Thermal printhead (s=0) – IBM TM7 User Manual
Page 142
v You must erase the sector of the flash EPROM where this data is stored
before you define the characters. (See “Erase Flash EPROM Sector” on
page 121.) You must also predefine the character matrix for the impact
DBCS code. (See “Microcode Tolerance (MCT) Information - Request” on
page 123.)
v The flash EPROM sector 6 contains the double-byte character set for
both the thermal and impact printheads. To redefine a character for an
address that is already downloaded, you must erase and reprogram all
double-byte characters.
v To define a character for an address that is not yet downloaded, you can
download a character using this command.
v The inter-character spacing should not be included in the character
matrix – it is set by a different command.
v The address range that can be defined is shown in Table 14.
Table 14. Address Ranges for DBCS Code Pages
Code Page
Address Range
Total Characters
932 – Japan
First byte: F0–F9; second byte:
40–7E, 80–FC (for example:
F040–F07E, F080–F0FC, ...
F940–F97E, F980–F9FC)
1880
949 – Korea
C9A1–C9FE, FEA1–FEFE
188
950 – Traditional Chinese
FA40–FA7E, FAA1–FAFE
157
1381 – Simplified Chinese
First byte: 8D-A0; second byte: A1–FE
(for example: 8DA1–8DFE,
8EA1–8EFE, ... A0A1–A0FE)
1880
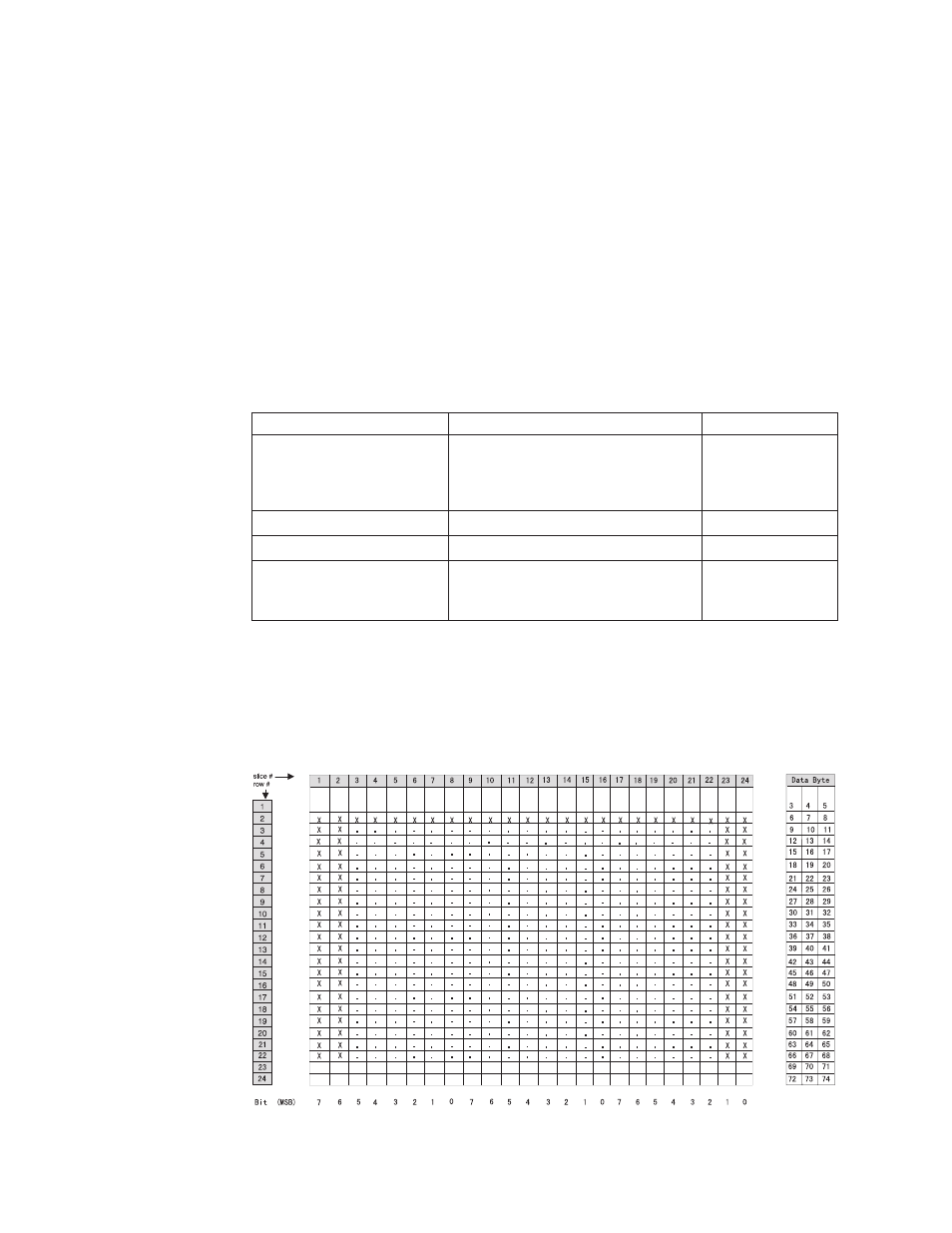
Thermal Printhead (s=0)
The height and width of these characters are always 24 dots = 3 mm. The first two
data bytes specify the address of the character being defined. Starting from the
third data byte, the data bytes contain the character matrix information consisting of
three bytes per row for 24 rows.
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
updated March 18, 2002
118
SureMark DBCS User’s Guide
