3 dama (demand assigned multiple access) -3, 2 vme demodulator card reed-solomon -3, 1 reed-solomon codec -3 – Comtech EF Data DD2401 VME User Manual
Page 21
DD2401 VME L-Band Demodulator Card Installation & Operational Manual
Theory of Operation
MN-VME2401 – Rev. B
3-3
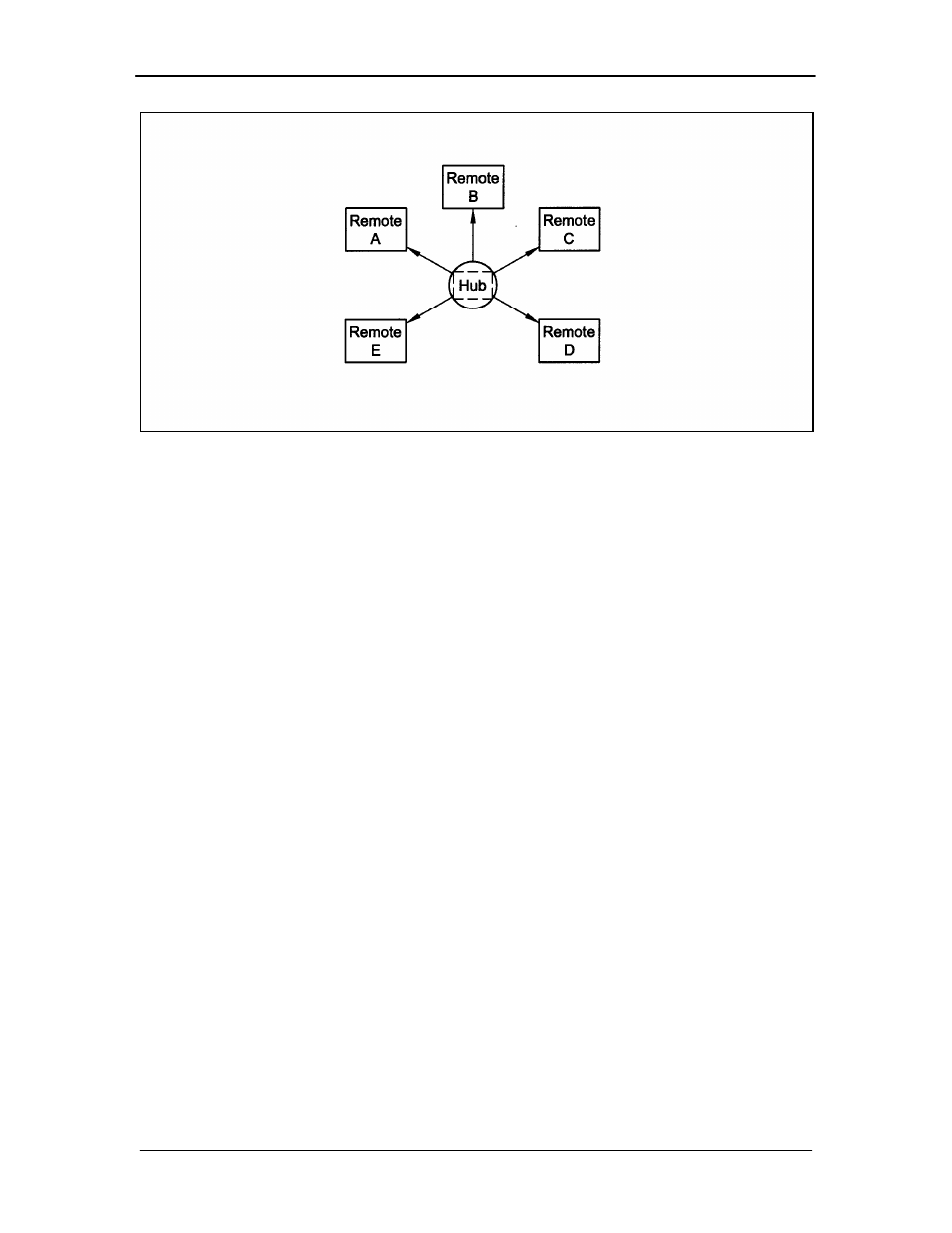
Figure 3-3. Star Network Configuration
3.1.3 DAMA (Demand Assigned Multiple Access)
If a telephone network is to be simulated with a virtual switch between demodulators carrying
digitized voice information. A central computer might be used to assign a pair of frequencies for
any conversation and send this connection information to the proper sites to set up the
connection. In this application, a new network called a “Mesh” Network is required. Any of the
voice demodulators at any site can be programmed to link with any other demodulator. The
resulting link diagram looks like a mesh of interconnects.
Since the frequencies can be assigned on demand, the network is called “Demand Assigned,
Multiple Access,” or DAMA.
3.1.4 TDMA (Time Division Multiple Access) Remote Site Application
In a TDMA Network, the central Hub continually transmits a stream of outbound data containing
information for multiple remote sites, while the remote sites transmit back to the Hub on a timed
basis. Each of these remotes is said to “burst” its information back on a specific frequency. This
may be the same inbound frequency for all sites.
Each of the remotes is responsible for accessing its own information from the outbound data
stream by reading the address assigned to specific parts of the data. The TDMA Network usually
looks like the Star network described above.
The DD2401 VME Demodulator Card is specifically designed to be usable as the remote site
Demodulator of a TDMA network when coupled with a proper “Burst” Demodulator at the hub site.
3.2 VME Demodulator Card Reed-Solomon
3.2.1 Reed-Solomon Codec
Utilizing a Reed-Solomon (RS) Outer Codec concatenated with a convolutional inner codec is an
effective way to produce very low error rates even for poor signal-to-noise ratios while requiring
only a small increase in transmission bandwidth. Typically, concatenating an RS Codec requires
an increase in transmission bandwidth of only nine to twelve percent while producing a greater
than 2 dB improvement in Eb/No. RS is a block codec where K data bytes are fed into the
