Data flow between the gateway and external host, Slave driver – ProSoft Technology 5201-MNET-101S User Manual
Page 68
Reference
IEC-101 Slave ♦ ProLinx Communication Gateway
Protocol Manual
IEC 60870-5-101 v3 Slave (Firmware version 3.xx)
Page 68 of 159
ProSoft Technology, Inc.
August 6, 2010
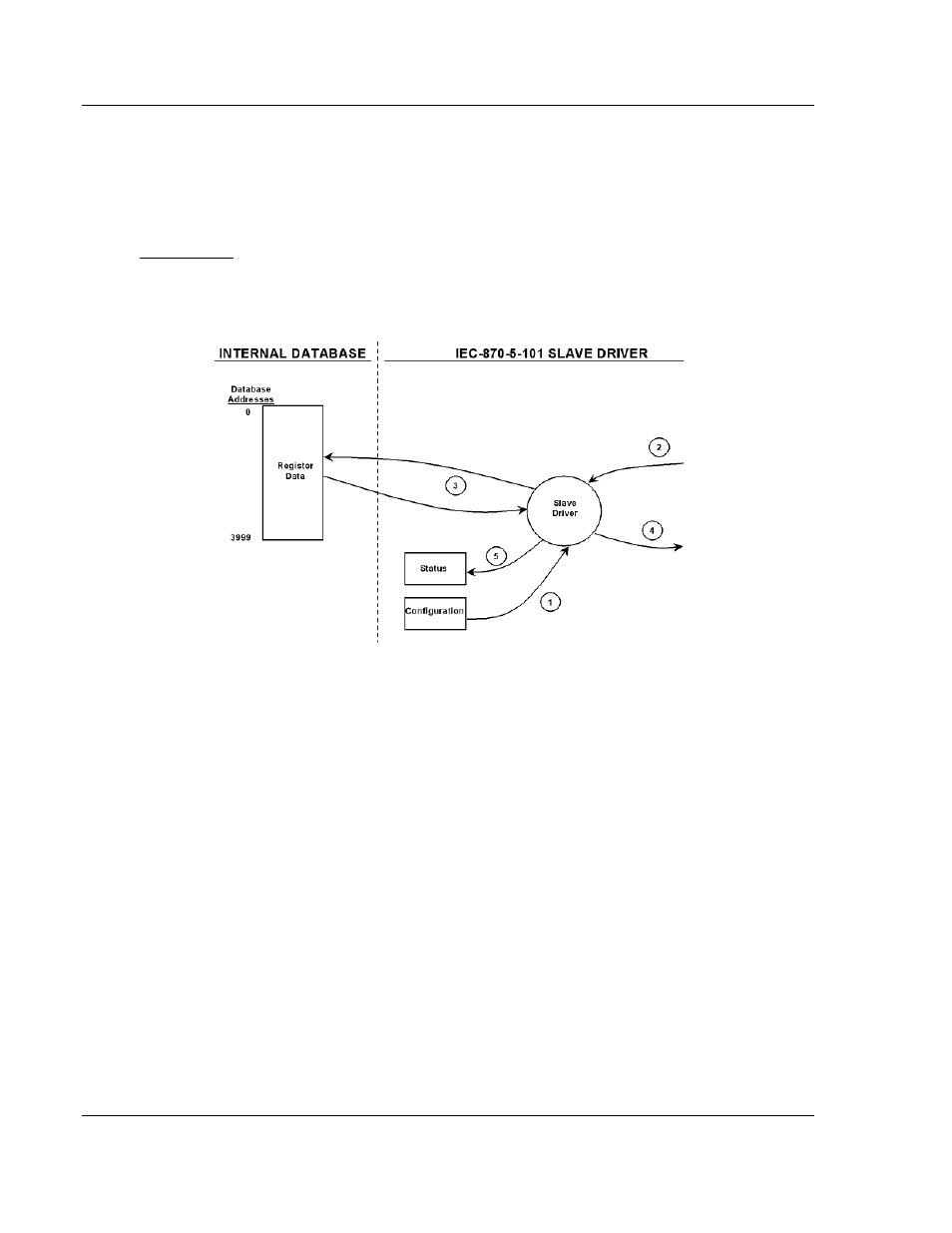
5.2.1 Data Flow Between the gateway and External Host
The following section describes the flow of data between the 101S gateway and
the IEC 60870-5-101 Master unit.
Slave Driver
The slave driver allows the 101S gateway to respond to data read and write
commands issued by a Master unit on the serial network. The following flow chart
and associated table describe the flow of data into and out of the gateway.
1 The slave driver receives the configuration information from the configuration
file in the gateway. This information configures the driver and defines the
node characteristics.
2 A host device issues read or write commands to the gateway's node address.
The driver qualifies the message before accepting it into the gateway.
3 Once the gateway accepts the message, the data is immediately transferred
to or from the internal database in the gateway. If the command is a read
command, the data is read out of the database and a response message is
built. If the command is a write command, the data is written directly into the
database and a response message is built. The gateway will also generate
messages without being queried by the host. These messages include
spontaneous and cyclic COT messages.
4 Once the data processing is complete, the response is issued to the
originating Master node.
5 Counters are available in the Status Block that permits the level of activity of
the driver to be determined.
The configuration section of this manual describes the complete list of
parameters that must be defined for a slave. The IEC-60870-5-101
Interoperability Document for the 101S slave contains a listing of the protocol
support supplied by the gateway.
