Configuring ipv4 server/firewall load balancing, Server load balancing configuration considerations – H3C Technologies H3C SecBlade LB Cards User Manual
Page 14
8
2.
LB product A forwards the traffic to a firewall based on the destination IP address range and the
pre-configured load balancing rules of the traffic.
3.
The firewall forwards the traffic to LB product B.
4.
As a level 2 LB product, LB product B records the firewall that forwards the traffic and then
forwards the traffic to the destination.
5.
LB product B receives the traffic sent from the destination.
6.
LB product B forwards the traffic to the firewall recorded in step 4.
7.
The firewall forwards the traffic to LB product A.
8.
LB product A forwards the traffic back to the source.
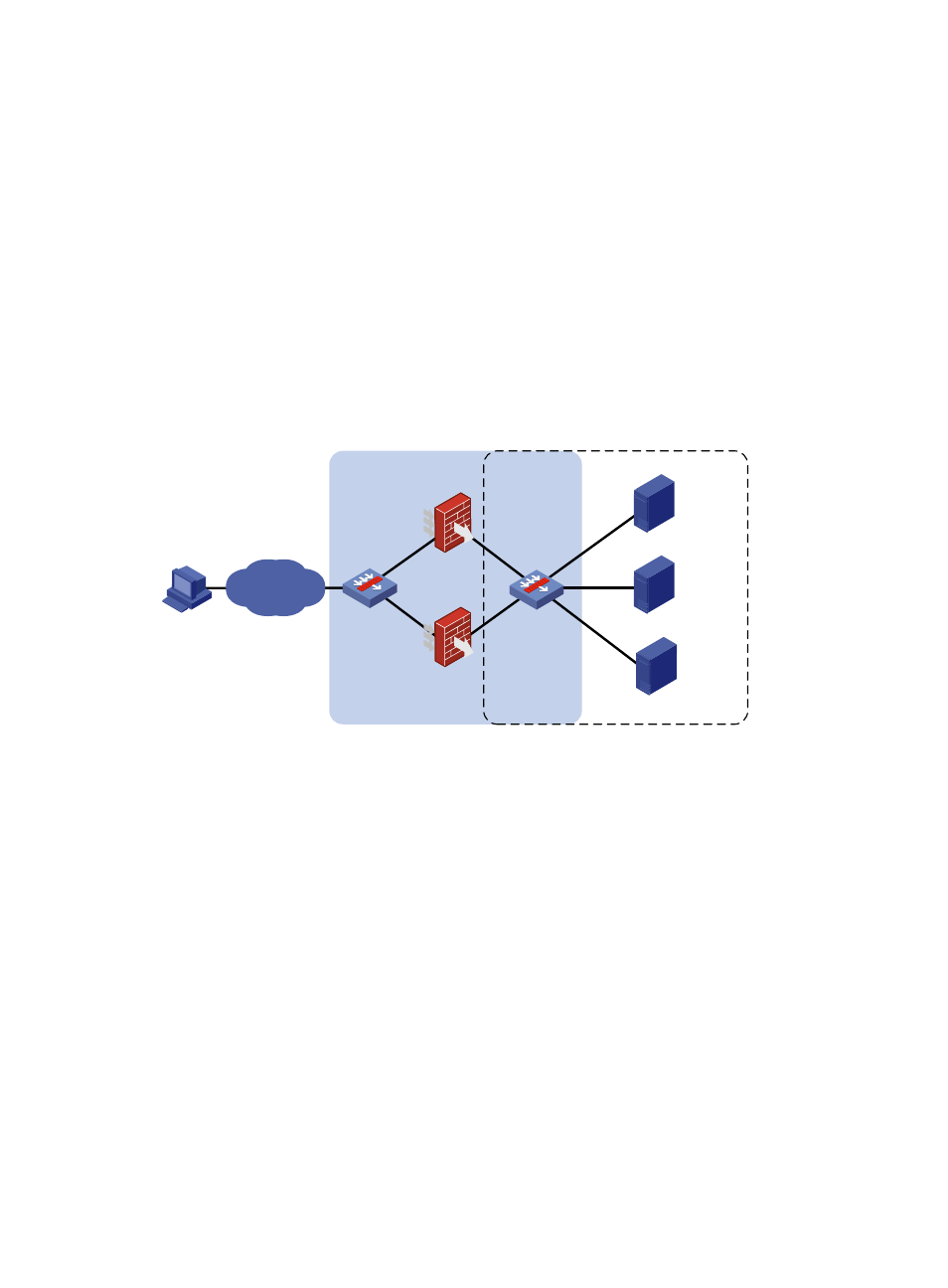
The load balanced firewalls between two LB products perform network traffic load balancing, and thus
network performance is increased. This load balancing mode is also called sandwich load balancing.
Firewall load balancing can be used together with server load balancing, as shown in
Figure 9 Network diagram
Cluster A adopts firewall load balancing, and Cluster B adopts NAT-mode server load balancing. This
networking mode not only prevents firewalls from becoming the bottleneck in the network, but also
enhances the performance and availability of multiple network services such as HTTP and FTP.
Configuring IPv4 server/firewall load balancing
IPv4 firewall load balancing and Layer 4 server load balancing are configured in the same way. This
section describes how to configure Layer 4 server load balancing.
Server load balancing configuration considerations
The server load balancing module comprises a real service group consisting of real services and a virtual
service, as shown in
.
Host
IP network
LB product B
Server A
IP A
Server B
IP B
Server C
IP C
Cluster A
VSIP
LB product A
Firewall A
Firewall B
Cluster B
