Recommended configuration procedure, N in, Figure 10 – H3C Technologies H3C SecBlade LB Cards User Manual
Page 15
9
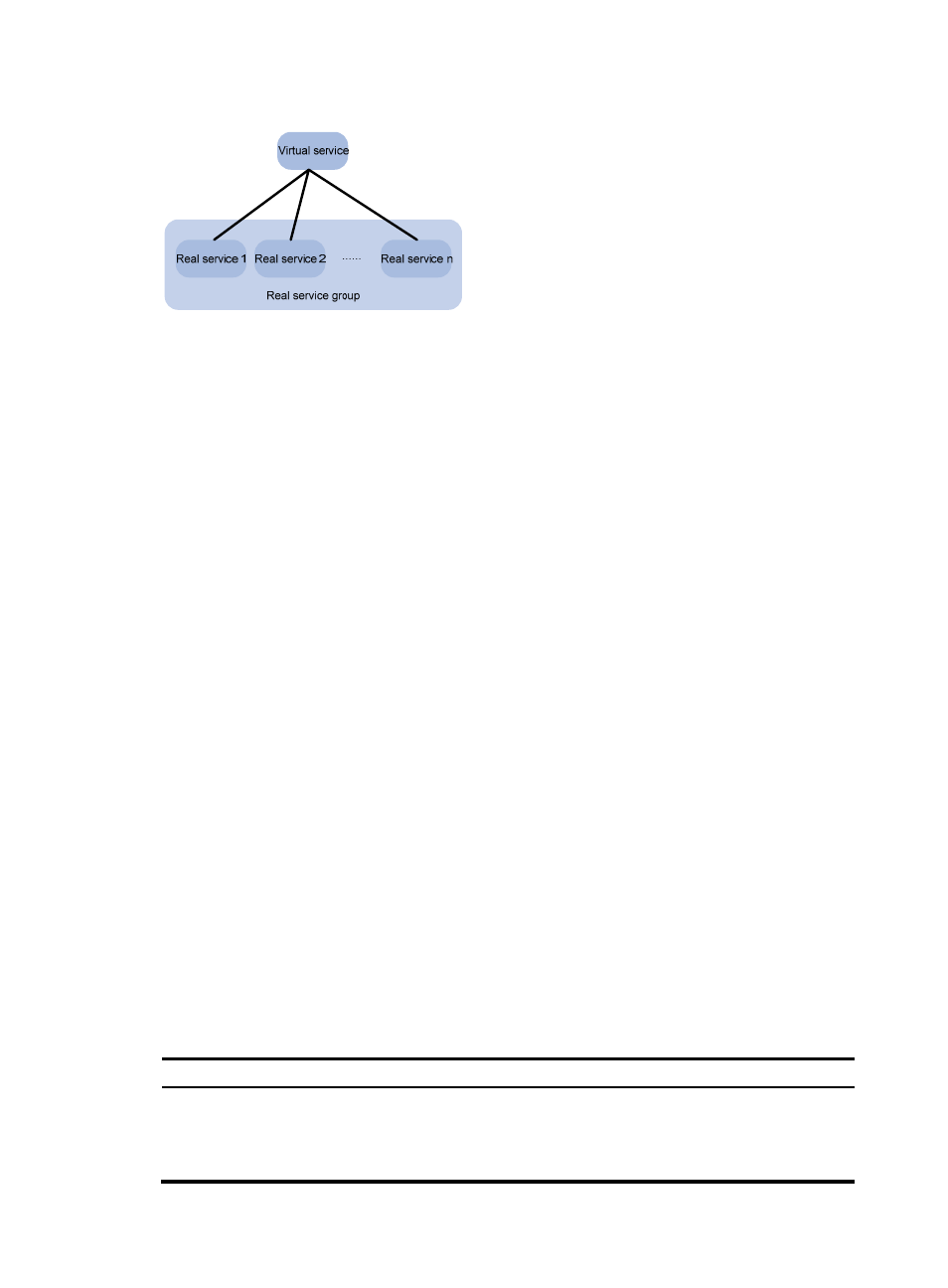
Figure 10 Relationship between the components of the server load balancing module
•
Real service group—A group of real services.
•
Real services—Entities that process services in a cluster (such as servers in
, and
,
and firewalls
. A real service group comprises multiple real services.
•
Virtual service—A logical entity that faces users. For Layer 4 server load balancing and firewall
load balancing, a virtual service corresponds to one real service group. For Layer 7 server load
balancing, a virtual service corresponds to multiple real service groups.
Layer 4 server load balancing operates in the following way:
1.
After a user sends a request to the virtual service of the LB product, if a persistence method is
specified in the virtual service, and matched persistence entries exist, the request is distributed
according to the persistence entries. Otherwise, the virtual service obtains the information of the
related real service group, and then continues the following procedure. For more information
about persistence methods, see
2.
Real services are matched against ACL rules specified in the real services one by one according
to the weights of the real services. Requests allowed by the ACL are distributed to the
corresponding real service; if requests are not allowed by the ACL or no matched real services
exist, the following procedure is continued.
3.
Distributes the request to a real service in the group based on the algorithm configured in the real
service group.
Layer 7 server load balancing operates in the following way:
1.
After a user sends a request to the virtual service of the LB product, if a persistence method is
specified in the virtual service, and matched persistence entries exist, the request is distributed
according to the persistence entries. Otherwise, the virtual service selects a real service group
according to the specified real service group method and obtains the information of the real
service group, and then continues the following procedure. For introduction to persistence method
and real service group method, see
.
2.
Distributes the request to a real service in the real service group based on the algorithm configured
in the real service group.
Recommended configuration procedure
Step Remarks
1.
Saving of the last hop information
Saving of the last hop information must be enabled on a level
2 LB product in firewall load balancing. This task is optional in
other cases.
For more information, see "
."
