Fcf mode – H3C Technologies H3C S12500-X Series Switches User Manual
Page 18
9
•
FCF mode—A switch operating in this mode is called an FCF switch. Its VFC interfaces support E
mode (E_Port) and F mode (F_Port).
•
NPV mode—A switch operating in this mode is called an N_Port Virtualization (NPV) switch. Its
VFC interfaces support F mode (F_Port) and NP mode (NP_Port).
•
Transit mode—A switch operating in this mode is called a Transit switch. Its Ethernet interfaces can
operate in ENode mode or FCF mode.
An FCoE-capable switch can operate in the following modes:
•
FCF mode—When the switch operates in this mode, it can connect to the E_Port on another FCF
switch through its E_Port, or connect to the N_Port on a node or the NP_Port on an NPV switch
through its F_Port.
•
NPV mode—When the switch operates in this mode, it can connect to the N_Port on a node
through its F_Port or to the F_Port on an FCF switch through its NP_Port.
•
Transit mode—When the switch operates in this mode, it can restrict its Ethernet interface to
receiving traffic only from an ENode or FCF switch by configuring the interface to operate in ENode
mode or FCF mode.
•
Non-FCoE mode—When the switch operates in this mode, it is a standard switch and does not
provide any FCoE capabilities.
FCF mode
An FCF switch encapsulates FC frames in Ethernet frames and uses FCoE virtual links to simulate physical
FC links. Therefore, it provides standard FC switching capabilities and features on a lossless Ethernet
network.
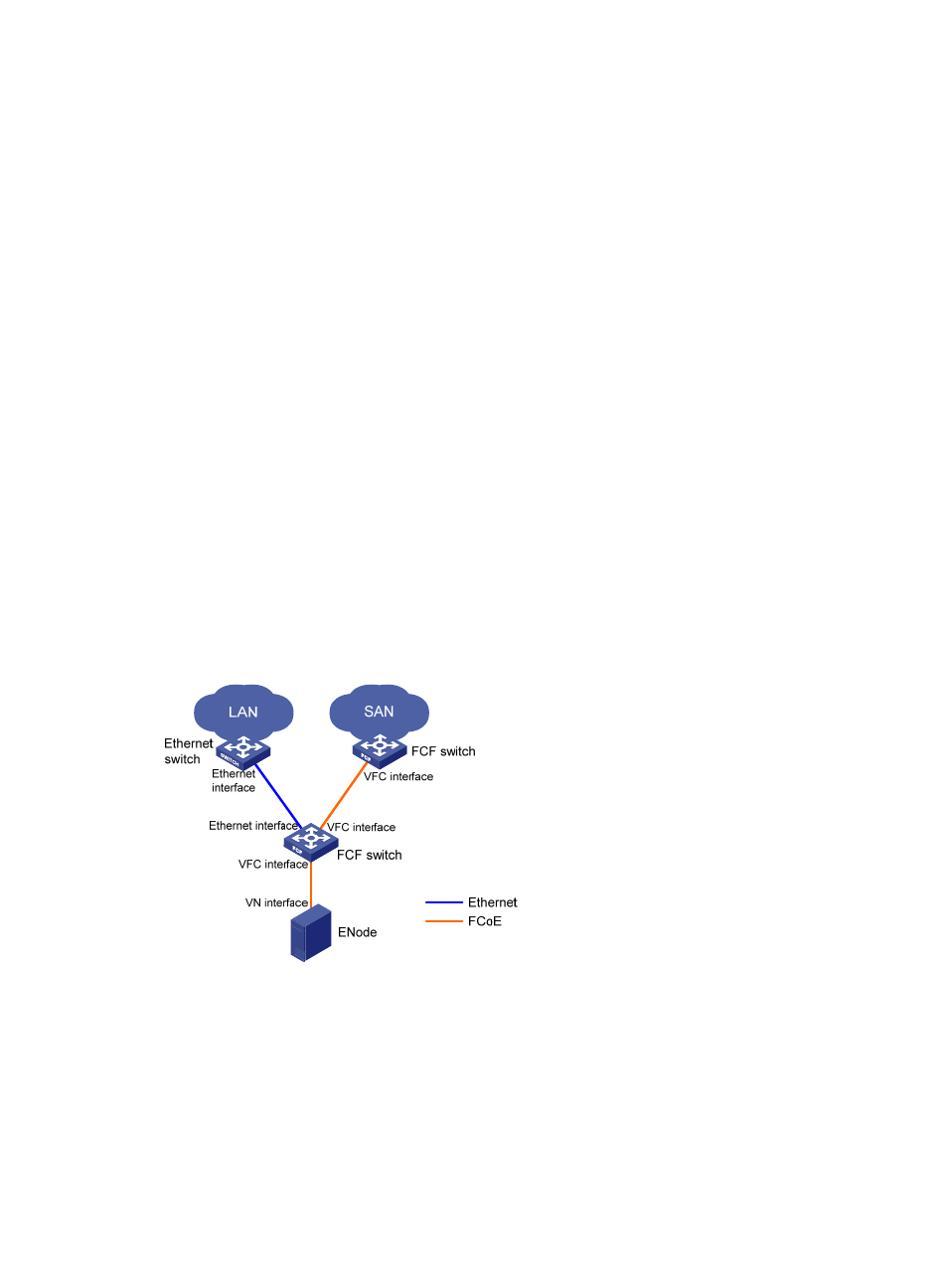
Figure 10 FCF network diagram
In an FCoE environment as shown in
, different from a pure FC network, the ENode and FCF
switch communicate over Ethernet interfaces on a lossless Ethernet network. The FCoE virtual link
connects a VN interface to a VFC interface or connects two VFC interfaces.
As with an FC switch, each FCF switch is assigned a domain ID. Each FC SAN supports a maximum
number of 239 domain IDs, so an FC SAN cannot have more than 239 switches.
