Bandwidth-efficient modulation, Indirect fm, Indirect am – Wavecom W61PC V7.5.0 User Manual
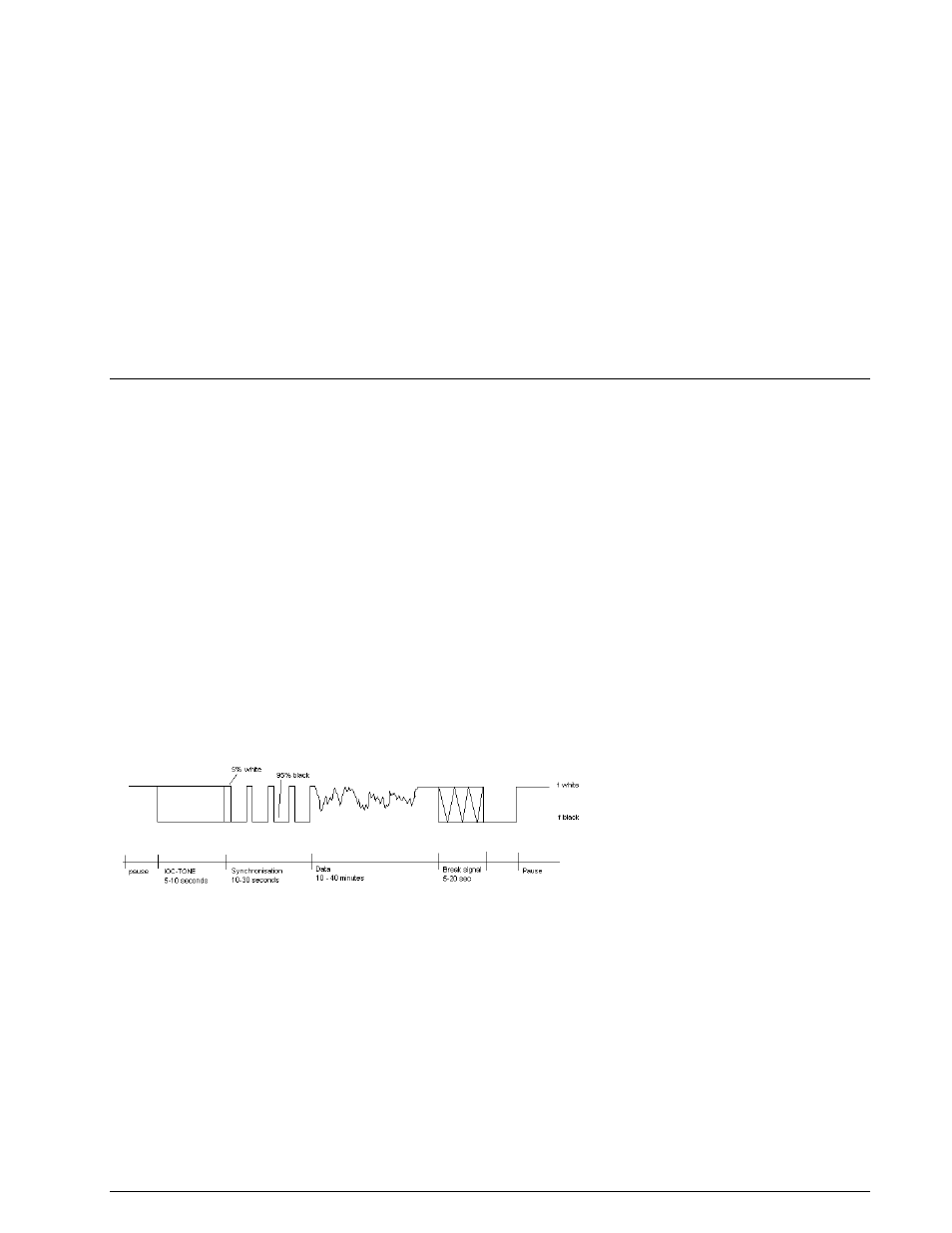
Page 113: Fax transmission sequence
WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5
Fundamentals of Radio Data Transmission
103
Bandwidth-efficient Modulation
Among newer modulations methods employed to make better use of the spectrum available are Offset
QPSK (OQPSK), Minimum Shift Keying (MSK) and Gaussian FSK (GFSK). MSK is used in DGPS and in GSM
systems. OQPSK is used in satellite communications and GFSK is used in various data modes.
INDIRECT FM
A frequency modulated carrier is modulated with an AF FSK sub-carrier. For decoding, the receiver FM
demodulator output is required. Examples of INDIRECT modulation are PACKET-1200, ATIS, and analogue
and digital tone call systems. Decoding is only possible from the receiver AF output.
INDIRECT AM
This modulation method uses AM carrier modulation, which is in turn modulated by an AF FSK sub-carrier.
For decoding the receiver AM demodulator output is required. At the time of writing, ACARS is the only
known mode using this modulation method. Decoding is only possible from the receiver AF output.
FAX
Weather charts to be transmitted are fastened to a revolving drum and illuminated by a light source. The
drum is then scanned by a light sensor moving along the axis of the drum. The voltage output from this
sensor is converted into tone frequencies modulating the transmitter.
The number of revolutions per minute (RPM) is a measure of the speed of the drum on the transmitting
side. The index of cooperation (IOC) is a measure of the speed with which the sensor moves along the ax-
is of the drum.
A fax transmission begins with a tone of 300 or 675 Hz. The start tone has duration of 5-10 seconds and is
very well suited for precise tuning. The frequency of the tone determines the IOC value. Then 30 seconds
of alternations between the frequencies representing black and white levels are transmitted, the switching
frequency being 1-4 Hz. This sequence carries the RPM information, and the receiver is now synchronized
so that the picture will start in the right position. Subsequently the transmission of the picture proper be-
gins.
At the end of transmission the stop signal is sent; this consists of a switch-off signal of 450 Hz having du-
ration of 5 seconds followed by 10 seconds of the frequency representing black level.
FAX Transmission Sequence
