Setting up a fabric, Overview, Principal switch selection – H3C Technologies H3C S12500-X Series Switches User Manual
Page 37: Configuring fip snooping, Fip snooping network diagram
28
Setting up a fabric
Overview
A fabric transmits data for servers and disk devices. When setting up a fabric, you must assign a domain
ID to each FCF switch in the fabric and assign an FC address to each node connected to the fabric.
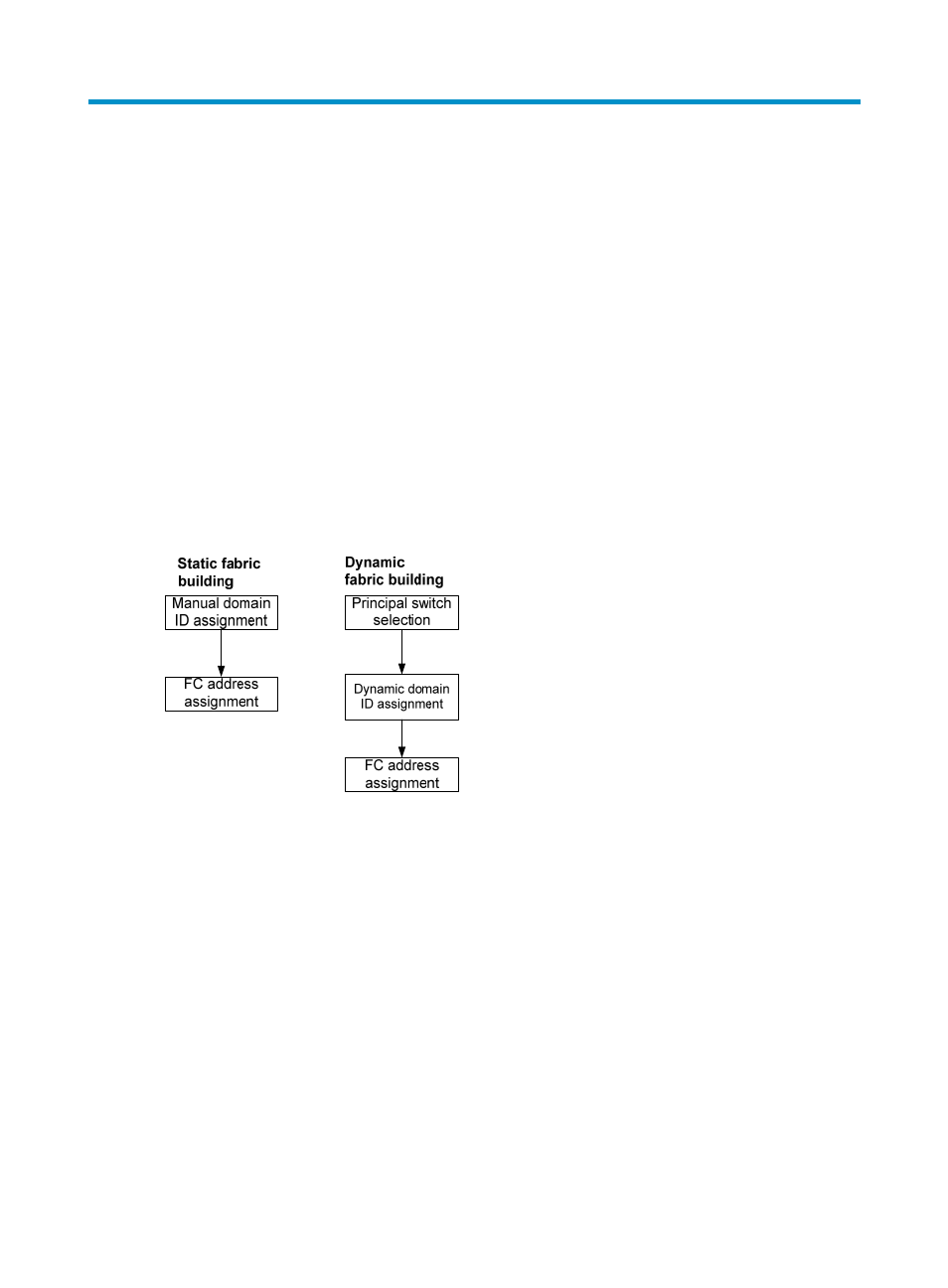
You can build a fabric through one of the following modes:
•
Static mode—You must manually assign domain IDs to all switches in the network, and then each
switch assigns FC addresses to the N_Ports connected to it. The static mode avoids network
flappings, but it is applicable only to simple, small-sized networks.
•
Dynamic mode—A principal switch is automatically elected to assign domain IDs to all switches in
the network, and then each switch assigns FC addresses to the N_Ports connected to it. The
dynamic mode enables centralized network management and is applicable to large-sized
networks.
Figure 18 Fabric setup workflows
The following section details each process in the fabric setup workflows.
Principal switch selection
During the dynamic fabric building process, it is the principal switch that assigns domain IDs to all
switches in the network.
The switch with the highest priority is selected as the principal switch. When multiple switches have the
same priority, the switch with the smallest WWN wins.
The principal switch selection process is as follows:
1.
When the principal switch selection starts, each switch considers itself to be the principal switch,
records itself in the principal switch information, and starts the Principal Switch Selection Timer
(PSST), which is 10 seconds.
2.
Before the PSST times out, the switches exchange packets carrying the principal switch information
to select a principal switch. On receiving such a packet, a switch compares the priority and WWN
of the principal switch carried in the packet against those locally recorded. If the priority carried
