Dr-mode layer 4 server load balancing – H3C Technologies H3C SecBlade LB Cards User Manual
Page 9
3
2.
Upon receiving the request, the LB product uses an algorithm to calculate to which server it
distributes the request.
3.
The LB product uses the Destination NAT (DNAT) technology to distribute the request, using the
host IP as the source IP and Server IP as the destination IP.
4.
The server receives and processes the request and then sends a response, using the server IP as the
source IP, and the host IP as the destination IP.
5.
The LB product receives the response, translates the source IP, and forwards the response, using
VSIP as the source IP, and the host IP as the destination IP.
The work flow shows that NAT is used in server load balancing, and NAT-mode server load balancing
is thus called.
DR-mode Layer 4 server load balancing
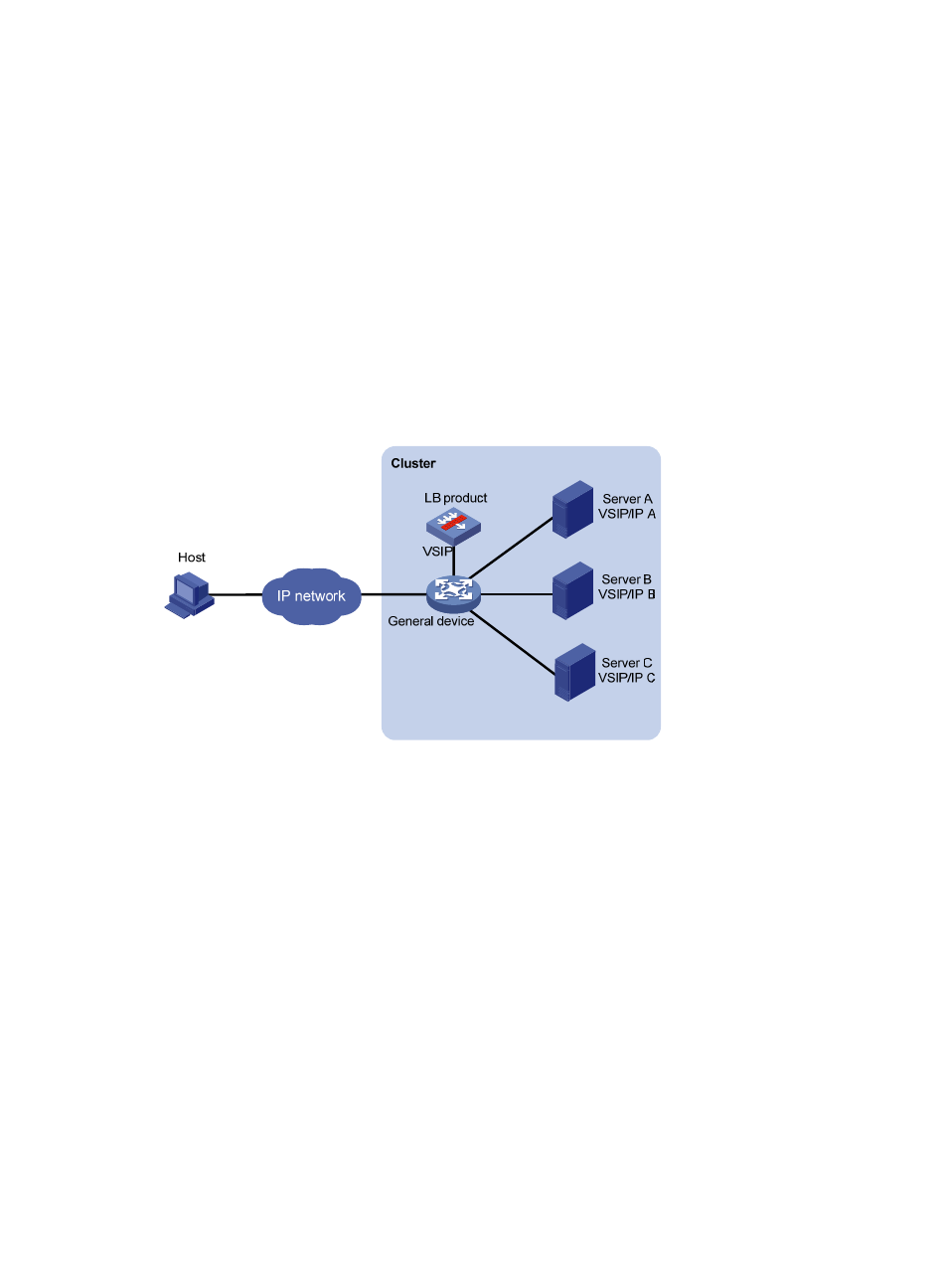
Figure 3 Network diagram
DR mode is different from NAT mode in that NAT is not used in load balancing. This means that besides
its local IP address, a server must have the VSIP configured.
DR-mode Layer 4 server load balancing comprises the following elements:
•
Cluster—A cluster consists of an LB product, a general device, and multiple servers to provide
specific services.
•
LB product—A device that distributes different service requests to multiple servers.
•
General device—A device that forwards data according to general forwarding rules.
•
Server—A server that responds to and processes different service requests.
•
VSIP—Virtual service IP address of the cluster, used for users to request services. Besides configuring
the VSIP on the LB product, you need to configure it on servers. (Because the VSIP on the server
cannot be contained in an ARP request and response, you can configure the VSIP on a loopback
interface.)
•
Server IP—IP address of a server, used by the LB product to distribute requests.
