1 output waveform, Time voltage – Magnum Energy ME Series User Manual
Page 14
©
2012 Magnum Energy, Inc
Page 6
Introduction
1.3 What Appliances will run from a Modifi ed Sine Wave Inverter
Today’s inverters come in two basic output waveforms: modifi ed sine wave (a modifi ed square
wave—see Figure 1-5) and pure sine wave. Modifi ed sine wave inverters approximate a pure sine
waveform and will run most appliances and electronics without any problems. These inverters are
less expensive, and therefore, offer a viable alternative to more expensive pure sine inverters.
The output of the ME Series is a modifi ed sine wave which will run most electronic and household
items, including but not limited to: TV, VCR, satellite dish receiver, computers, and printers. Some
devices such as rechargeable power supplies for phones, drills, and other like items may not run,
and could even be at risk for damage from modifi ed sine wave inverters.
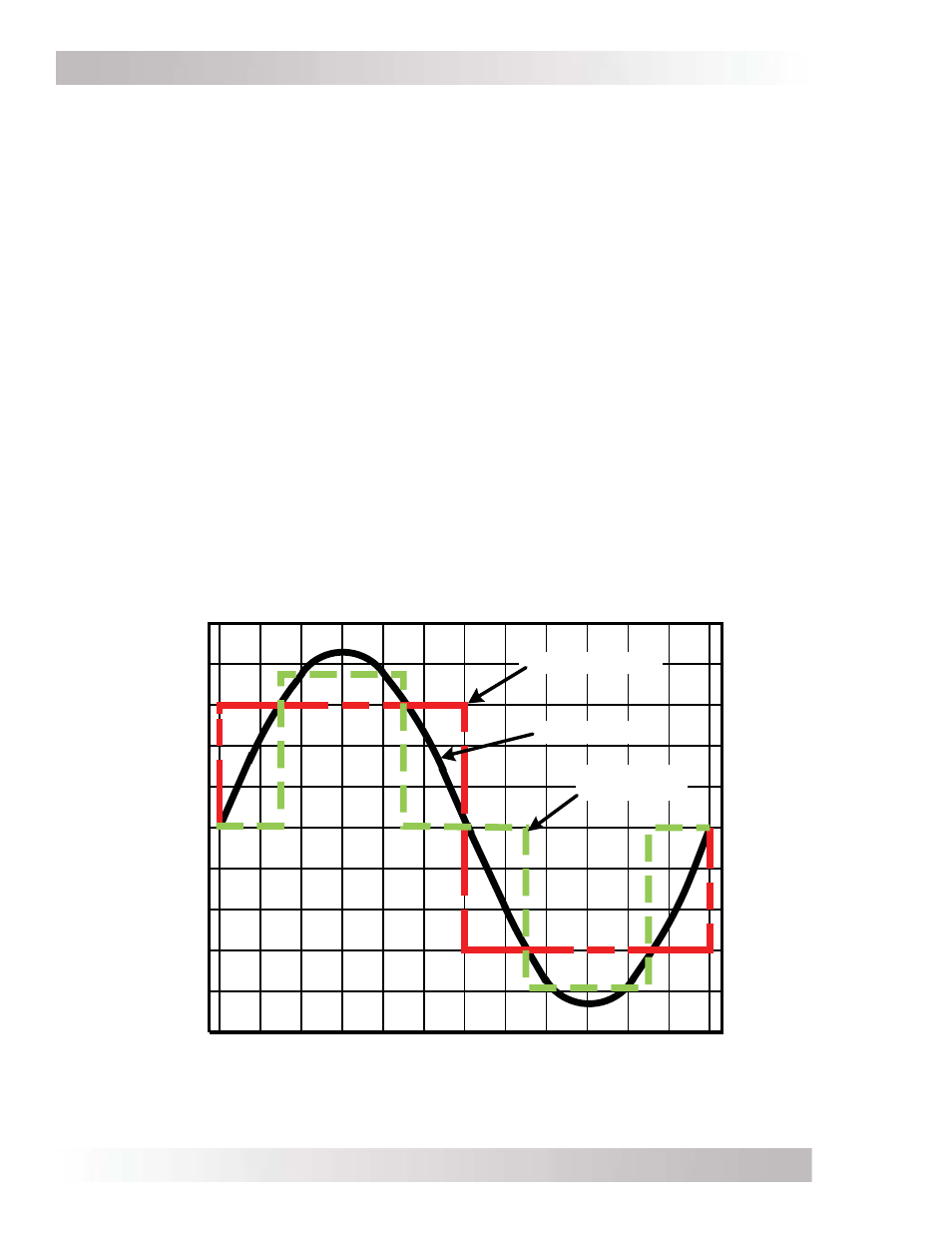
1.3.1 Output Waveform
The inverter’s output waveform is the shape of the wave that alternating current makes as its
voltage rises and falls with time (see Figure 1-5 below). The three basic output waveforms are:
• Modifi ed Sine Wave – Also referred to as a “quasi sine wave” or a “modifi ed square wave”.
This output looks like a one-step staircase and the waveform changes its width to continually
provide the correct RMS output voltage regardless of the battery voltage. Most loads that run
from a sine wave will also run from a modifi ed sine wave. However, things such as clocks and
furnace controllers may have trouble.
• Sine
Wave – An AC waveform that looks like rolling waves on water. It rises and falls smoothly
with time. The grid puts out a sine waveform. Any plug-in AC equipment will operate from a
sine wave output inverter.
• Square Wave – The simplest AC waveform. Some types of equipment behave strangely
when powered from a square wave inverter.
Figure 1-5, AC Waveforms
TIME
VOLTAGE
40
80
0
120
40
160
200
80
120
160
200
Modified
Sine Wave
Sine Wave
Square Wave
