Vsan, Fc zone, Communication flow – H3C Technologies H3C S12500-X Series Switches User Manual
Page 13
4
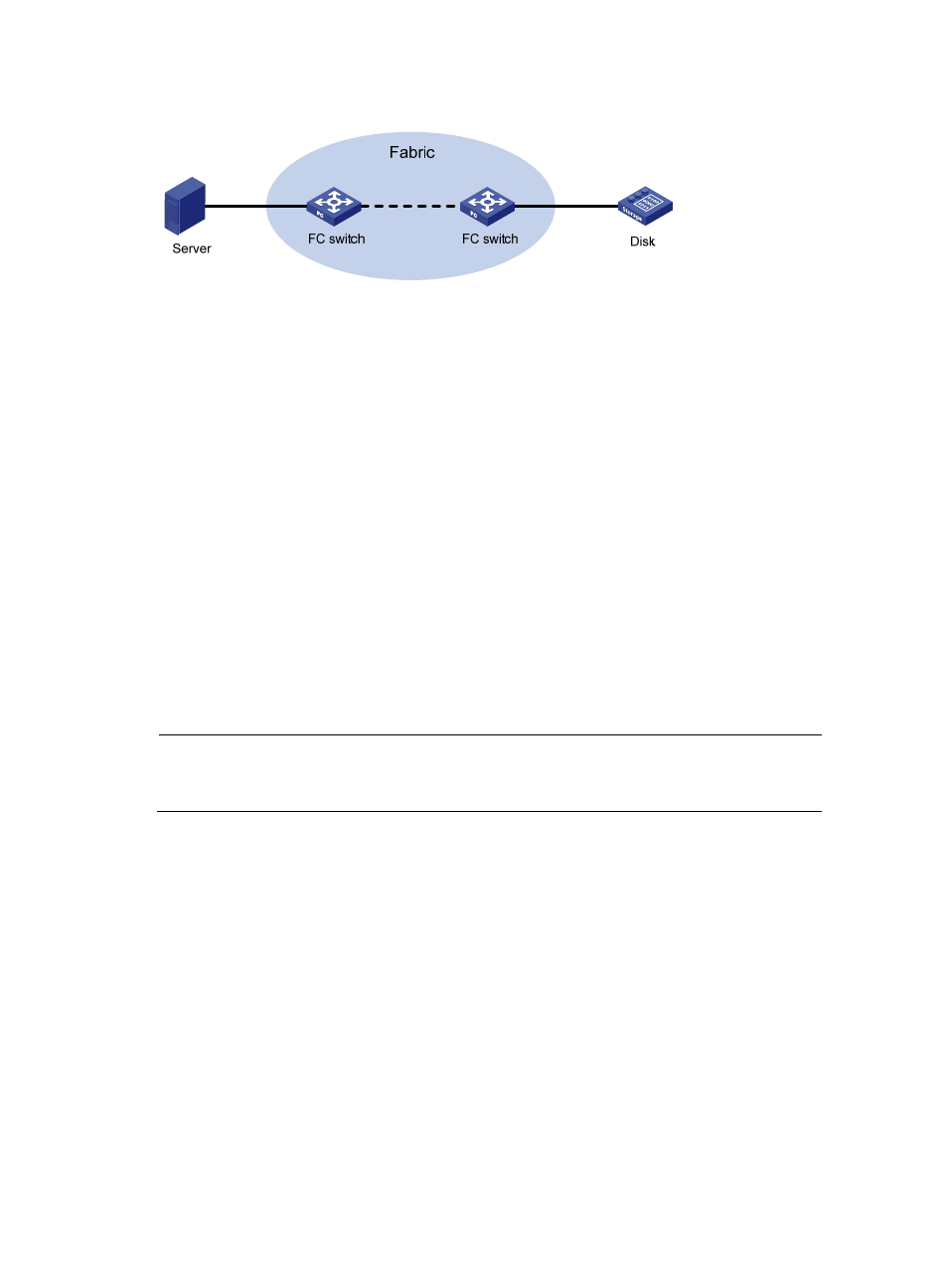
Figure 4 FC SAN communication model
The following takes a server accessing a disk device as an example to see how data communication
occurs in an FC SAN.
1.
The server and the disk device use the fabric login (FLOGI) protocol to register with the FC switches,
which then assign FC addresses to each directly-connected node. A FLOGI packet contains such
information as the port WWN, node WWN, and the expected FC address.
2.
The registered server and disk device send name service registration requests to their respective
access FC switches to register name service information, including FC4 information (see
"
Configuring and obtaining FC4 information of nodes
"). Finally, each FC switch in the fabric
stores the name service information for all nodes.
3.
To access a disk device, the server needs to send a name service query request to its
directly-connected FC switch to obtain the list of disk devices in the fabric and their WWNs and FC
addresses.
4.
After the server obtains the FC address of the disk device, the server can send FC frames (with the
FC address of the disk device as the destination FC address) to the FC switch nearby.
5.
When the FC switch receives the FC frame from the server, it queries its FIB table for a data
forwarding path according to the destination FC address, and forwards the FC frame to the
next-hop FC switch. The next-hop FC switch forwards the FC frame in the same way, until the FC
switch at the last hop forwards the FC frame to the destination disk device.
NOTE:
A FIB table is generated by the FC switch through calculation based on the FC routing protocol or
configured static routes.
VSAN
In actual applications, the data is insecure because the data of all users is transmitted in the same FC
SAN. You can divide one physical FC SAN into multiple Virtual Storage Area Networks (VSANs). In this
manner, VSANs are separated from one another and provide independent services, enhancing
adaptability and security of the network and offering more effective services for users. For more
information about VSAN, see "
FC zone
With VSAN, one physical SAN is divided into multiple logical SANs. A VSAN, however, cannot perform
access control over the servers and disk devices (or the N_Ports) connected to a fabric. N_Ports in the
same VSAN can access one another only if these N_Ports register name services. This creates data
security risks.
