Inter-as option c, Enabling rsvp – H3C Technologies H3C S12500-X Series Switches User Manual
Page 119
108
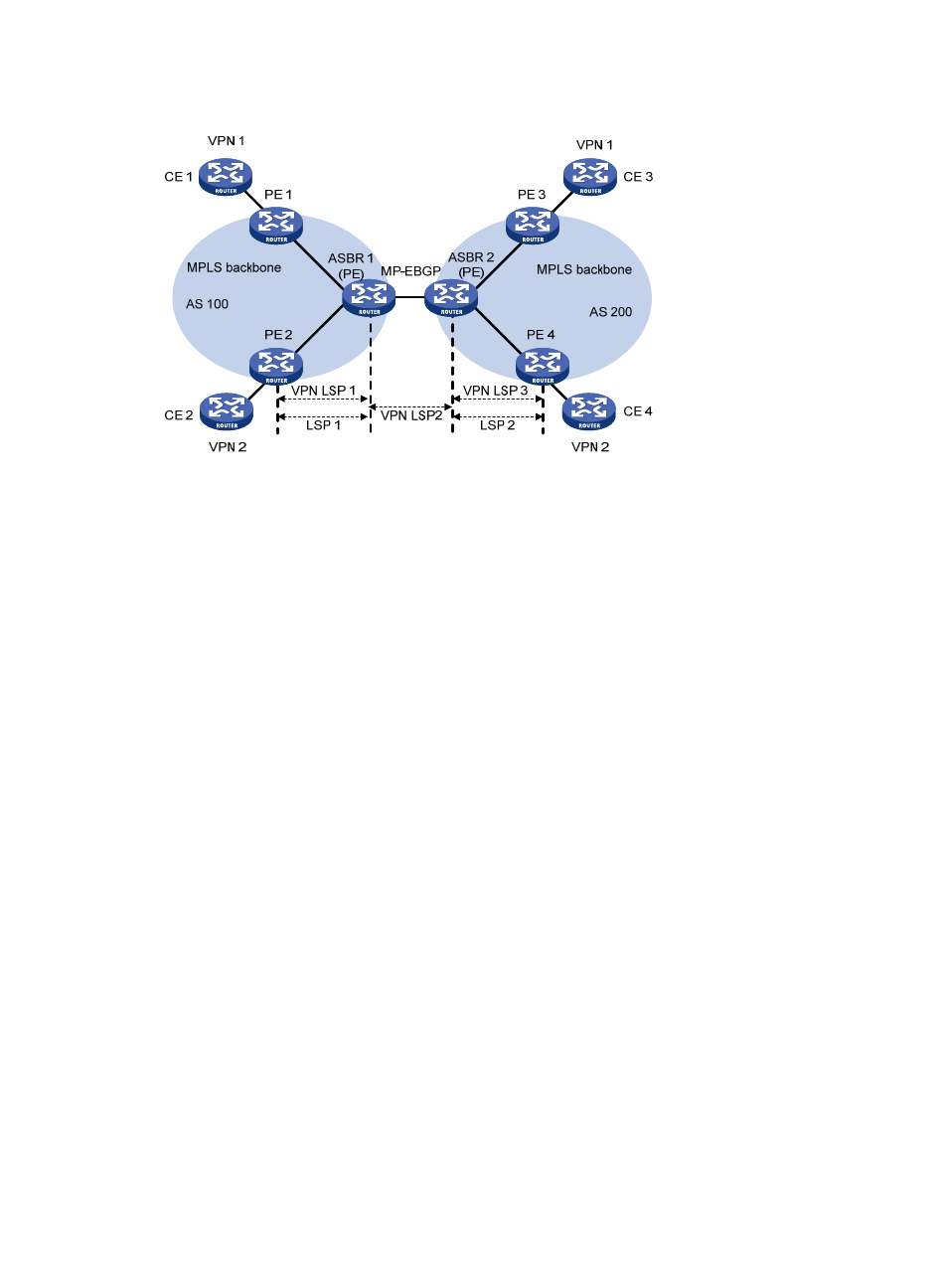
Figure 36 Network diagram for inter-AS option B
Inter-AS option B has better scalability than option A.
When adopting the MP-EBGP method, note the following:
•
ASBRs do not perform route target filtering on VPN-IPv4 routes that they receive from each other.
Therefore, the ISPs in different ASs must agree on the route exchange.
•
VPN-IPv4 routes are exchanged only between VPN peers. A VPN site can exchange VPN-IPv4
routes neither with the public network nor with MP-EBGP peers with whom it has not reached
agreement on the route exchange.
Inter-AS option C
The Inter-AS option A and option B solutions can meet the needs for inter-AS VPNs. However, they require
that the ASBRs maintain and advertise VPN-IPv4 routes. When every AS needs to exchange a great
amount of VPN routes, the ASBRs might become bottlenecks, which hinders network extension.
Inter-AS option C can solve the problem by making PEs directly exchange VPN-IPv4 routes without the
participation of ASBRs:
•
Two ASBRs advertise labeled IPv4 routes to PEs in their respective ASs through IBGP.
•
The ASBRs neither maintain VPN-IPv4 routes nor advertise VPN-IPv4 routes to each other.
•
An ASBR maintains labeled IPv4 routes of the PEs in the AS and advertises them to the peers in the
other ASs. The ASBR of another AS also advertises labeled IPv4 routes. Thus, an LSP is established
between the ingress PE and egress PE.
•
Between PEs of different ASs, multi-hop EBGP connections are established to exchange VPN-IPv4
routes.
M
P-
IBGP
M
P-
IBGP
MP
-IB
G
P
M
P
-IBG
P
