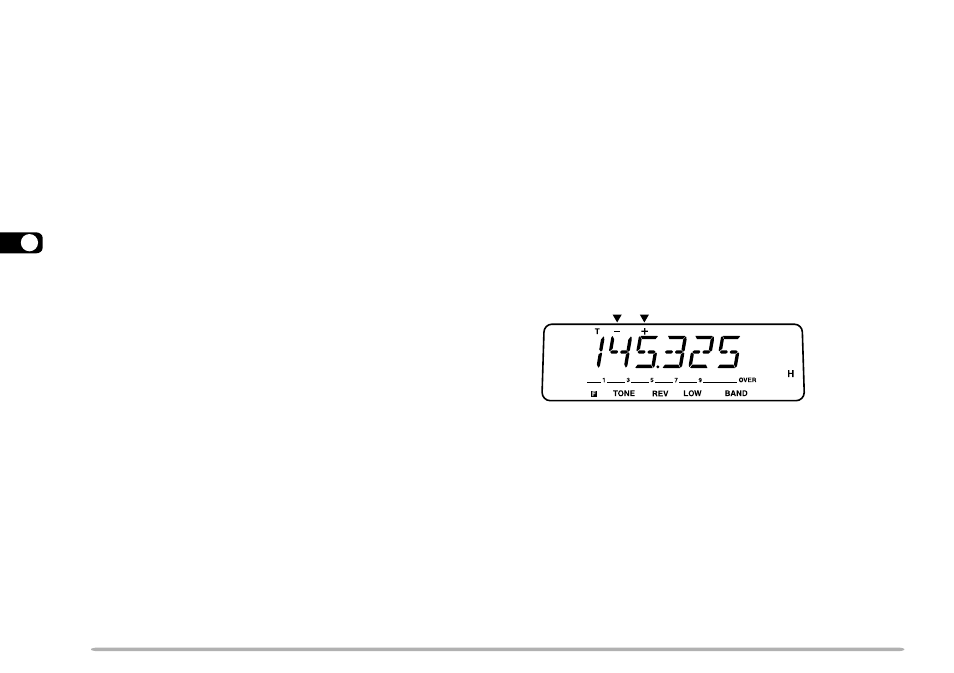
• “–” and “+” appear.
3 Select the appropriate transmit frequency (within
approx. 10 seconds).
4 Press [MR].
• The selected transmit frequency is stored in the memory
channel.
Note:
◆
When you recall an odd-split memory channel, “–” and “+” appear on
the display. Press [REV] to display the transmit frequency.
◆
In step 2 you cannot use Mic [MR], nor Mic [PF] programmed with
Memory Recall.
◆
Transmit Offset status and Reverse status are not stored in an
odd-split memory channel.
